| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2038955 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 8 Pages |
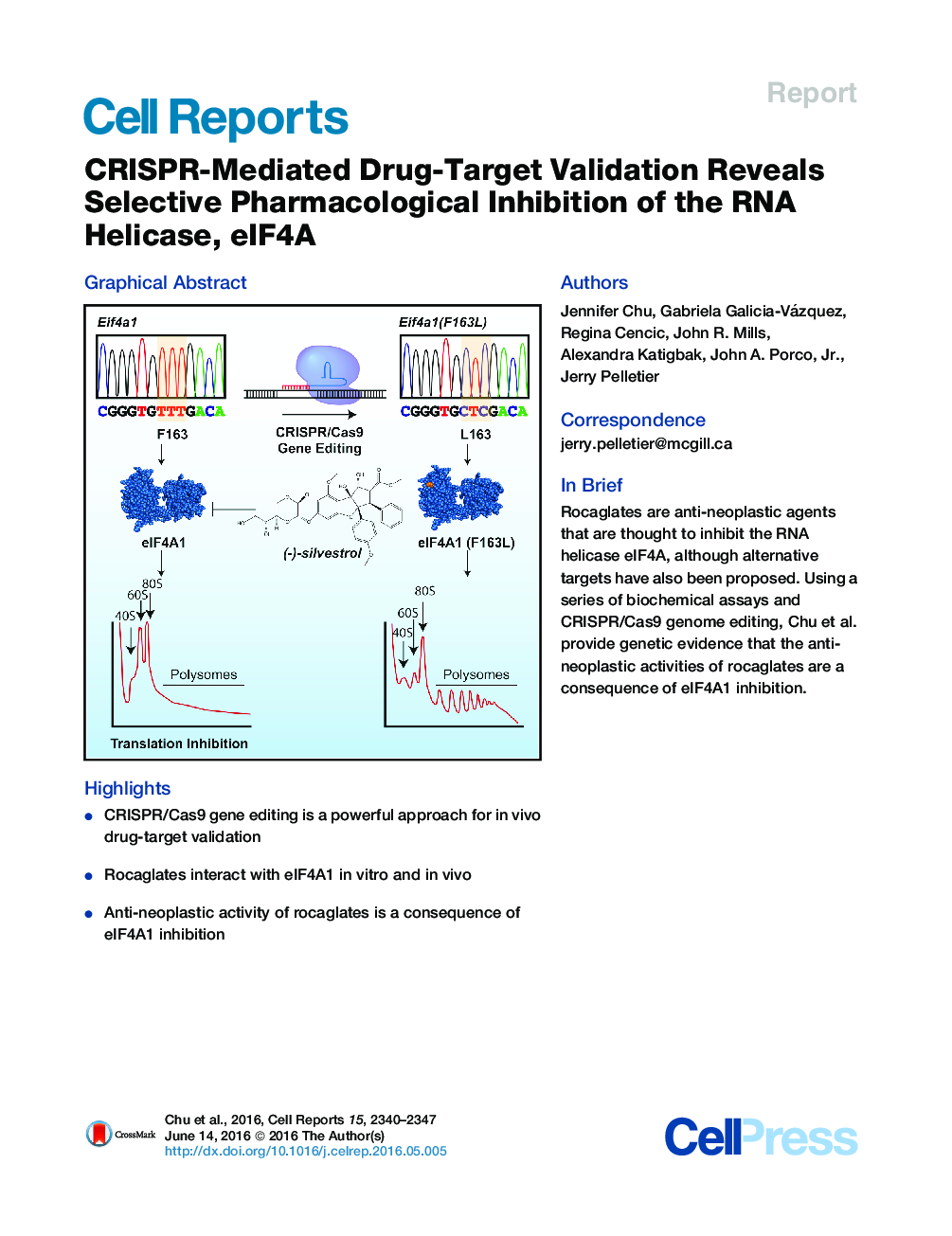
•CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing is a powerful approach for in vivo drug-target validation•Rocaglates interact with eIF4A1 in vitro and in vivo•Anti-neoplastic activity of rocaglates is a consequence of eIF4A1 inhibition
SummaryTargeting translation initiation is an emerging anti-neoplastic strategy that capitalizes on de-regulated upstream MAPK and PI3K-mTOR signaling pathways in cancers. A key regulator of translation that controls ribosome recruitment flux is eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4F, a hetero-trimeric complex composed of the cap binding protein eIF4E, the scaffolding protein eIF4G, and the RNA helicase eIF4A. Small molecule inhibitors targeting eIF4F display promising anti-neoplastic activity in preclinical settings. Among these are some rocaglate family members that are well tolerated in vivo, deplete eIF4F of its eIF4A helicase subunit, have shown activity as single agents in several xenograft models, and can reverse acquired resistance to MAPK and PI3K-mTOR targeted therapies. Herein, we highlight the power of using genetic complementation approaches and CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing for drug-target validation ex vivo and in vivo, linking the anti-tumor properties of rocaglates to eIF4A inhibition.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide