| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465706 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 11 Pages |
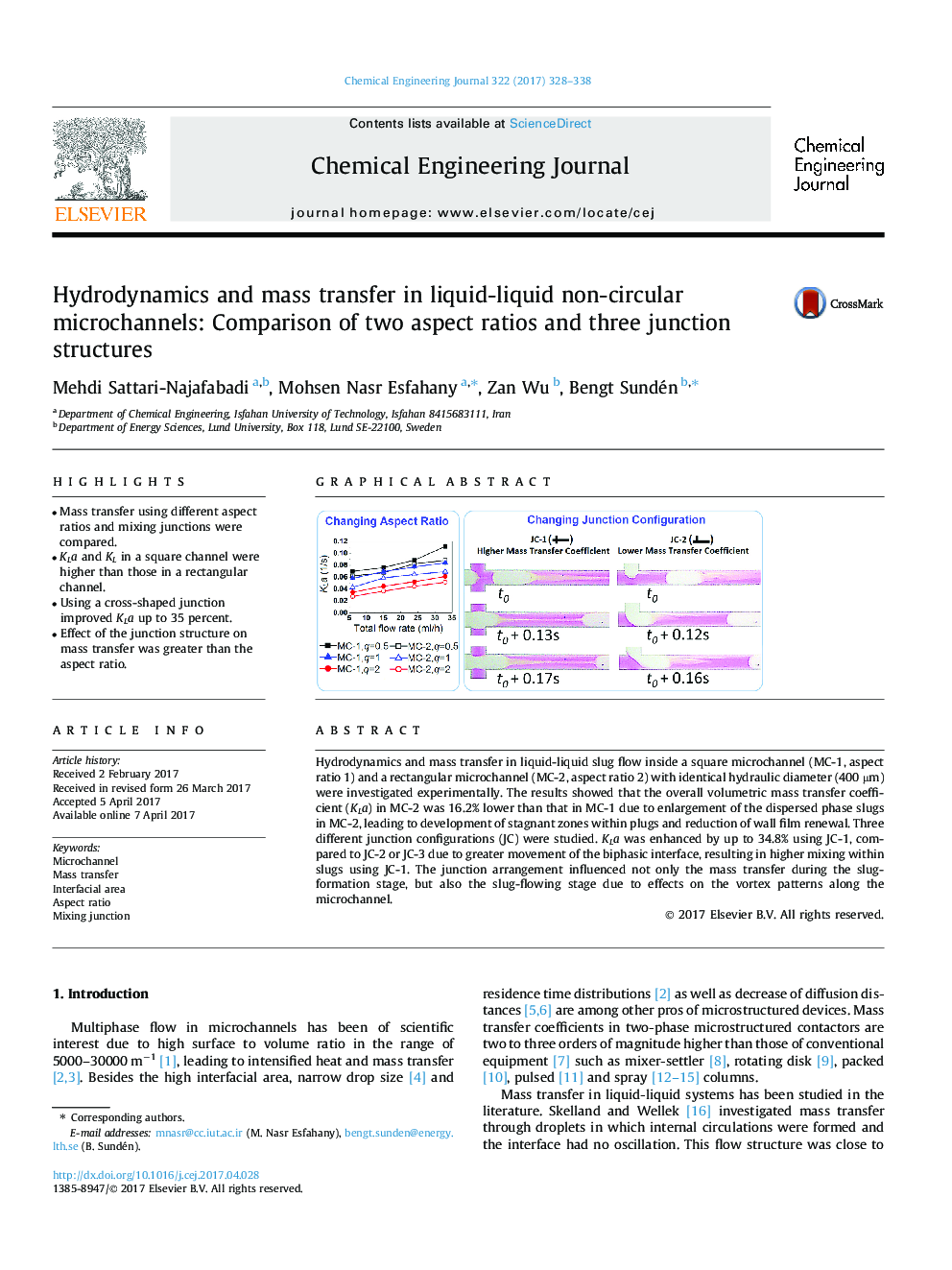
â¢Mass transfer using different aspect ratios and mixing junctions were compared.â¢KLa and KL in a square channel were higher than those in a rectangular channel.â¢Using a cross-shaped junction improved KLa up to 35 percent.â¢Effect of the junction structure on mass transfer was greater than the aspect ratio.
Hydrodynamics and mass transfer in liquid-liquid slug flow inside a square microchannel (MC-1, aspect ratio 1) and a rectangular microchannel (MC-2, aspect ratio 2) with identical hydraulic diameter (400 µm) were investigated experimentally. The results showed that the overall volumetric mass transfer coefficient (KLa) in MC-2 was 16.2% lower than that in MC-1 due to enlargement of the dispersed phase slugs in MC-2, leading to development of stagnant zones within plugs and reduction of wall film renewal. Three different junction configurations (JC) were studied. KLa was enhanced by up to 34.8% using JC-1, compared to JC-2 or JC-3 due to greater movement of the biphasic interface, resulting in higher mixing within slugs using JC-1. The junction arrangement influenced not only the mass transfer during the slug-formation stage, but also the slug-flowing stage due to effects on the vortex patterns along the microchannel.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (298KB)Download full-size image