| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149224 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2012 | 7 Pages |
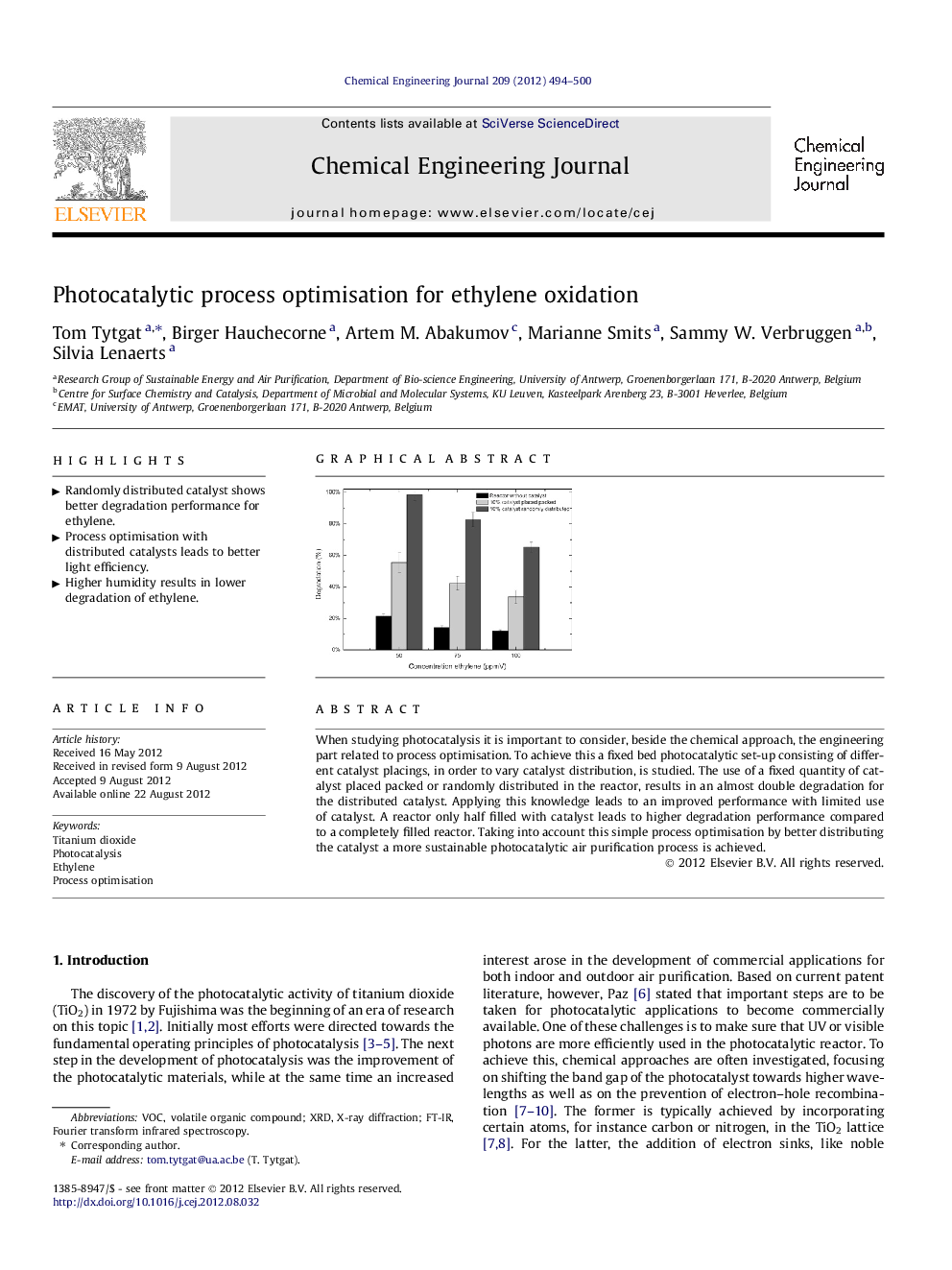
When studying photocatalysis it is important to consider, beside the chemical approach, the engineering part related to process optimisation. To achieve this a fixed bed photocatalytic set-up consisting of different catalyst placings, in order to vary catalyst distribution, is studied. The use of a fixed quantity of catalyst placed packed or randomly distributed in the reactor, results in an almost double degradation for the distributed catalyst. Applying this knowledge leads to an improved performance with limited use of catalyst. A reactor only half filled with catalyst leads to higher degradation performance compared to a completely filled reactor. Taking into account this simple process optimisation by better distributing the catalyst a more sustainable photocatalytic air purification process is achieved.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Randomly distributed catalyst shows better degradation performance for ethylene. ► Process optimisation with distributed catalysts leads to better light efficiency. ► Higher humidity results in lower degradation of ethylene.