| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149212 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2012 | 10 Pages |
In this study, the development and characterization of a novel adsorbent, prepared by ethylation of glycidylmethacrylate grafted aminated titanium dioxide densified cellulose (Et-AMPGDC), for the removal of arsenic(V) [As(V)] from aqueous solutions are reported. The adsorbent was characterized using FTIR, XRD, SEM and TG-DTG measurements. Batch experiments were performed to evaluate the adsorption efficiency of Et-AMPGDC towards As(V) ions. The optimum pH was found to be 6.0. Kinetic studies reveal that the uptake was rapid and equilibrium was established in 1 h. The pseudo-second-order rate model fitted the adsorption kinetics perfectly. Langmuir isotherm model adequately described the homogeneous nature of the surface of adsorbent. The maximum adsorption capacity was evaluated to be 108.70 mg/g. Adsorbed As(V) ions were desorbed effectively by 0.1 M HCl. The present investigation shows that Et-AMPGDC would be a promising adsorbent for the removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions.
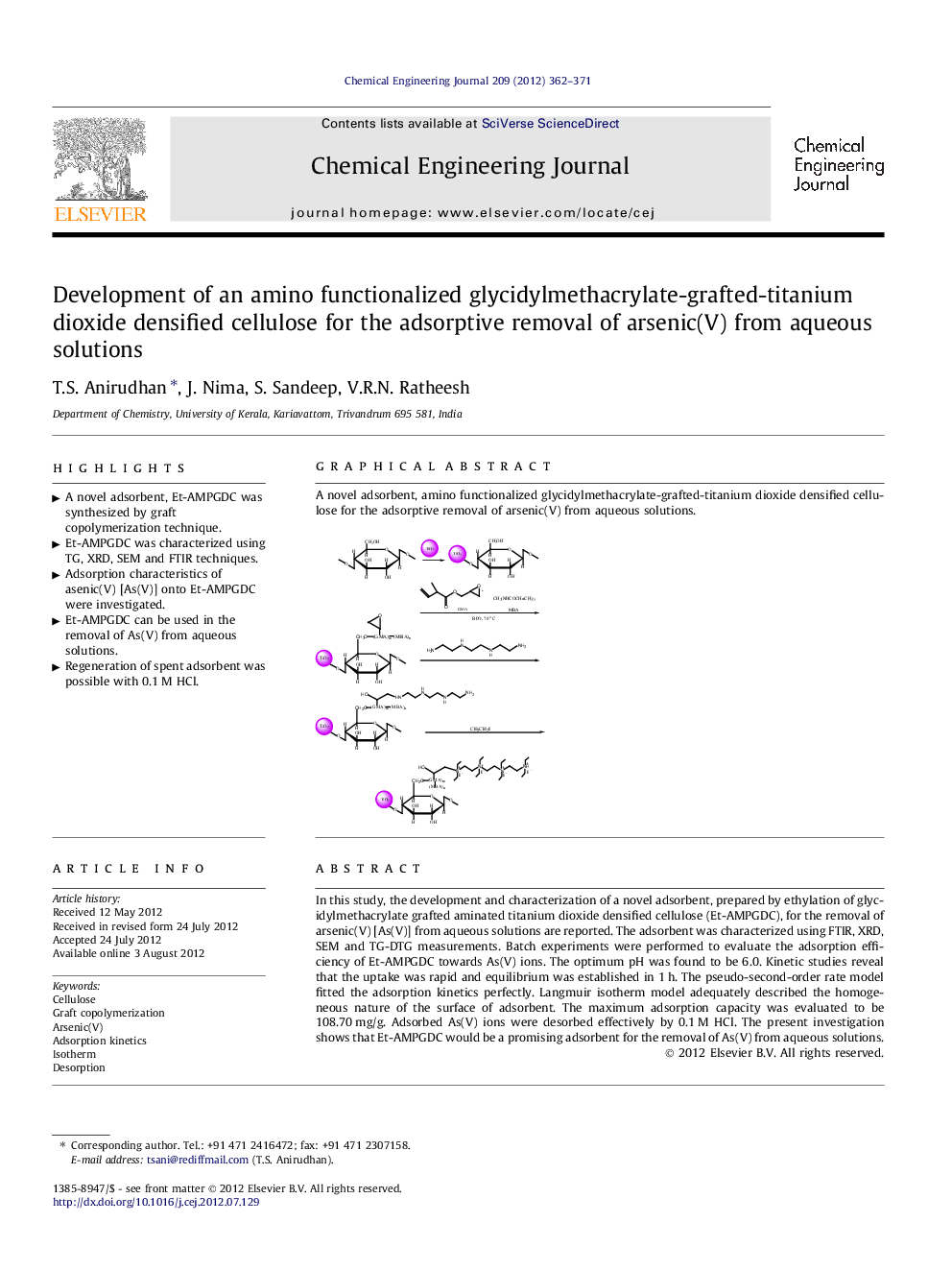
Graphical abstractA novel adsorbent, amino functionalized glycidylmethacrylate-grafted-titanium dioxide densified cellulose for the adsorptive removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous solutions.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► A novel adsorbent, Et-AMPGDC was synthesized by graft copolymerization technique. ► Et-AMPGDC was characterized using TG, XRD, SEM and FTIR techniques. ► Adsorption characteristics of asenic(V) [As(V)] onto Et-AMPGDC were investigated. ► Et-AMPGDC can be used in the removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions. ► Regeneration of spent adsorbent was possible with 0.1 M HCl.