| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148755 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2013 | 10 Pages |
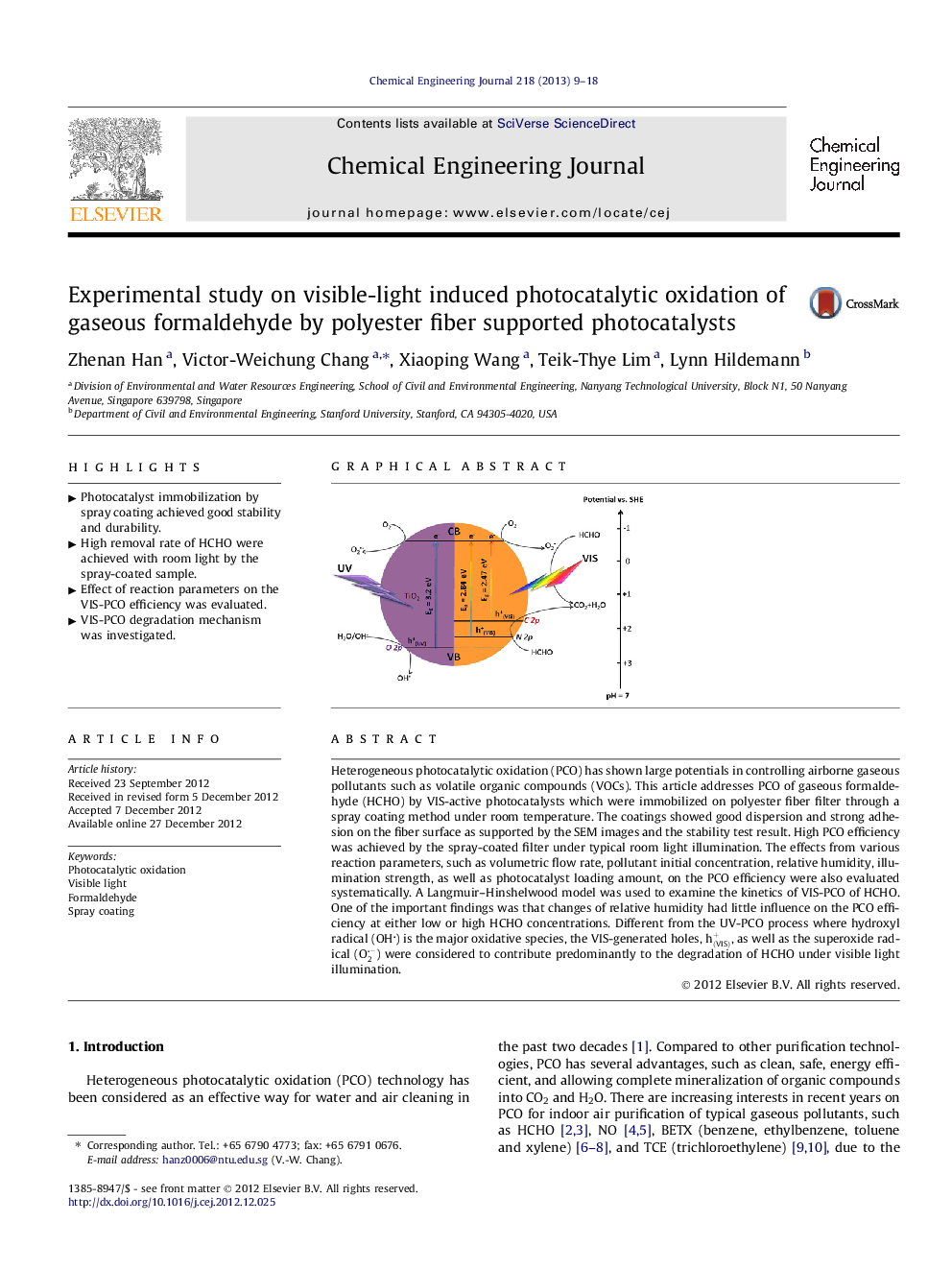
Heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) has shown large potentials in controlling airborne gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This article addresses PCO of gaseous formaldehyde (HCHO) by VIS-active photocatalysts which were immobilized on polyester fiber filter through a spray coating method under room temperature. The coatings showed good dispersion and strong adhesion on the fiber surface as supported by the SEM images and the stability test result. High PCO efficiency was achieved by the spray-coated filter under typical room light illumination. The effects from various reaction parameters, such as volumetric flow rate, pollutant initial concentration, relative humidity, illumination strength, as well as photocatalyst loading amount, on the PCO efficiency were also evaluated systematically. A Langmuir–Hinshelwood model was used to examine the kinetics of VIS-PCO of HCHO. One of the important findings was that changes of relative humidity had little influence on the PCO efficiency at either low or high HCHO concentrations. Different from the UV-PCO process where hydroxyl radical (OH) is the major oxidative species, the VIS-generated holes, hVIS+, as well as the superoxide radical (O2-) were considered to contribute predominantly to the degradation of HCHO under visible light illumination.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights• Photocatalyst immobilization by spray coating achieved good stability and durability. • High removal rate of HCHO were achieved with room light by the spray-coated sample. • Effect of reaction parameters on the VIS-PCO efficiency was evaluated. • VIS-PCO degradation mechanism was investigated.