| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4503806 | Biological Control | 2015 | 7 Pages |
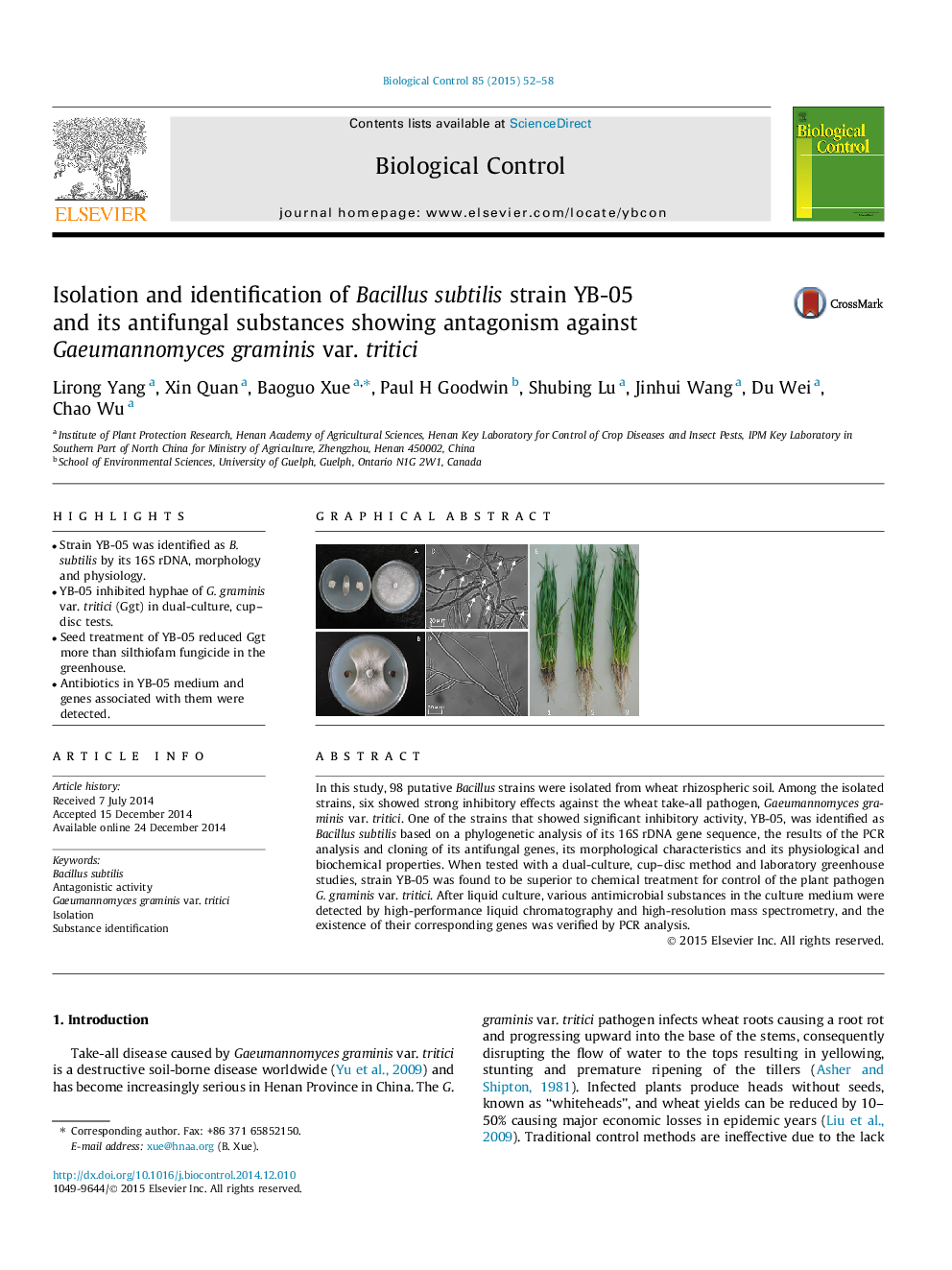
•Strain YB-05 was identified as B. subtilis by its 16S rDNA, morphology and physiology.•YB-05 inhibited hyphae of G. graminis var. tritici (Ggt) in dual-culture, cup–disc tests.•Seed treatment of YB-05 reduced Ggt more than silthiofam fungicide in the greenhouse.•Antibiotics in YB-05 medium and genes associated with them were detected.
In this study, 98 putative Bacillus strains were isolated from wheat rhizospheric soil. Among the isolated strains, six showed strong inhibitory effects against the wheat take-all pathogen, Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici. One of the strains that showed significant inhibitory activity, YB-05, was identified as Bacillus subtilis based on a phylogenetic analysis of its 16S rDNA gene sequence, the results of the PCR analysis and cloning of its antifungal genes, its morphological characteristics and its physiological and biochemical properties. When tested with a dual-culture, cup–disc method and laboratory greenhouse studies, strain YB-05 was found to be superior to chemical treatment for control of the plant pathogen G. graminis var. tritici. After liquid culture, various antimicrobial substances in the culture medium were detected by high-performance liquid chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry, and the existence of their corresponding genes was verified by PCR analysis.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide