| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466704 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 13 Pages |
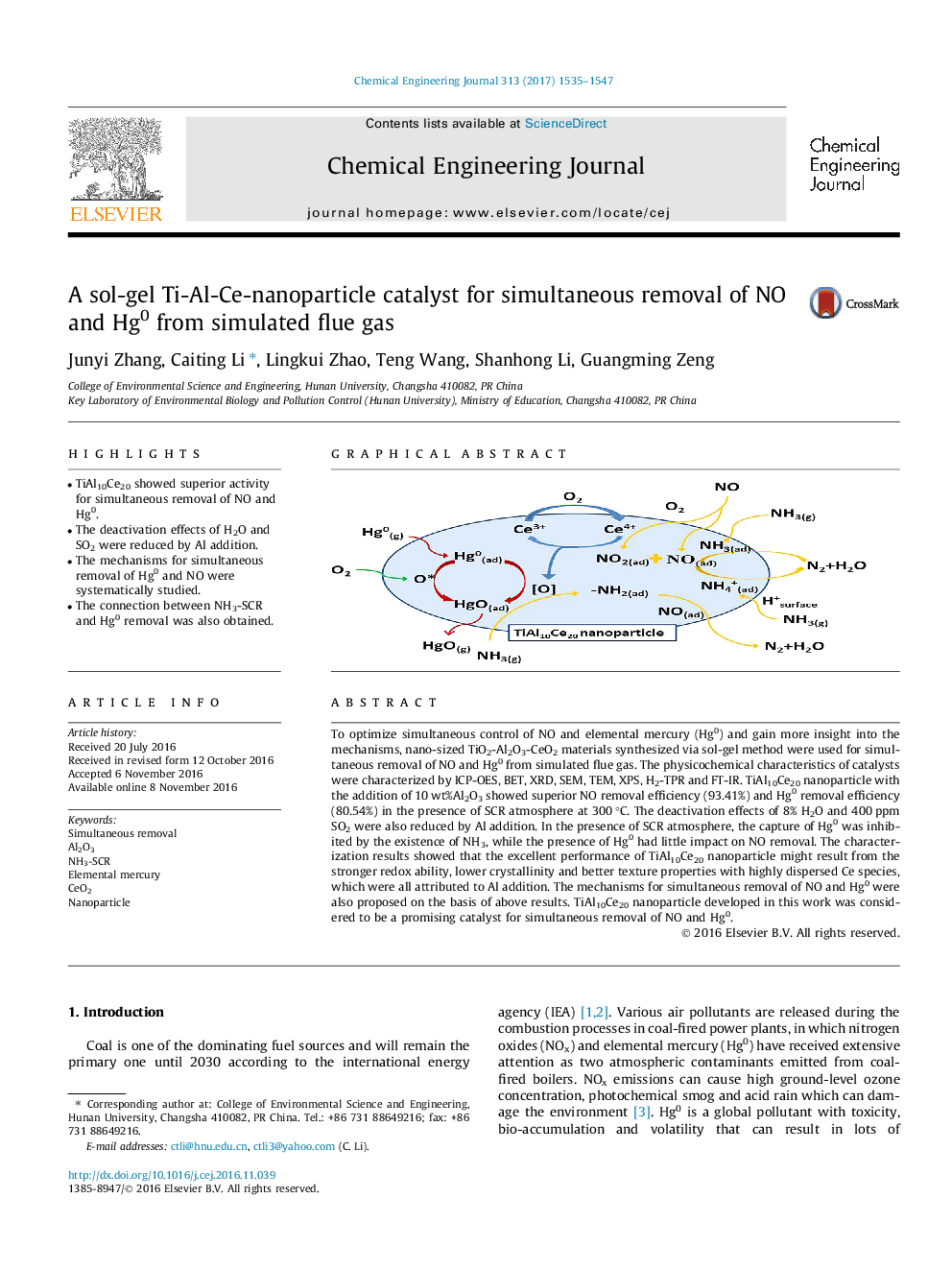
â¢TiAl10Ce20 showed superior activity for simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0.â¢The deactivation effects of H2O and SO2 were reduced by Al addition.â¢The mechanisms for simultaneous removal of Hg0 and NO were systematically studied.â¢The connection between NH3-SCR and Hg0 removal was also obtained.
To optimize simultaneous control of NO and elemental mercury (Hg0) and gain more insight into the mechanisms, nano-sized TiO2-Al2O3-CeO2 materials synthesized via sol-gel method were used for simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 from simulated flue gas. The physicochemical characteristics of catalysts were characterized by ICP-OES, BET, XRD, SEM, TEM, XPS, H2-TPR and FT-IR. TiAl10Ce20 nanoparticle with the addition of 10 wt%Al2O3 showed superior NO removal efficiency (93.41%) and Hg0 removal efficiency (80.54%) in the presence of SCR atmosphere at 300 °C. The deactivation effects of 8% H2O and 400 ppm SO2 were also reduced by Al addition. In the presence of SCR atmosphere, the capture of Hg0 was inhibited by the existence of NH3, while the presence of Hg0 had little impact on NO removal. The characterization results showed that the excellent performance of TiAl10Ce20 nanoparticle might result from the stronger redox ability, lower crystallinity and better texture properties with highly dispersed Ce species, which were all attributed to Al addition. The mechanisms for simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 were also proposed on the basis of above results. TiAl10Ce20 nanoparticle developed in this work was considered to be a promising catalyst for simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (166KB)Download full-size image