| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466178 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 10 Pages |
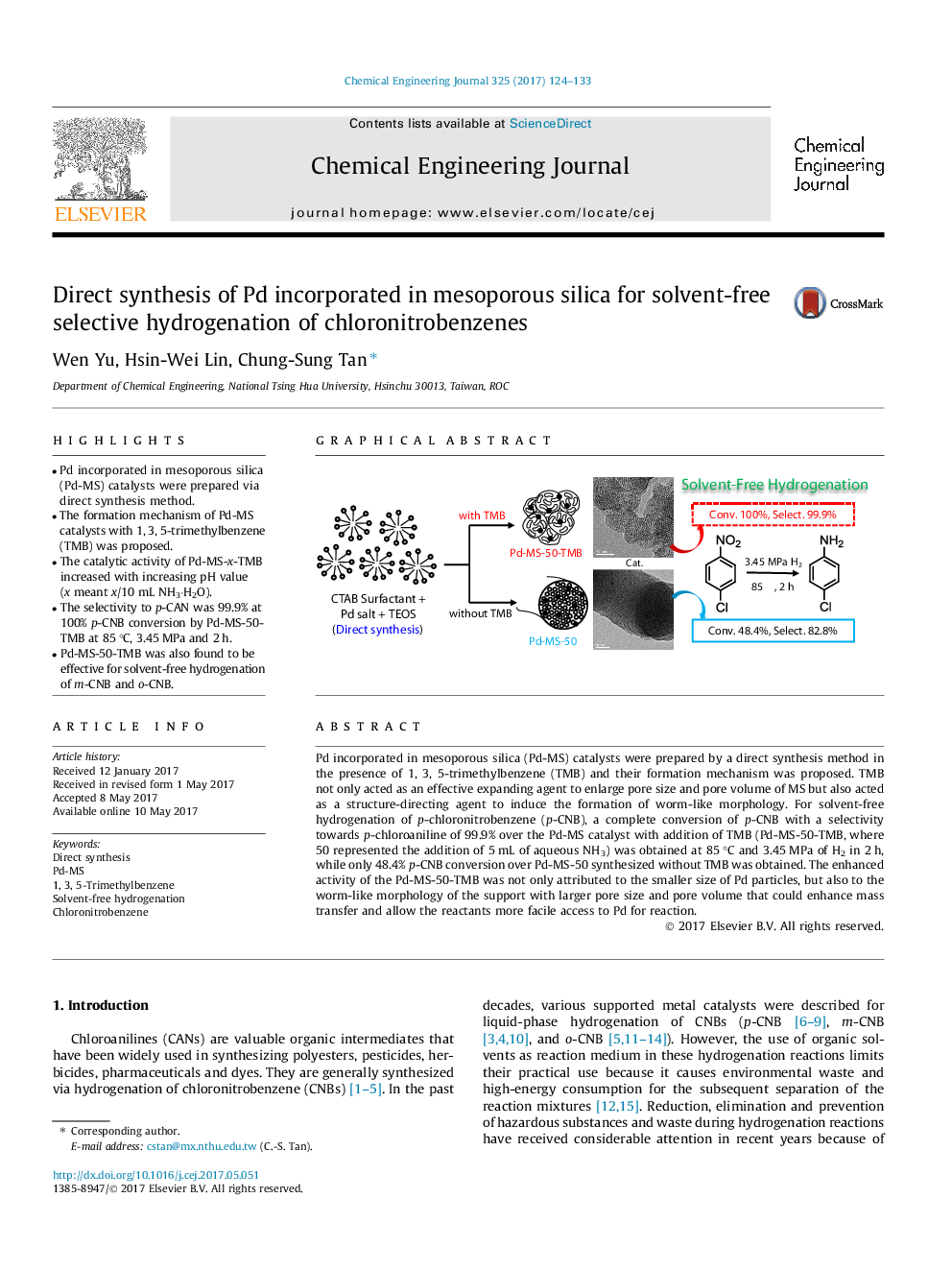
â¢Pd incorporated in mesoporous silica (Pd-MS) catalysts were prepared via direct synthesis method.â¢The formation mechanism of Pd-MS catalysts with 1, 3, 5-trimethylbenzene (TMB) was proposed.â¢The catalytic activity of Pd-MS-x-TMB increased with increasing pH value (x meant x/10 mL NH3·H2O).â¢The selectivity to p-CAN was 99.9% at 100% p-CNB conversion by Pd-MS-50-TMB at 85 °C, 3.45 MPa and 2 h.â¢Pd-MS-50-TMB was also found to be effective for solvent-free hydrogenation of m-CNB and o-CNB.
Pd incorporated in mesoporous silica (Pd-MS) catalysts were prepared by a direct synthesis method in the presence of 1, 3, 5-trimethylbenzene (TMB) and their formation mechanism was proposed. TMB not only acted as an effective expanding agent to enlarge pore size and pore volume of MS but also acted as a structure-directing agent to induce the formation of worm-like morphology. For solvent-free hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene (p-CNB), a complete conversion of p-CNB with a selectivity towards p-chloroaniline of 99.9% over the Pd-MS catalyst with addition of TMB (Pd-MS-50-TMB, where 50 represented the addition of 5 mL of aqueous NH3) was obtained at 85 °C and 3.45 MPa of H2 in 2 h, while only 48.4% p-CNB conversion over Pd-MS-50 synthesized without TMB was obtained. The enhanced activity of the Pd-MS-50-TMB was not only attributed to the smaller size of Pd particles, but also to the worm-like morphology of the support with larger pore size and pore volume that could enhance mass transfer and allow the reactants more facile access to Pd for reaction.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (276KB)Download full-size image