| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149054 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2013 | 9 Pages |
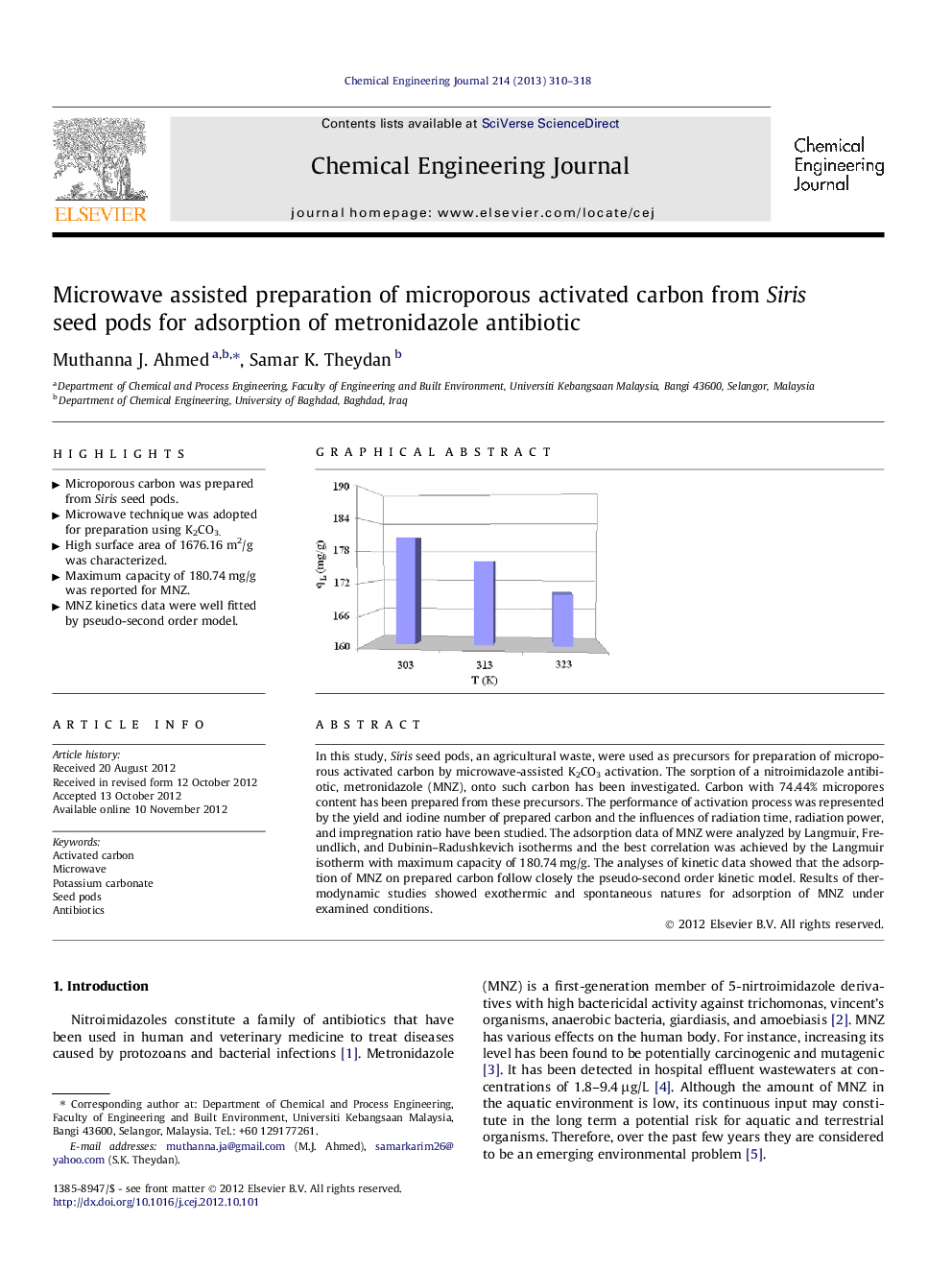
In this study, Siris seed pods, an agricultural waste, were used as precursors for preparation of microporous activated carbon by microwave-assisted K2CO3 activation. The sorption of a nitroimidazole antibiotic, metronidazole (MNZ), onto such carbon has been investigated. Carbon with 74.44% micropores content has been prepared from these precursors. The performance of activation process was represented by the yield and iodine number of prepared carbon and the influences of radiation time, radiation power, and impregnation ratio have been studied. The adsorption data of MNZ were analyzed by Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms and the best correlation was achieved by the Langmuir isotherm with maximum capacity of 180.74 mg/g. The analyses of kinetic data showed that the adsorption of MNZ on prepared carbon follow closely the pseudo-second order kinetic model. Results of thermodynamic studies showed exothermic and spontaneous natures for adsorption of MNZ under examined conditions.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Microporous carbon was prepared from Siris seed pods. ► Microwave technique was adopted for preparation using K2CO3. ► High surface area of 1676.16 m2/g was characterized. ► Maximum capacity of 180.74 mg/g was reported for MNZ. ► MNZ kinetics data were well fitted by pseudo-second order model.