| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465065 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 8 Pages |
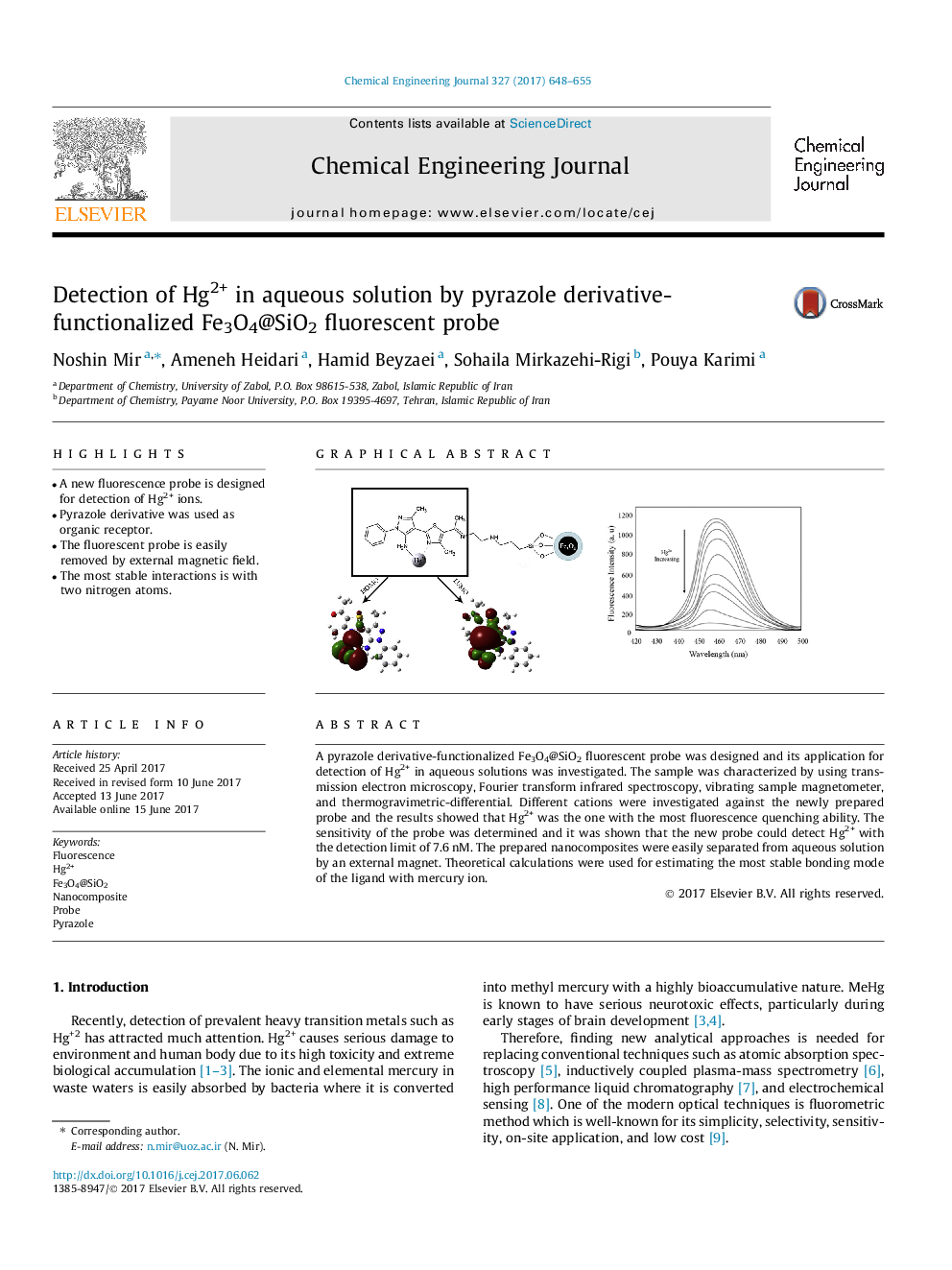
â¢A new fluorescence probe is designed for detection of Hg2+ ions.â¢Pyrazole derivative was used as organic receptor.â¢The fluorescent probe is easily removed by external magnetic field.â¢The most stable interactions is with two nitrogen atoms.
A pyrazole derivative-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 fluorescent probe was designed and its application for detection of Hg2+ in aqueous solutions was investigated. The sample was characterized by using transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer, and thermogravimetric-differential. Different cations were investigated against the newly prepared probe and the results showed that Hg2+ was the one with the most fluorescence quenching ability. The sensitivity of the probe was determined and it was shown that the new probe could detect Hg2+ with the detection limit of 7.6Â nM. The prepared nanocomposites were easily separated from aqueous solution by an external magnet. Theoretical calculations were used for estimating the most stable bonding mode of the ligand with mercury ion.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (67KB)Download full-size image