| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465897 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 7 Pages |
â¢A composite of Co3O4, Co, graphitized carbon is proposed for LIBs which is seldom reported.â¢It is prepared by Co-catalytic-graphitization of carboxymethyl chitosan derived carbon.â¢The composite delivers improved electrochemical performance.â¢The enhanced performance is due to the conductive Co and graphitic carbon and high-capacity Co3O4.
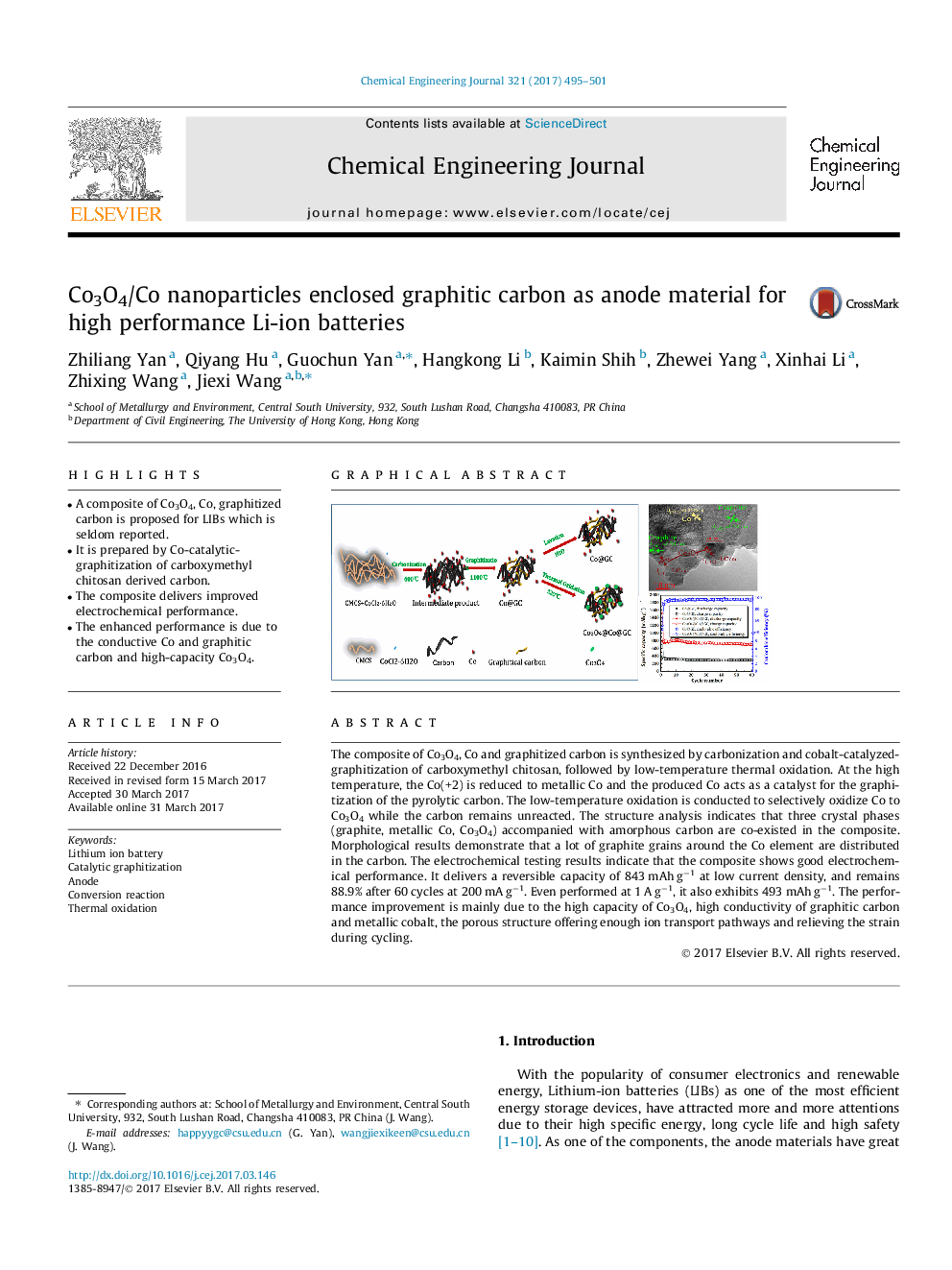
The composite of Co3O4, Co and graphitized carbon is synthesized by carbonization and cobalt-catalyzed-graphitization of carboxymethyl chitosan, followed by low-temperature thermal oxidation. At the high temperature, the Co(+2) is reduced to metallic Co and the produced Co acts as a catalyst for the graphitization of the pyrolytic carbon. The low-temperature oxidation is conducted to selectively oxidize Co to Co3O4 while the carbon remains unreacted. The structure analysis indicates that three crystal phases (graphite, metallic Co, Co3O4) accompanied with amorphous carbon are co-existed in the composite. Morphological results demonstrate that a lot of graphite grains around the Co element are distributed in the carbon. The electrochemical testing results indicate that the composite shows good electrochemical performance. It delivers a reversible capacity of 843 mAh gâ1 at low current density, and remains 88.9% after 60 cycles at 200 mA gâ1. Even performed at 1 A gâ1, it also exhibits 493 mAh gâ1. The performance improvement is mainly due to the high capacity of Co3O4, high conductivity of graphitic carbon and metallic cobalt, the porous structure offering enough ion transport pathways and relieving the strain during cycling.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (313KB)Download full-size image