| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465032 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 10 Pages |
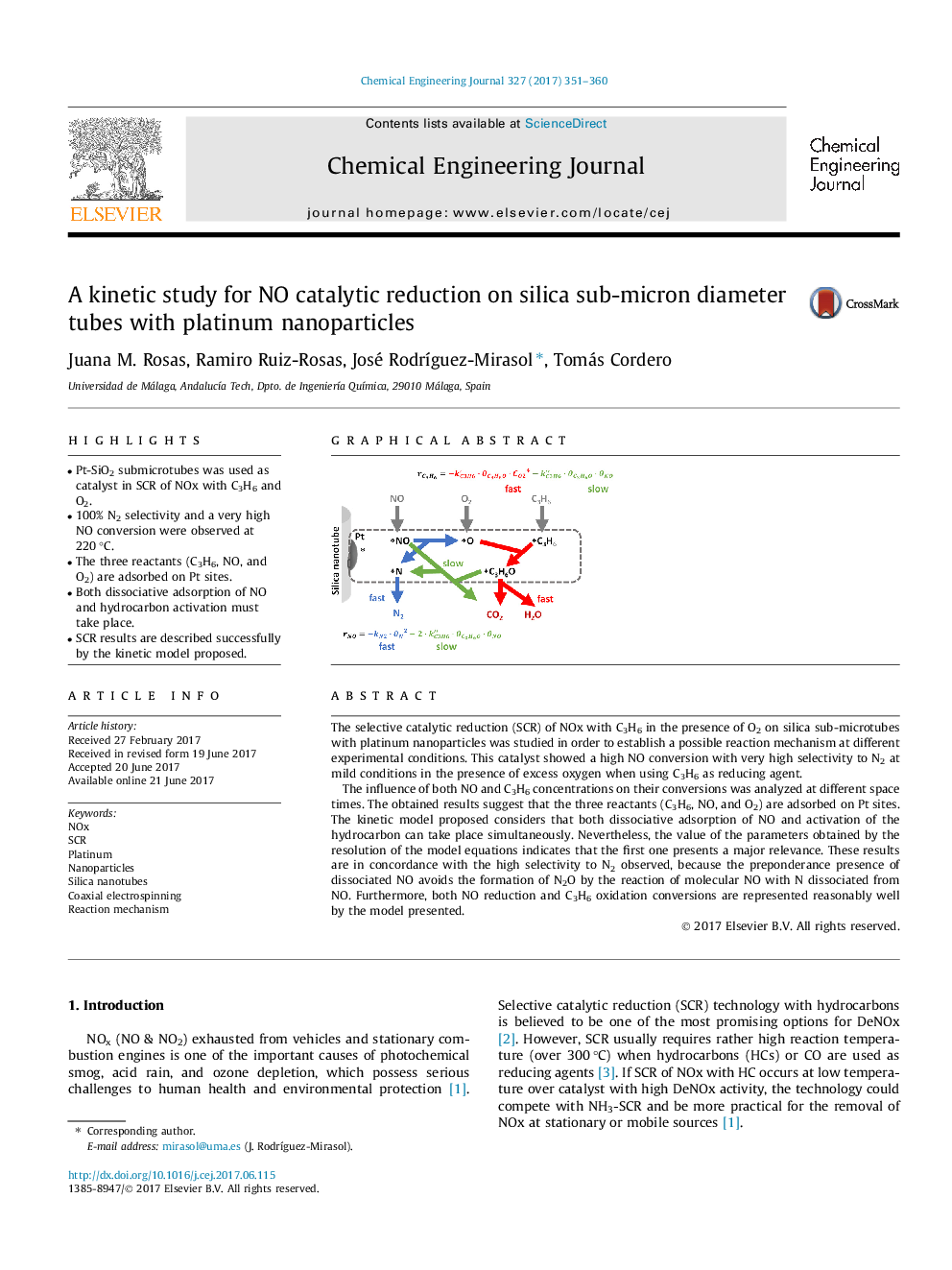
â¢Pt-SiO2 submicrotubes was used as catalyst in SCR of NOx with C3H6 and O2.â¢100% N2 selectivity and a very high NO conversion were observed at 220 °C.â¢The three reactants (C3H6, NO, and O2) are adsorbed on Pt sites.â¢Both dissociative adsorption of NO and hydrocarbon activation must take place.â¢SCR results are described successfully by the kinetic model proposed.
The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx with C3H6 in the presence of O2 on silica sub-microtubes with platinum nanoparticles was studied in order to establish a possible reaction mechanism at different experimental conditions. This catalyst showed a high NO conversion with very high selectivity to N2 at mild conditions in the presence of excess oxygen when using C3H6 as reducing agent.The influence of both NO and C3H6 concentrations on their conversions was analyzed at different space times. The obtained results suggest that the three reactants (C3H6, NO, and O2) are adsorbed on Pt sites. The kinetic model proposed considers that both dissociative adsorption of NO and activation of the hydrocarbon can take place simultaneously. Nevertheless, the value of the parameters obtained by the resolution of the model equations indicates that the first one presents a major relevance. These results are in concordance with the high selectivity to N2 observed, because the preponderance presence of dissociated NO avoids the formation of N2O by the reaction of molecular NO with N dissociated from NO. Furthermore, both NO reduction and C3H6 oxidation conversions are represented reasonably well by the model presented.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (104KB)Download full-size image