| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148622 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2013 | 9 Pages |
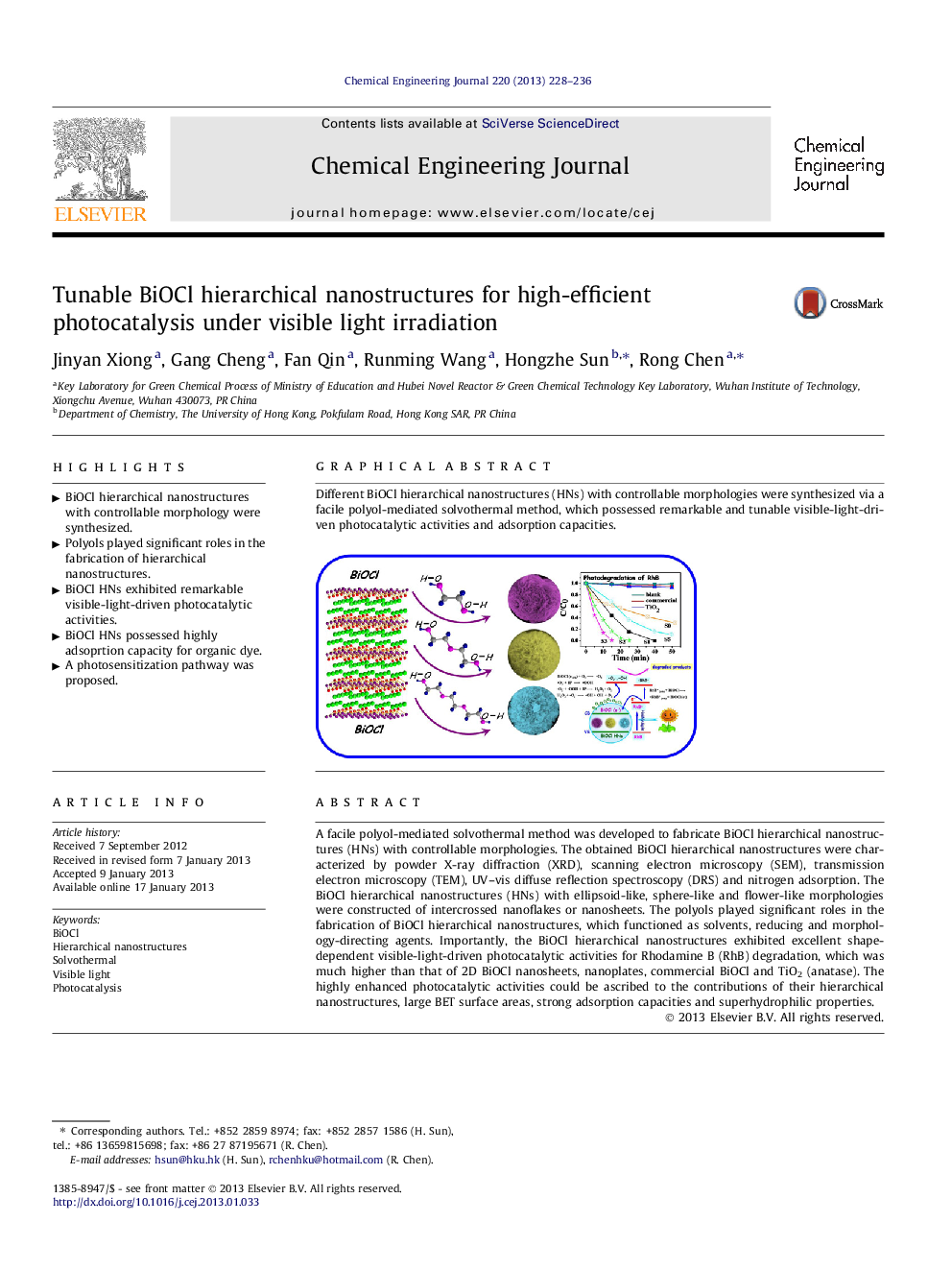
A facile polyol-mediated solvothermal method was developed to fabricate BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures (HNs) with controllable morphologies. The obtained BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV–vis diffuse reflection spectroscopy (DRS) and nitrogen adsorption. The BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures (HNs) with ellipsoid-like, sphere-like and flower-like morphologies were constructed of intercrossed nanoflakes or nanosheets. The polyols played significant roles in the fabrication of BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures, which functioned as solvents, reducing and morphology-directing agents. Importantly, the BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures exhibited excellent shape-dependent visible-light-driven photocatalytic activities for Rhodamine B (RhB) degradation, which was much higher than that of 2D BiOCl nanosheets, nanoplates, commercial BiOCl and TiO2 (anatase). The highly enhanced photocatalytic activities could be ascribed to the contributions of their hierarchical nanostructures, large BET surface areas, strong adsorption capacities and superhydrophilic properties.
Graphical abstractDifferent BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures (HNs) with controllable morphologies were synthesized via a facile polyol-mediated solvothermal method, which possessed remarkable and tunable visible-light-driven photocatalytic activities and adsorption capacities.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► BiOCl hierarchical nanostructures with controllable morphology were synthesized. ► Polyols played significant roles in the fabrication of hierarchical nanostructures. ► BiOCl HNs exhibited remarkable visible-light-driven photocatalytic activities. ► BiOCl HNs possessed highly adsoprtion capacity for organic dye. ► A photosensitization pathway was proposed.