| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148919 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2013 | 9 Pages |
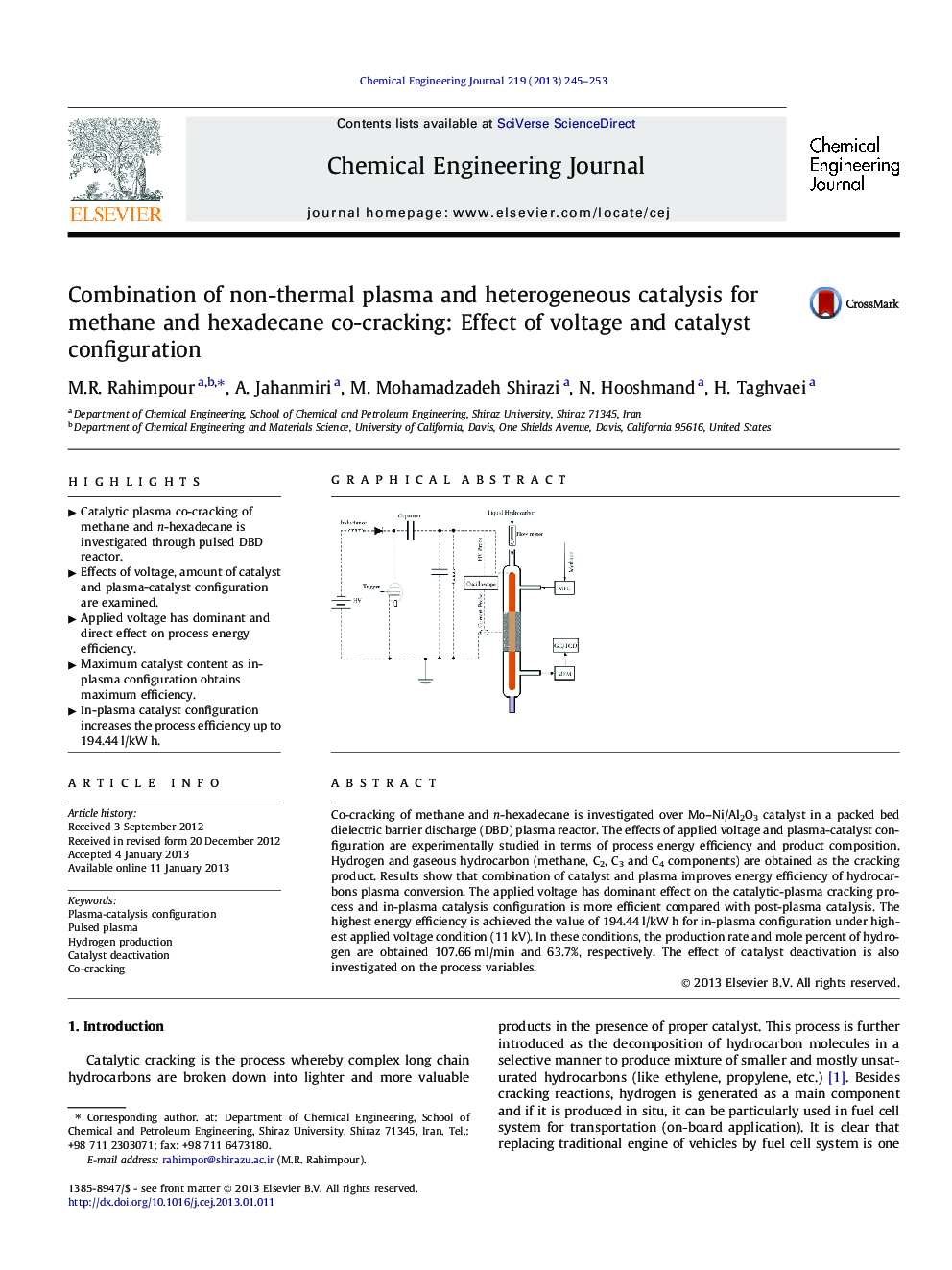
Co-cracking of methane and n-hexadecane is investigated over Mo–Ni/Al2O3 catalyst in a packed bed dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma reactor. The effects of applied voltage and plasma-catalyst configuration are experimentally studied in terms of process energy efficiency and product composition. Hydrogen and gaseous hydrocarbon (methane, C2, C3 and C4 components) are obtained as the cracking product. Results show that combination of catalyst and plasma improves energy efficiency of hydrocarbons plasma conversion. The applied voltage has dominant effect on the catalytic-plasma cracking process and in-plasma catalysis configuration is more efficient compared with post-plasma catalysis. The highest energy efficiency is achieved the value of 194.44 l/kW h for in-plasma configuration under highest applied voltage condition (11 kV). In these conditions, the production rate and mole percent of hydrogen are obtained 107.66 ml/min and 63.7%, respectively. The effect of catalyst deactivation is also investigated on the process variables.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Catalytic plasma co-cracking of methane and n-hexadecane is investigated through pulsed DBD reactor. ► Effects of voltage, amount of catalyst and plasma-catalyst configuration are examined. ► Applied voltage has dominant and direct effect on process energy efficiency. ► Maximum catalyst content as in-plasma configuration obtains maximum efficiency. ► In-plasma catalyst configuration increases the process efficiency up to 194.44 l/kW h.