| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591890 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•Effect of slip velocity on rotating electroosmotic flow is studiedin a micro-channel.•The electro-osmotic flow takes place in a wavy micro-channel.•The problem is solved numerically by developing Crank–Nicolson scheme.•Rotating Reynolds number plays an important role in controlling EOF.•Higher zeta potential can facilitate the transport of fluids in a microfluidic devise.
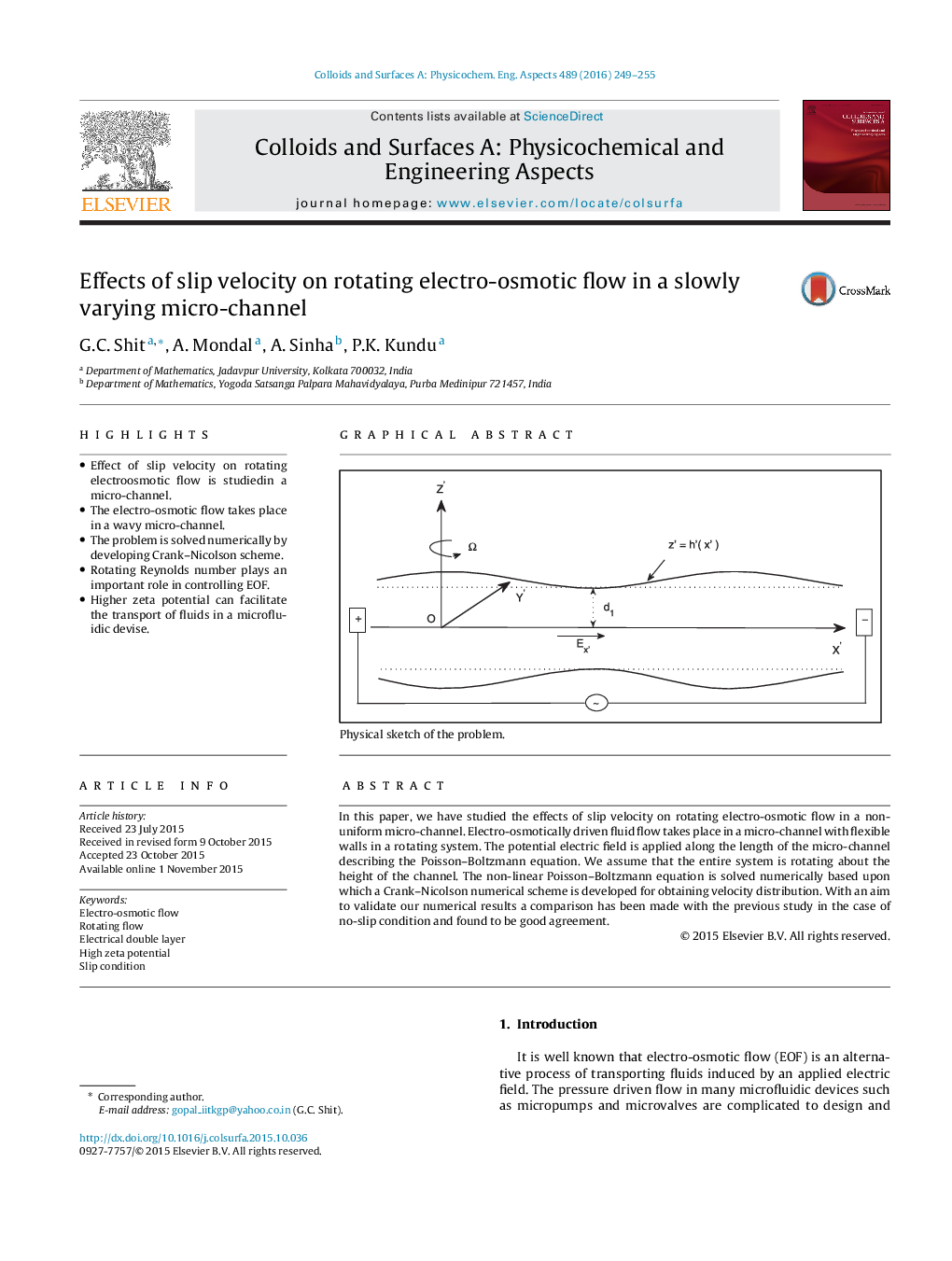
In this paper, we have studied the effects of slip velocity on rotating electro-osmotic flow in a non-uniform micro-channel. Electro-osmotically driven fluid flow takes place in a micro-channel with flexible walls in a rotating system. The potential electric field is applied along the length of the micro-channel describing the Poisson–Boltzmann equation. We assume that the entire system is rotating about the height of the channel. The non-linear Poisson–Boltzmann equation is solved numerically based upon which a Crank–Nicolson numerical scheme is developed for obtaining velocity distribution. With an aim to validate our numerical results a comparison has been made with the previous study in the case of no-slip condition and found to be good agreement.
Graphical abstract Physical sketch of the problem.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide