| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148399 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2013 | 7 Pages |
•ZnS photocatalysts were prepared via three different methods respectively.•Various Ni-doped ZnS photocatalysts were synthesized by hydrothermal method.•Suitable doping of Ni2+ could enhance the photocatalytic activity.•Methyl formate was produced through photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in methanol.
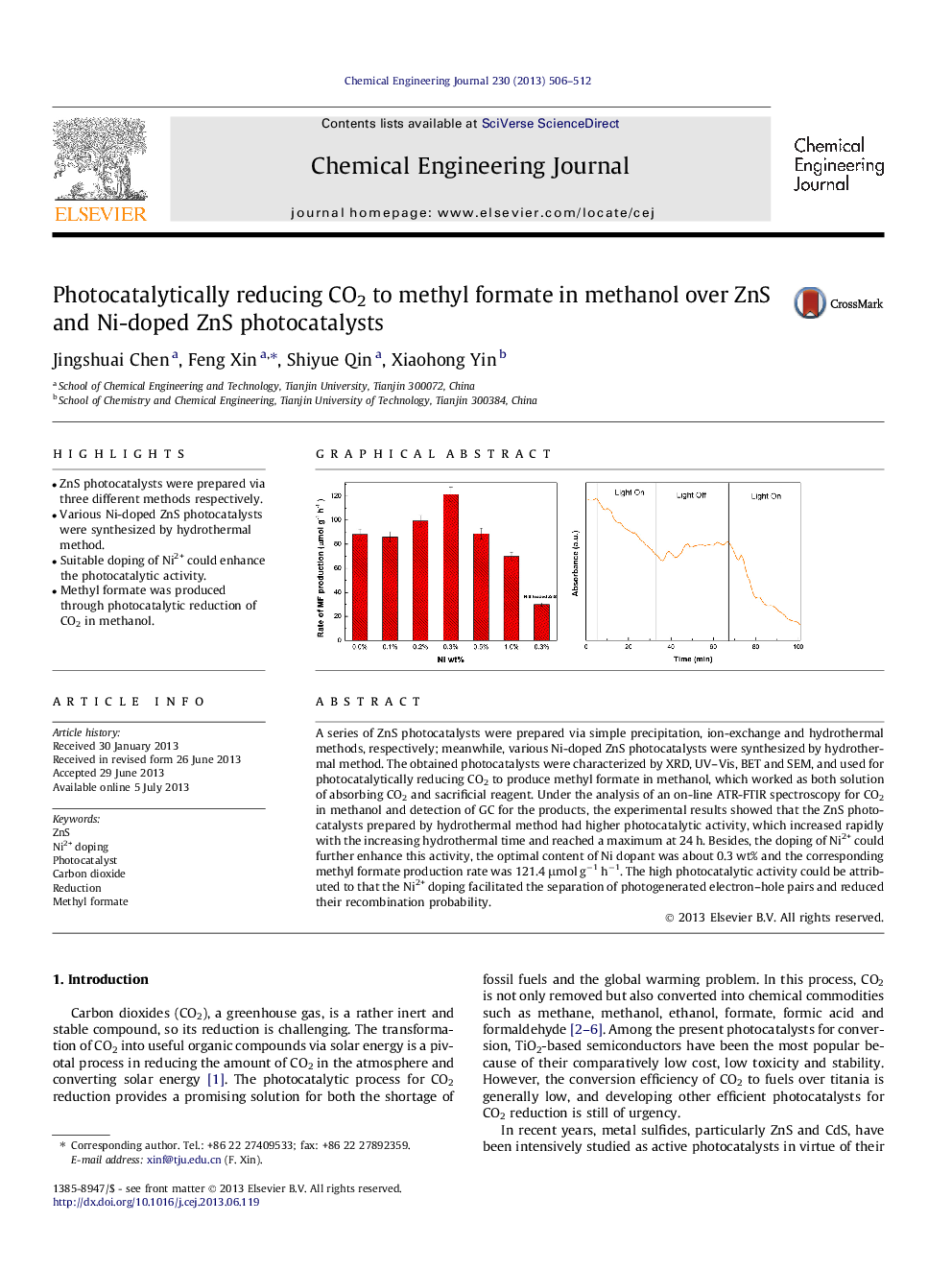
A series of ZnS photocatalysts were prepared via simple precipitation, ion-exchange and hydrothermal methods, respectively; meanwhile, various Ni-doped ZnS photocatalysts were synthesized by hydrothermal method. The obtained photocatalysts were characterized by XRD, UV–Vis, BET and SEM, and used for photocatalytically reducing CO2 to produce methyl formate in methanol, which worked as both solution of absorbing CO2 and sacrificial reagent. Under the analysis of an on-line ATR-FTIR spectroscopy for CO2 in methanol and detection of GC for the products, the experimental results showed that the ZnS photocatalysts prepared by hydrothermal method had higher photocatalytic activity, which increased rapidly with the increasing hydrothermal time and reached a maximum at 24 h. Besides, the doping of Ni2+ could further enhance this activity, the optimal content of Ni dopant was about 0.3 wt% and the corresponding methyl formate production rate was 121.4 μmol g−1 h−1. The high photocatalytic activity could be attributed to that the Ni2+ doping facilitated the separation of photogenerated electron–hole pairs and reduced their recombination probability.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide