| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149522 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2012 | 7 Pages |
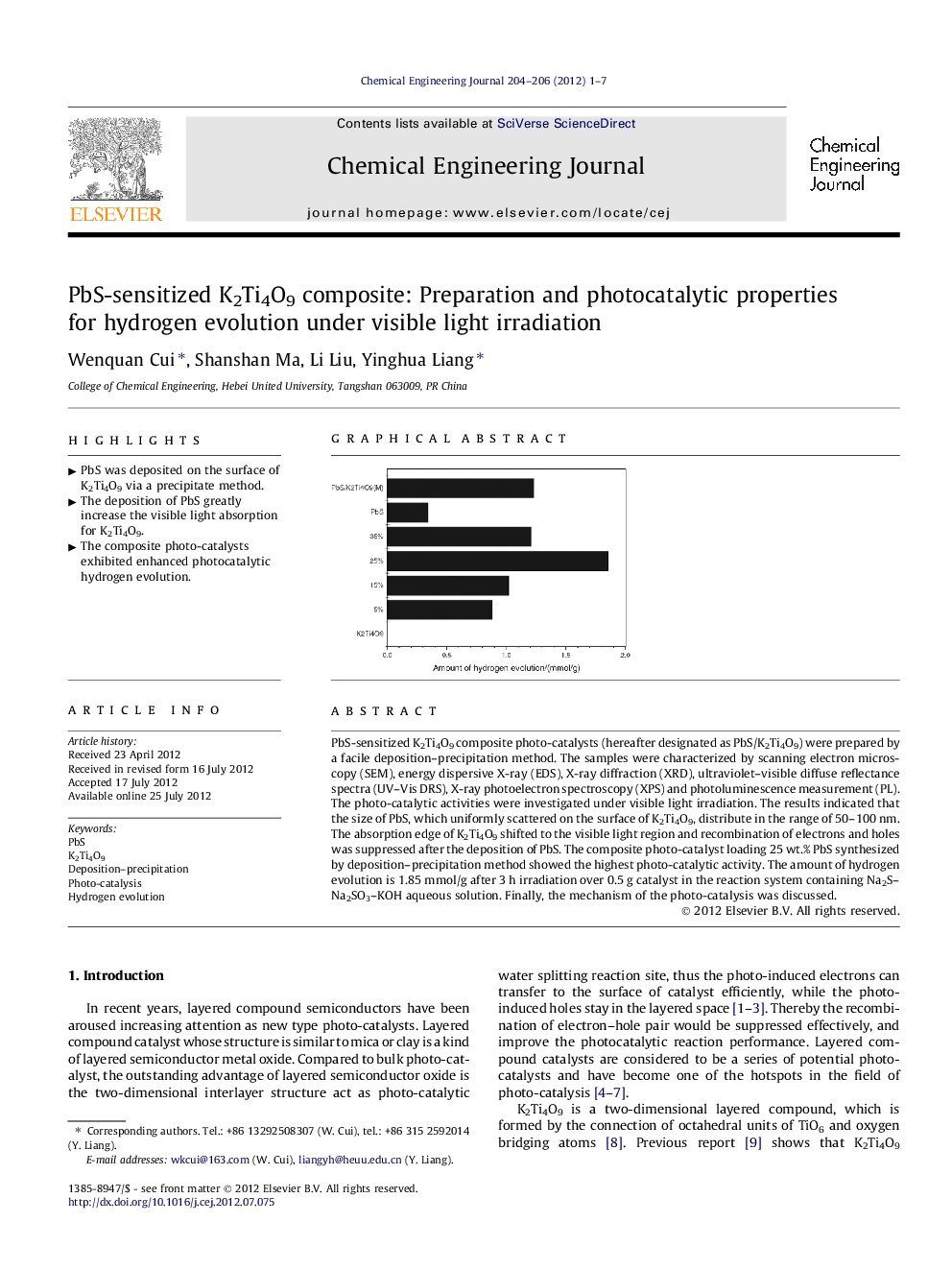
PbS-sensitized K2Ti4O9 composite photo-catalysts (hereafter designated as PbS/K2Ti4O9) were prepared by a facile deposition–precipitation method. The samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), ultraviolet–visible diffuse reflectance spectra (UV–Vis DRS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and photoluminescence measurement (PL). The photo-catalytic activities were investigated under visible light irradiation. The results indicated that the size of PbS, which uniformly scattered on the surface of K2Ti4O9, distribute in the range of 50–100 nm. The absorption edge of K2Ti4O9 shifted to the visible light region and recombination of electrons and holes was suppressed after the deposition of PbS. The composite photo-catalyst loading 25 wt.% PbS synthesized by deposition–precipitation method showed the highest photo-catalytic activity. The amount of hydrogen evolution is 1.85 mmol/g after 3 h irradiation over 0.5 g catalyst in the reaction system containing Na2S–Na2SO3–KOH aqueous solution. Finally, the mechanism of the photo-catalysis was discussed.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► PbS was deposited on the surface of K2Ti4O9 via a precipitate method. ► The deposition of PbS greatly increase the visible light absorption for K2Ti4O9. ► The composite photo-catalysts exhibited enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution.