| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466196 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 13 Pages |
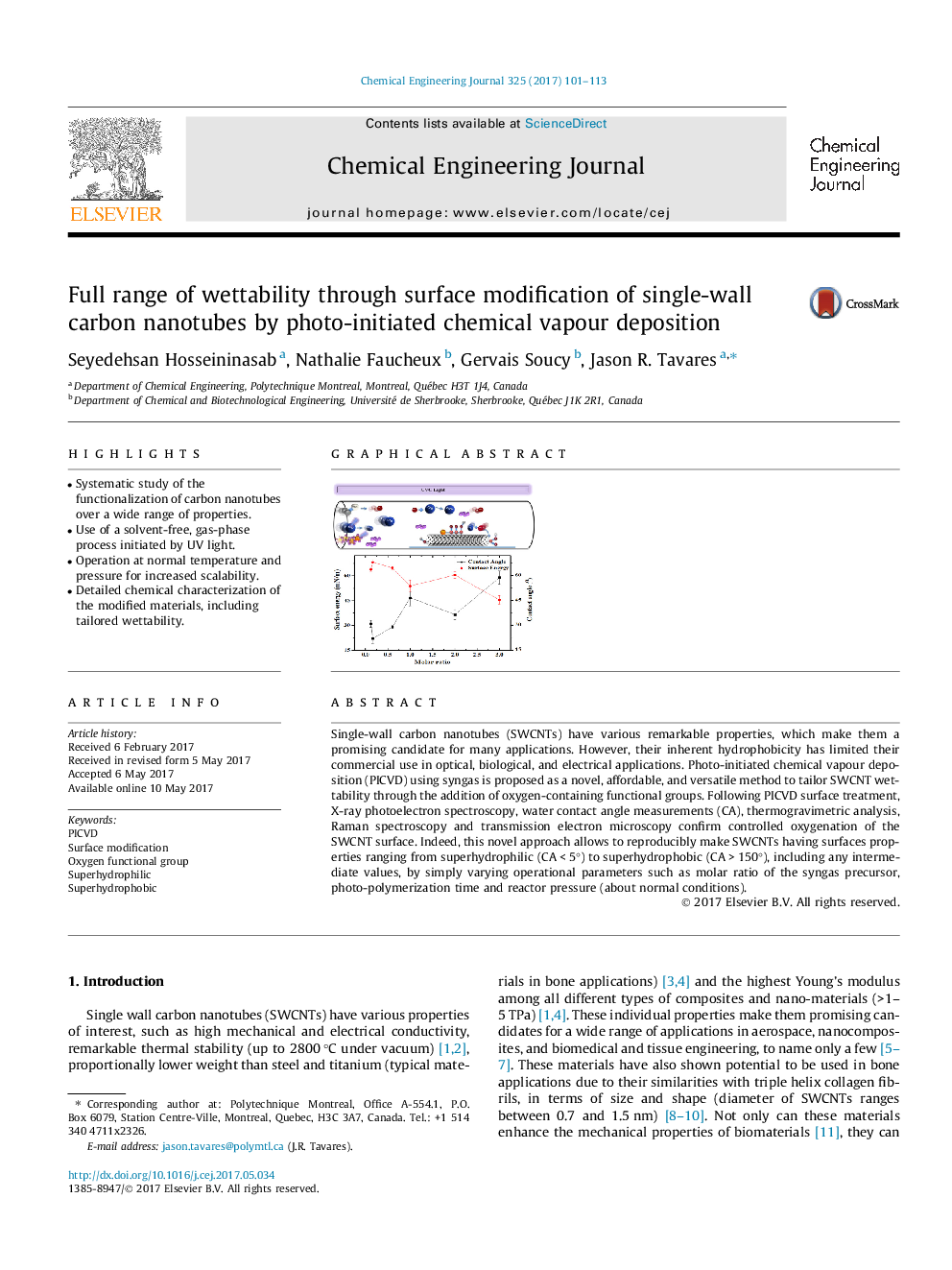
â¢Systematic study of the functionalization of carbon nanotubes over a wide range of properties.â¢Use of a solvent-free, gas-phase process initiated by UV light.â¢Operation at normal temperature and pressure for increased scalability.â¢Detailed chemical characterization of the modified materials, including tailored wettability.
Single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have various remarkable properties, which make them a promising candidate for many applications. However, their inherent hydrophobicity has limited their commercial use in optical, biological, and electrical applications. Photo-initiated chemical vapour deposition (PICVD) using syngas is proposed as a novel, affordable, and versatile method to tailor SWCNT wettability through the addition of oxygen-containing functional groups. Following PICVD surface treatment, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, water contact angle measurements (CA), thermogravimetric analysis, Raman spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy confirm controlled oxygenation of the SWCNT surface. Indeed, this novel approach allows to reproducibly make SWCNTs having surfaces properties ranging from superhydrophilic (CA < 5°) to superhydrophobic (CA > 150°), including any intermediate values, by simply varying operational parameters such as molar ratio of the syngas precursor, photo-polymerization time and reactor pressure (about normal conditions).
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (77KB)Download full-size image