| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039361 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 13 Pages |
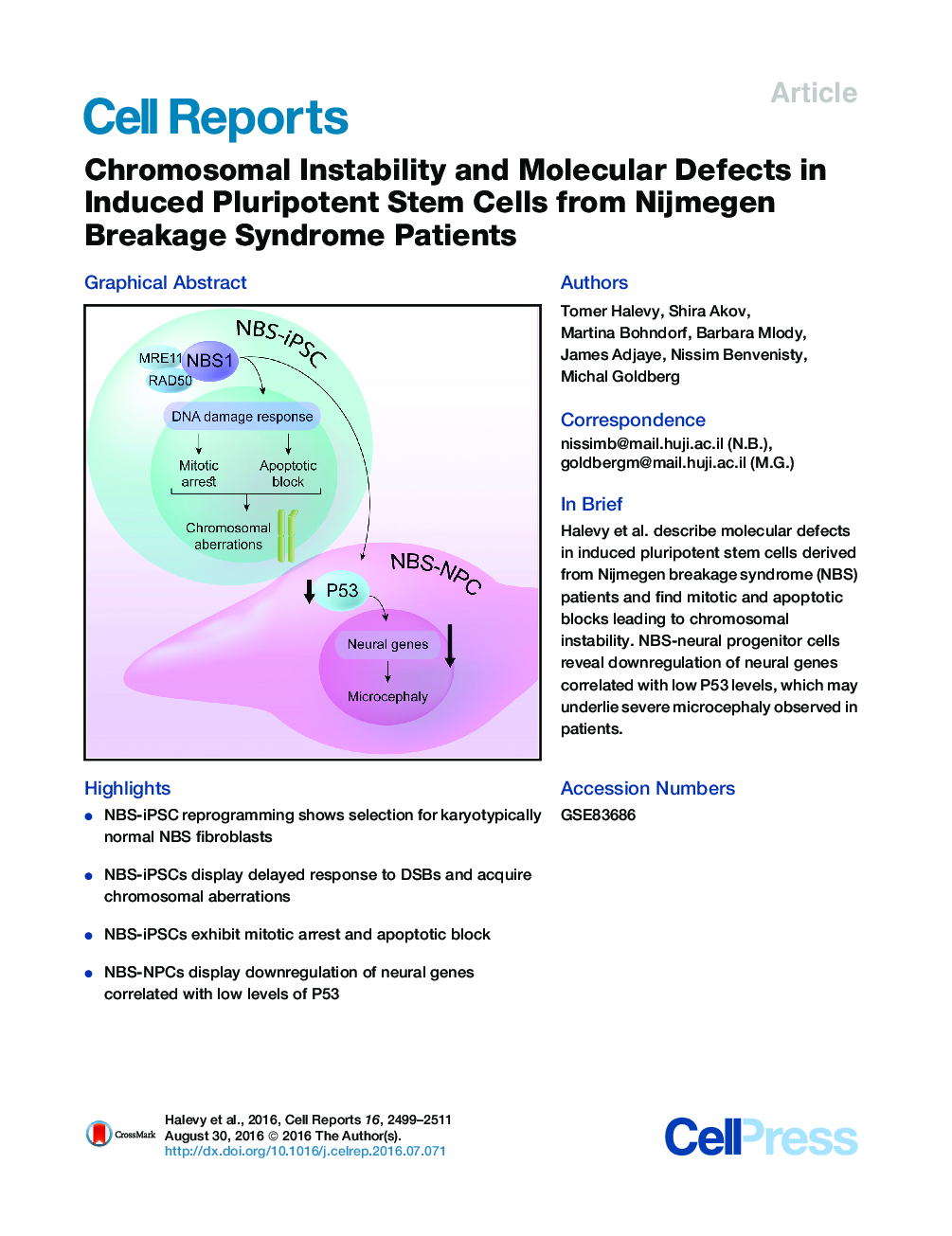
•NBS-iPSC reprogramming shows selection for karyotypically normal NBS fibroblasts•NBS-iPSCs display delayed response to DSBs and acquire chromosomal aberrations•NBS-iPSCs exhibit mitotic arrest and apoptotic block•NBS-NPCs display downregulation of neural genes correlated with low levels of P53
SummaryNijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) results from the absence of the NBS1 protein, responsible for detection of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). NBS is characterized by microcephaly, growth retardation, immunodeficiency, and cancer predisposition. Here, we show successful reprogramming of NBS fibroblasts into induced pluripotent stem cells (NBS-iPSCs). Our data suggest a strong selection for karyotypically normal fibroblasts to go through the reprogramming process. NBS-iPSCs then acquire numerous chromosomal aberrations and show a delayed response to DSB induction. Furthermore, NBS-iPSCs display slower growth, mitotic inhibition, a reduced apoptotic response to stress, and abnormal cell-cycle-related gene expression. Importantly, NBS neural progenitor cells (NBS-NPCs) show downregulation of neural developmental genes, which seems to be mediated by P53. Our results demonstrate the importance of NBS1 in early human development, shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying this severe syndrome, and further expand our knowledge of the genomic stress cells experience during the reprogramming process.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide