| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465535 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 10 Pages |
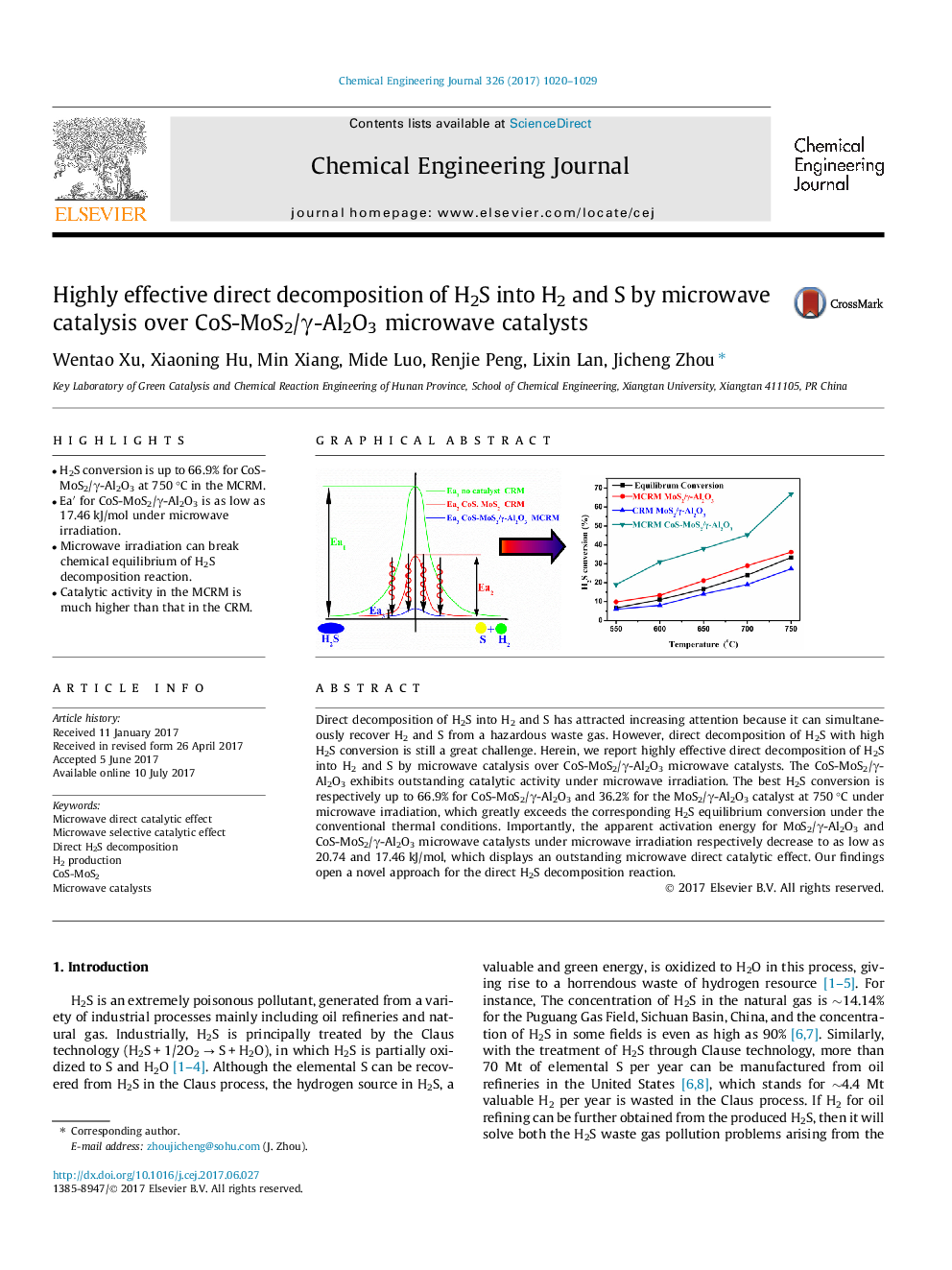
â¢H2S conversion is up to 66.9% for CoS-MoS2/γ-Al2O3 at 750 °C in the MCRM.â¢Eaâ² for CoS-MoS2/γ-Al2O3 is as low as 17.46 kJ/mol under microwave irradiation.â¢Microwave irradiation can break chemical equilibrium of H2S decomposition reaction.â¢Catalytic activity in the MCRM is much higher than that in the CRM.
Direct decomposition of H2S into H2 and S has attracted increasing attention because it can simultaneously recover H2 and S from a hazardous waste gas. However, direct decomposition of H2S with high H2S conversion is still a great challenge. Herein, we report highly effective direct decomposition of H2S into H2 and S by microwave catalysis over CoS-MoS2/γ-Al2O3 microwave catalysts. The CoS-MoS2/γ-Al2O3 exhibits outstanding catalytic activity under microwave irradiation. The best H2S conversion is respectively up to 66.9% for CoS-MoS2/γ-Al2O3 and 36.2% for the MoS2/γ-Al2O3 catalyst at 750 °C under microwave irradiation, which greatly exceeds the corresponding H2S equilibrium conversion under the conventional thermal conditions. Importantly, the apparent activation energy for MoS2/γ-Al2O3 and CoS-MoS2/γ-Al2O3 microwave catalysts under microwave irradiation respectively decrease to as low as 20.74 and 17.46 kJ/mol, which displays an outstanding microwave direct catalytic effect. Our findings open a novel approach for the direct H2S decomposition reaction.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (242KB)Download full-size image