| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466263 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 10 Pages |
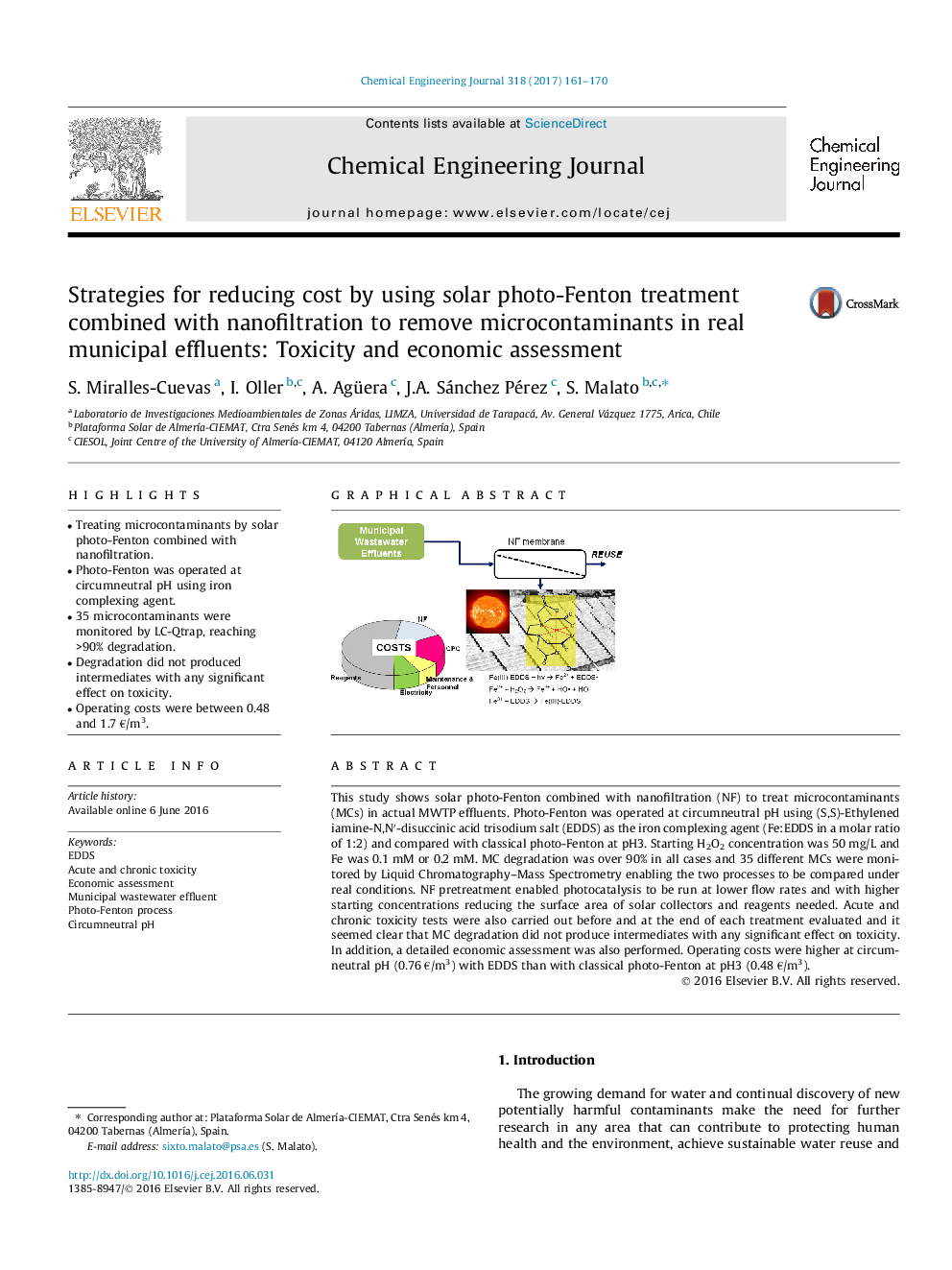
â¢Treating microcontaminants by solar photo-Fenton combined with nanofiltration.â¢Photo-Fenton was operated at circumneutral pH using iron complexing agent.â¢35 microcontaminants were monitored by LC-Qtrap, reaching >90% degradation.â¢Degradation did not produced intermediates with any significant effect on toxicity.â¢Operating costs were between 0.48 and 1.7 â¬/m3.
This study shows solar photo-Fenton combined with nanofiltration (NF) to treat microcontaminants (MCs) in actual MWTP effluents. Photo-Fenton was operated at circumneutral pH using (S,S)-Ethylenediamine-N,Nâ²-disuccinic acid trisodium salt (EDDS) as the iron complexing agent (Fe:EDDS in a molar ratio of 1:2) and compared with classical photo-Fenton at pH3. Starting H2O2 concentration was 50 mg/L and Fe was 0.1 mM or 0.2 mM. MC degradation was over 90% in all cases and 35 different MCs were monitored by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry enabling the two processes to be compared under real conditions. NF pretreatment enabled photocatalysis to be run at lower flow rates and with higher starting concentrations reducing the surface area of solar collectors and reagents needed. Acute and chronic toxicity tests were also carried out before and at the end of each treatment evaluated and it seemed clear that MC degradation did not produce intermediates with any significant effect on toxicity. In addition, a detailed economic assessment was also performed. Operating costs were higher at circumneutral pH (0.76 â¬/m3) with EDDS than with classical photo-Fenton at pH3 (0.48 â¬/m3).
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (157KB)Download full-size image