| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466664 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 10 Pages |
â¢As-prepared Fe nanoparticles (NPs) sorbent were not significantly affected by the CO and H2.â¢The activities of the as-prepared sorbent with different carbon aerogel were tested.â¢50%Fe/C700 sorbent had the highest sulfur capacity of 12.54 g S/100 g sorbent.
To solve the effect of the strong reduction gas, sintering problem and improve the desulfurization activity. Fe nanoparticles (NPs) into carbon aerogel desulfurizers were fabricated with by 50%Fe/C700 precursor and their performance for H2S removal in hot coal gas was studied. The Fe nanoparticles loading in mesoporous carbon aerogels with larger specific surface area and pore volume sorbent were designed and firstly applied to remove H2S with high efficiency in hot coal gas. The H2S removal experiments were conducted in the temperature range of 500-650 °C using hot coal gas containing 0.2 vol% H2S. We explored the optimum temperature conditions and the influence of textural parameters of carbon aerogels and tested the Fe nanoparticles desulfurizers with 10-20% H2 and 10-20% CO. The fresh, used, regenerated samples were characterized by N2 adsorption, X-ray diffraction, high-resolution scanning electron microscope techniques (HRSEM) and high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). The results confirmed that Fe nanoparticle sorbent had high desulfurization performance. This work could provide a new direction and new field in hot coal gas desulfurization and would be important to research on the development sector of the coal industry.
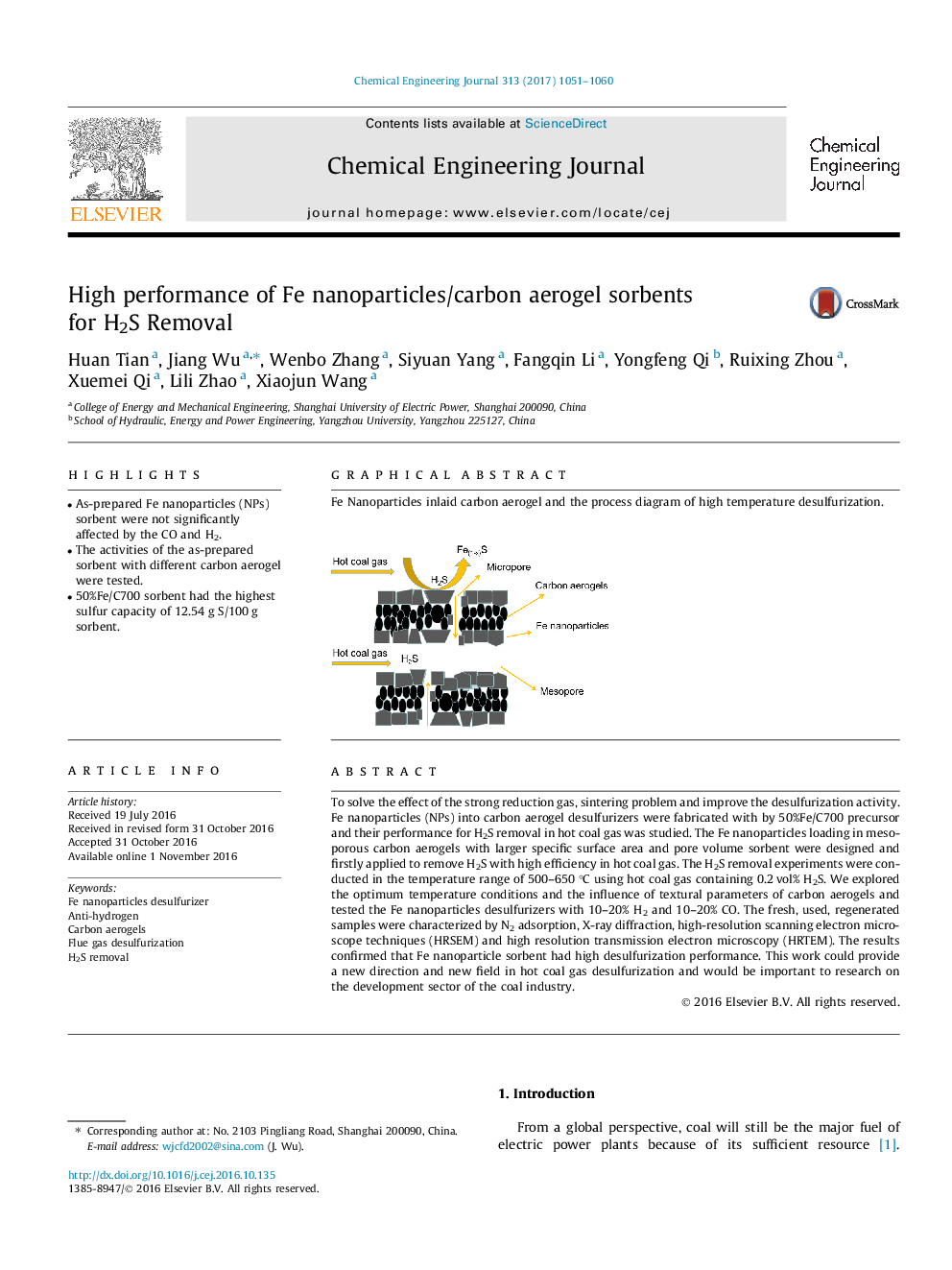
Graphical abstractFe Nanoparticles inlaid carbon aerogel and the process diagram of high temperature desulfurization.Download high-res image (127KB)Download full-size image