| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466705 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2017 | 6 Pages |
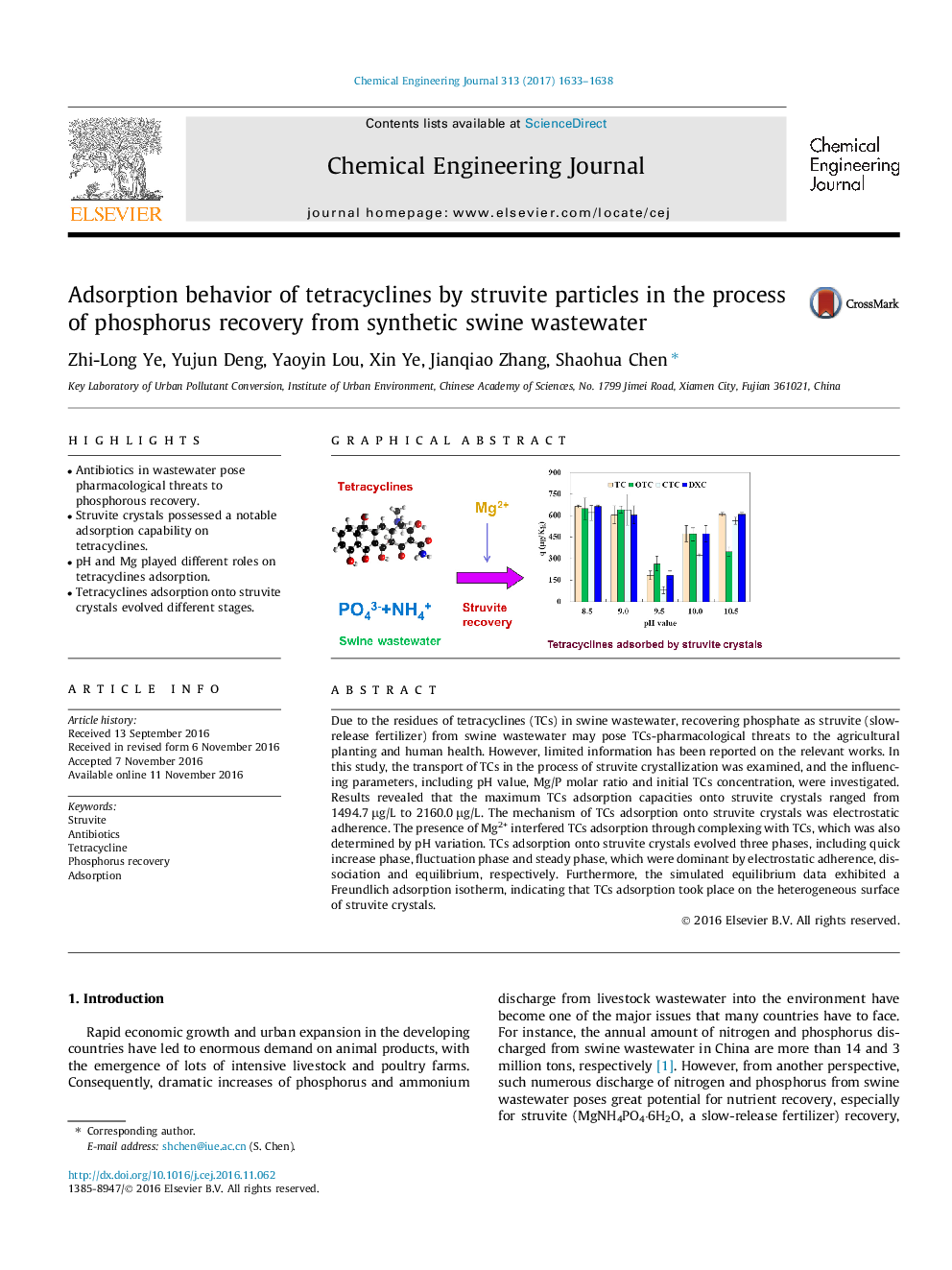
â¢Antibiotics in wastewater pose pharmacological threats to phosphorous recovery.â¢Struvite crystals possessed a notable adsorption capability on tetracyclines.â¢pH and Mg played different roles on tetracyclines adsorption.â¢Tetracyclines adsorption onto struvite crystals evolved different stages.
Due to the residues of tetracyclines (TCs) in swine wastewater, recovering phosphate as struvite (slow-release fertilizer) from swine wastewater may pose TCs-pharmacological threats to the agricultural planting and human health. However, limited information has been reported on the relevant works. In this study, the transport of TCs in the process of struvite crystallization was examined, and the influencing parameters, including pH value, Mg/P molar ratio and initial TCs concentration, were investigated. Results revealed that the maximum TCs adsorption capacities onto struvite crystals ranged from 1494.7 μg/L to 2160.0 μg/L. The mechanism of TCs adsorption onto struvite crystals was electrostatic adherence. The presence of Mg2+ interfered TCs adsorption through complexing with TCs, which was also determined by pH variation. TCs adsorption onto struvite crystals evolved three phases, including quick increase phase, fluctuation phase and steady phase, which were dominant by electrostatic adherence, dissociation and equilibrium, respectively. Furthermore, the simulated equilibrium data exhibited a Freundlich adsorption isotherm, indicating that TCs adsorption took place on the heterogeneous surface of struvite crystals.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (98KB)Download full-size image