| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1284153 | Journal of Power Sources | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•Lithium storage process in Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O is studied by various ex-situ techniques.•Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O reveals quasi-reversible conversion mechanism for lithium storage.•Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O shows a lithium storage capacity of 2285.0 mAh g−1.
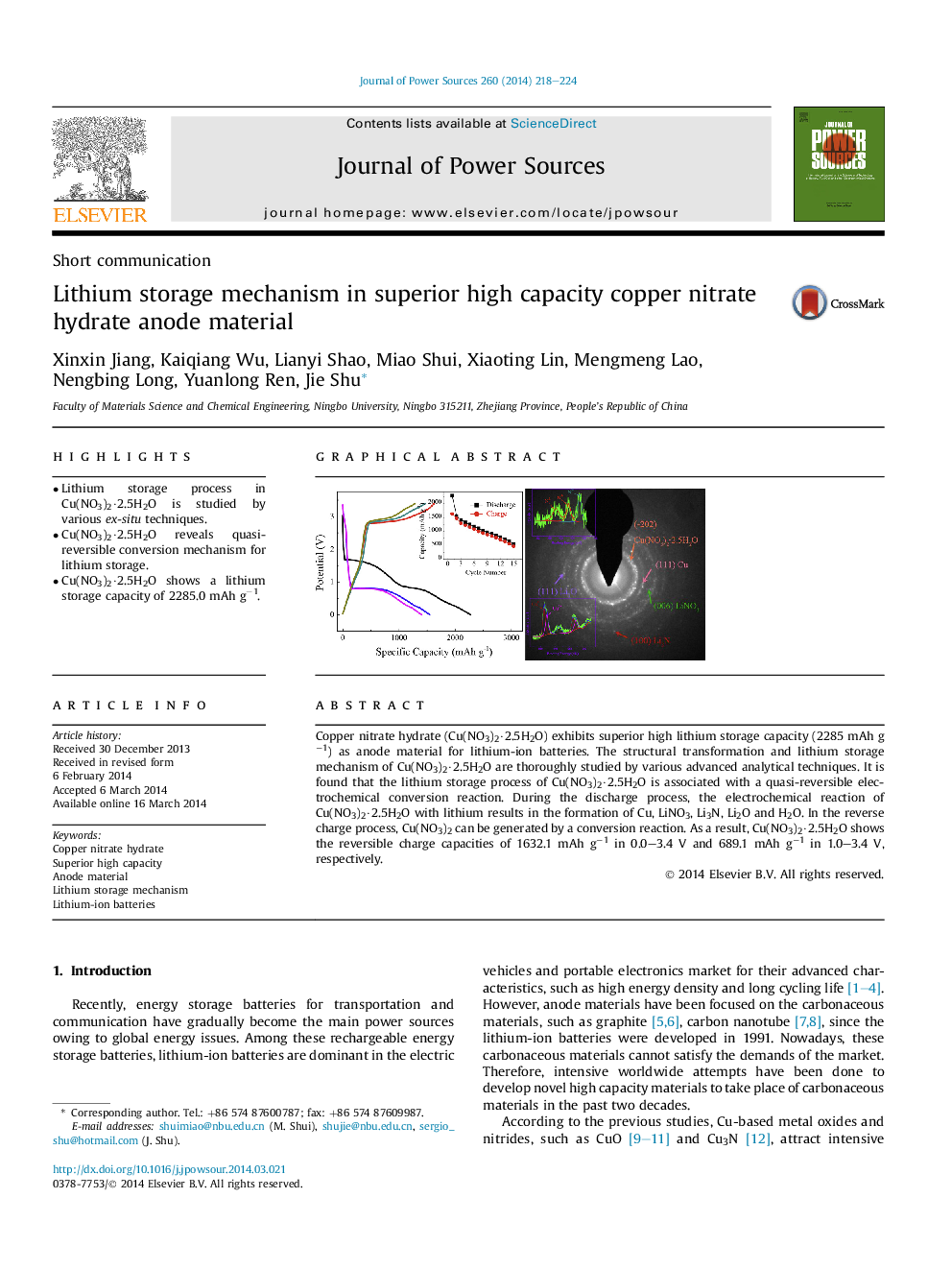
Copper nitrate hydrate (Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O) exhibits superior high lithium storage capacity (2285 mAh g−1) as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. The structural transformation and lithium storage mechanism of Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O are thoroughly studied by various advanced analytical techniques. It is found that the lithium storage process of Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O is associated with a quasi-reversible electrochemical conversion reaction. During the discharge process, the electrochemical reaction of Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O with lithium results in the formation of Cu, LiNO3, Li3N, Li2O and H2O. In the reverse charge process, Cu(NO3)2 can be generated by a conversion reaction. As a result, Cu(NO3)2·2.5H2O shows the reversible charge capacities of 1632.1 mAh g−1 in 0.0–3.4 V and 689.1 mAh g−1 in 1.0–3.4 V, respectively.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide