| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4503947 | Biological Control | 2014 | 9 Pages |
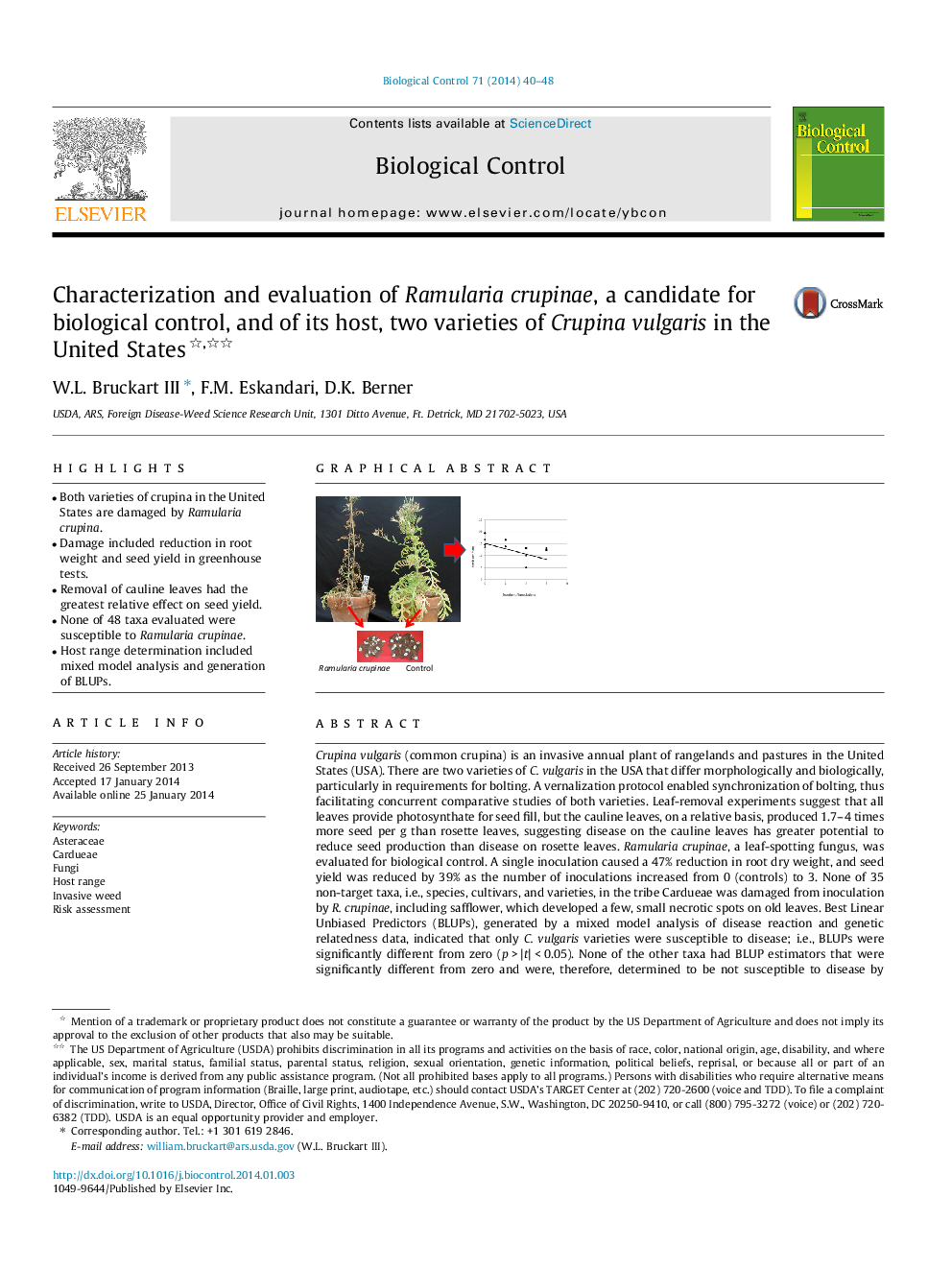
•Both varieties of crupina in the United States are damaged by Ramularia crupina.•Damage included reduction in root weight and seed yield in greenhouse tests.•Removal of cauline leaves had the greatest relative effect on seed yield.•None of 48 taxa evaluated were susceptible to Ramularia crupinae.•Host range determination included mixed model analysis and generation of BLUPs.
Crupina vulgaris (common crupina) is an invasive annual plant of rangelands and pastures in the United States (USA). There are two varieties of C. vulgaris in the USA that differ morphologically and biologically, particularly in requirements for bolting. A vernalization protocol enabled synchronization of bolting, thus facilitating concurrent comparative studies of both varieties. Leaf-removal experiments suggest that all leaves provide photosynthate for seed fill, but the cauline leaves, on a relative basis, produced 1.7–4 times more seed per g than rosette leaves, suggesting disease on the cauline leaves has greater potential to reduce seed production than disease on rosette leaves. Ramularia crupinae, a leaf-spotting fungus, was evaluated for biological control. A single inoculation caused a 47% reduction in root dry weight, and seed yield was reduced by 39% as the number of inoculations increased from 0 (controls) to 3. None of 35 non-target taxa, i.e., species, cultivars, and varieties, in the tribe Cardueae was damaged from inoculation by R. crupinae, including safflower, which developed a few, small necrotic spots on old leaves. Best Linear Unbiased Predictors (BLUPs), generated by a mixed model analysis of disease reaction and genetic relatedness data, indicated that only C. vulgaris varieties were susceptible to disease; i.e., BLUPs were significantly different from zero (p > |t| < 0.05). None of the other taxa had BLUP estimators that were significantly different from zero and were, therefore, determined to be not susceptible to disease by R. crupinae. Results suggest that R. crupinae is a potentially good candidate for biological control of this important weed pest and would likely not affect other species of importance in the USA.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide