| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2038986 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 15 Pages |
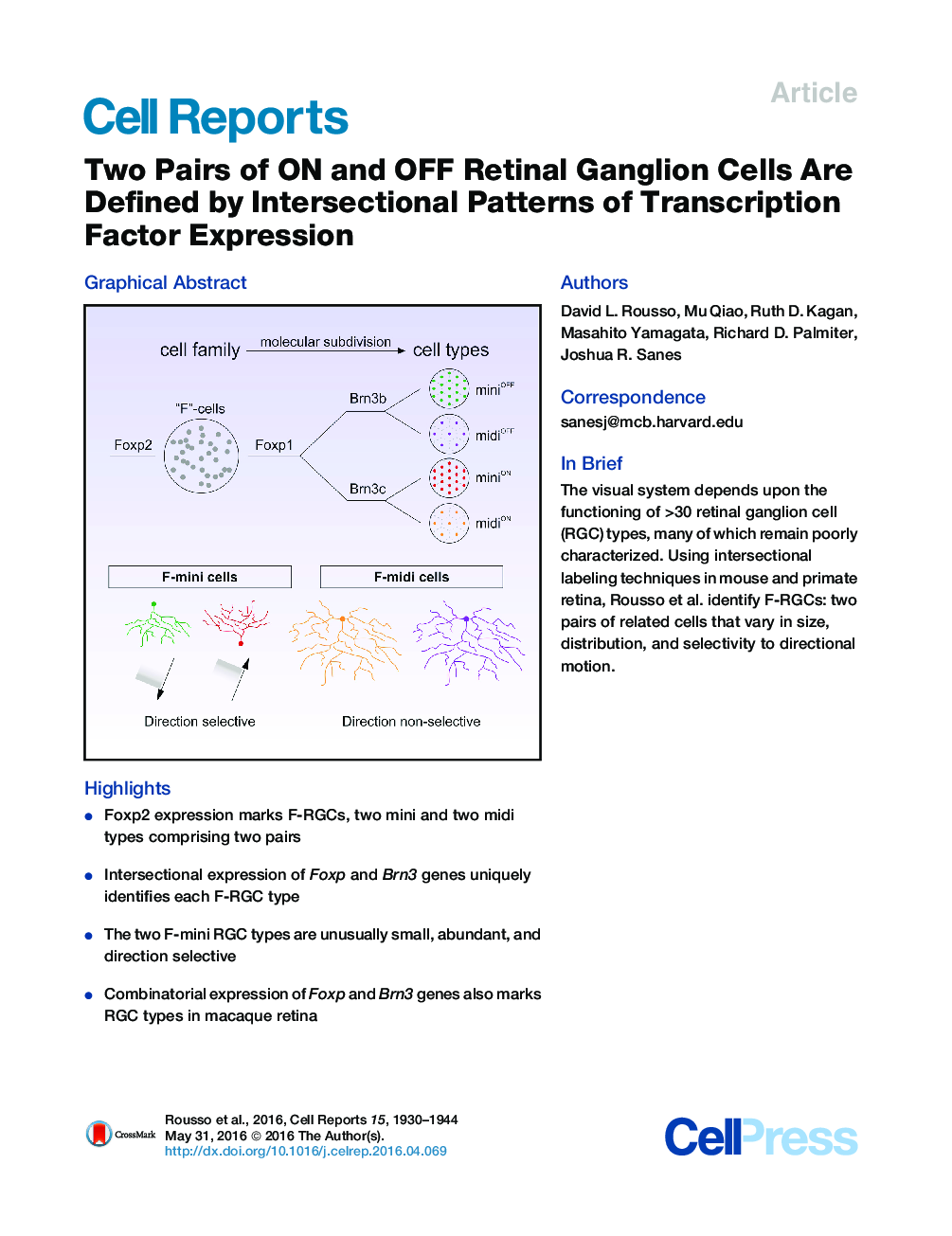
•Foxp2 expression marks F-RGCs, two mini and two midi types comprising two pairs•Intersectional expression of Foxp and Brn3 genes uniquely identifies each F-RGC type•The two F-mini RGC types are unusually small, abundant, and direction selective•Combinatorial expression of Foxp and Brn3 genes also marks RGC types in macaque retina
SummaryVisual information is conveyed to the brain by axons of >30 retinal ganglion cell (RGC) types. Characterization of these types is a prerequisite to understanding visual perception. Here, we identify a family of RGCs that we call F-RGCs on the basis of expression of the transcription factor Foxp2. Intersectional expression of Foxp1 and Brn3 transcription factors divides F-RGCs into four types, comprising two pairs, each composed of closely related cells. One pair, F-miniON and F-miniOFF, shows robust direction selectivity. They are among the smallest RGCs in the mouse retina. The other pair, F-midiON and F-midiOFF, is larger and not direction selective. Together, F-RGCs comprise >20% of RGCs in the mouse retina, halving the number that remain to be classified and doubling the number of known direction-selective cells. Co-expression of Foxp and Brn3 genes also marks subsets of RGCs in macaques that could be primate homologs of F-RGCs.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide