| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149501 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2012 | 7 Pages |
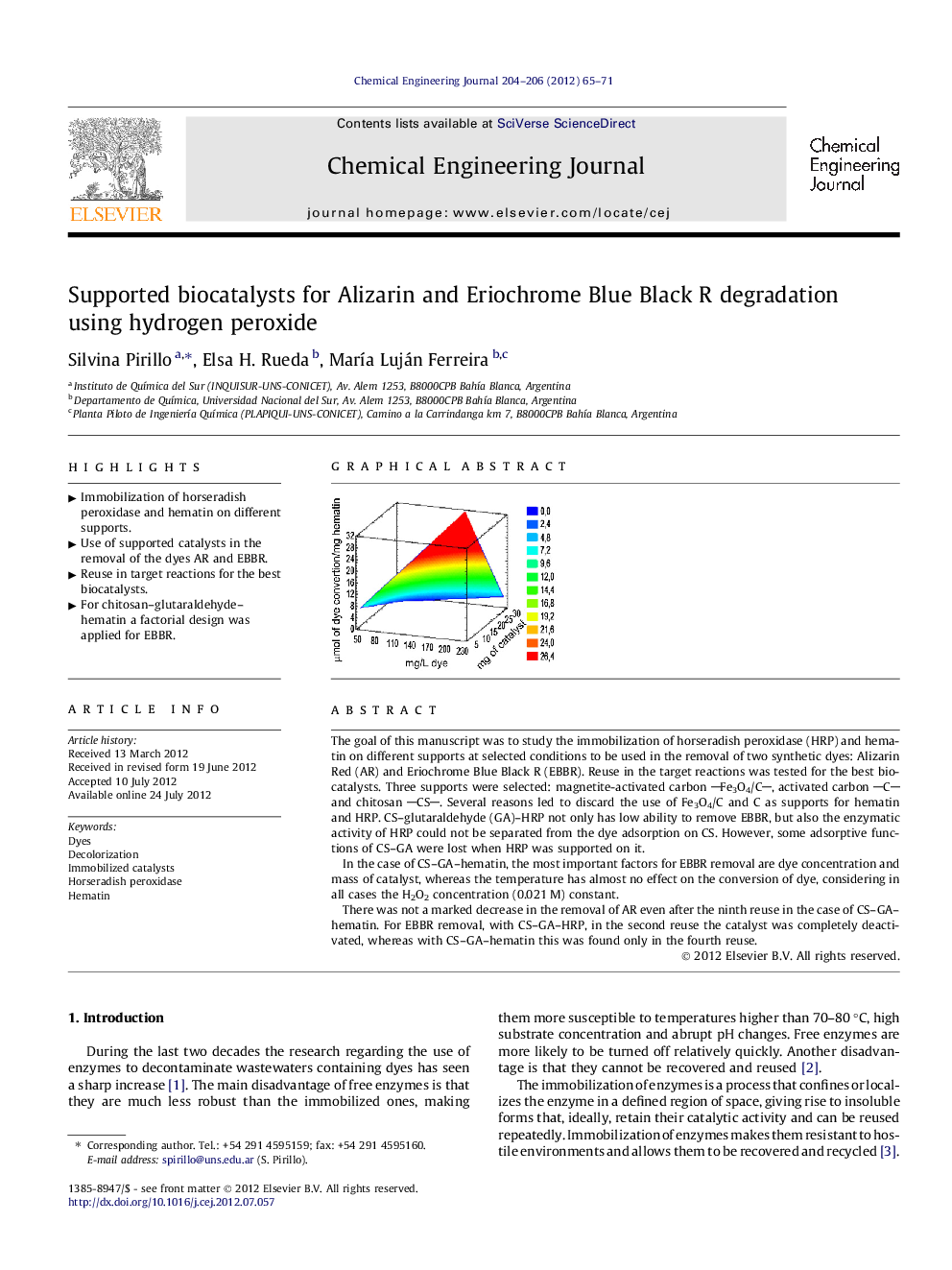
The goal of this manuscript was to study the immobilization of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and hematin on different supports at selected conditions to be used in the removal of two synthetic dyes: Alizarin Red (AR) and Eriochrome Blue Black R (EBBR). Reuse in the target reactions was tested for the best biocatalysts. Three supports were selected: magnetite-activated carbon Fe3O4/C, activated carbon C and chitosan CS. Several reasons led to discard the use of Fe3O4/C and C as supports for hematin and HRP. CS–glutaraldehyde (GA)–HRP not only has low ability to remove EBBR, but also the enzymatic activity of HRP could not be separated from the dye adsorption on CS. However, some adsorptive functions of CS–GA were lost when HRP was supported on it.In the case of CS–GA–hematin, the most important factors for EBBR removal are dye concentration and mass of catalyst, whereas the temperature has almost no effect on the conversion of dye, considering in all cases the H2O2 concentration (0.021 M) constant.There was not a marked decrease in the removal of AR even after the ninth reuse in the case of CS–GA–hematin. For EBBR removal, with CS–GA–HRP, in the second reuse the catalyst was completely deactivated, whereas with CS–GA–hematin this was found only in the fourth reuse.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase and hematin on different supports. ► Use of supported catalysts in the removal of the dyes AR and EBBR. ► Reuse in target reactions for the best biocatalysts. ► For chitosan–glutaraldehyde–hematin a factorial design was applied for EBBR.