| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148971 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2013 | 9 Pages |
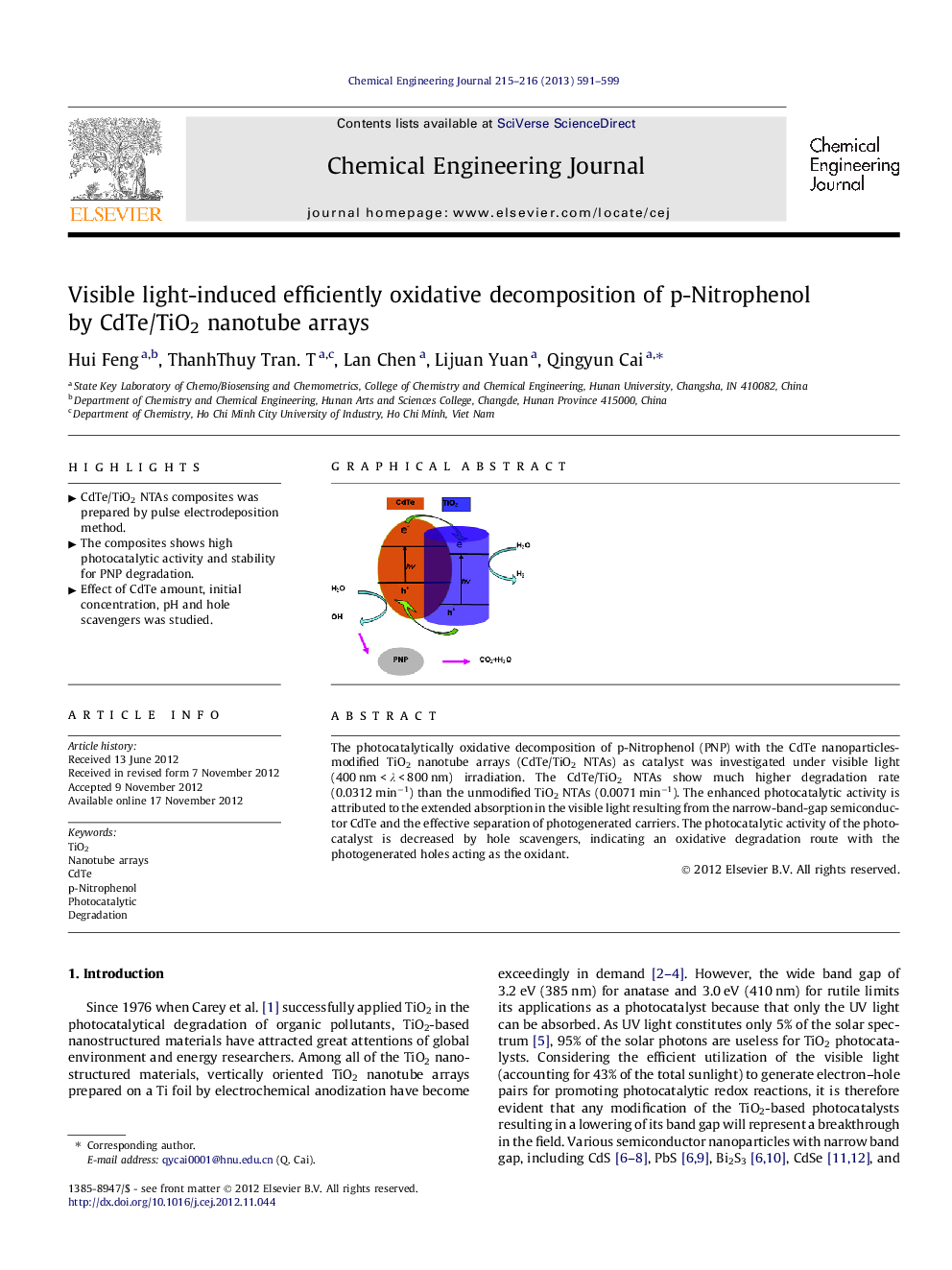
The photocatalytically oxidative decomposition of p-Nitrophenol (PNP) with the CdTe nanoparticles-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays (CdTe/TiO2 NTAs) as catalyst was investigated under visible light (400 nm < λ < 800 nm) irradiation. The CdTe/TiO2 NTAs show much higher degradation rate (0.0312 min−1) than the unmodified TiO2 NTAs (0.0071 min−1). The enhanced photocatalytic activity is attributed to the extended absorption in the visible light resulting from the narrow-band-gap semiconductor CdTe and the effective separation of photogenerated carriers. The photocatalytic activity of the photocatalyst is decreased by hole scavengers, indicating an oxidative degradation route with the photogenerated holes acting as the oxidant.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights• CdTe/TiO2 NTAs composites was prepared by pulse electrodeposition method. • The composites shows high photocatalytic activity and stability for PNP degradation. • Effect of CdTe amount, initial concentration, pH and hole scavengers was studied.