| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039362 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 13 Pages |
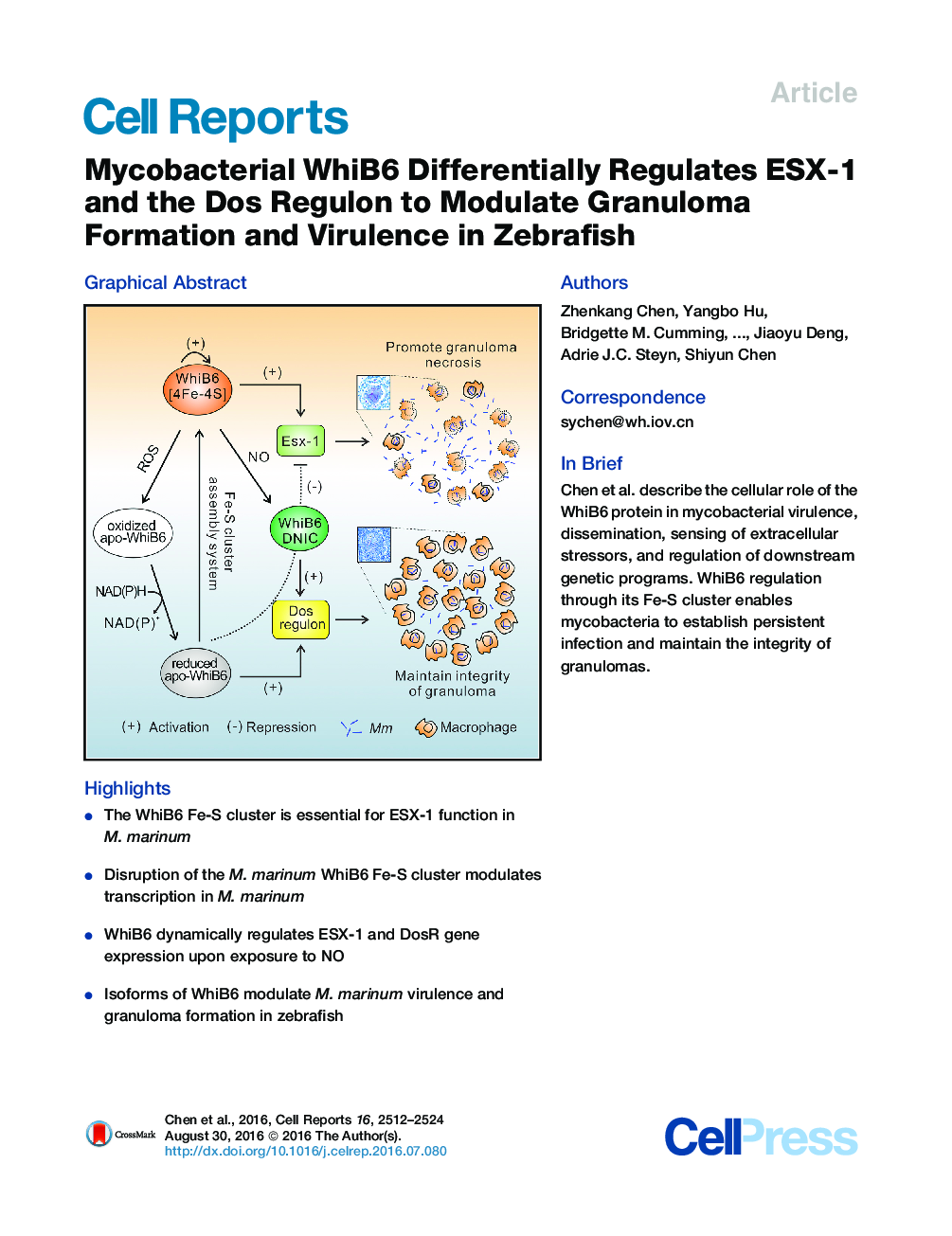
•The WhiB6 Fe-S cluster is essential for ESX-1 function in M. marinum•Disruption of the M. marinum WhiB6 Fe-S cluster modulates transcription in M. marinum•WhiB6 dynamically regulates ESX-1 and DosR gene expression upon exposure to NO•Isoforms of WhiB6 modulate M. marinum virulence and granuloma formation in zebrafish
SummaryDuring the course of infection, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is exposed to diverse redox stresses that trigger metabolic and physiological changes. How these stressors are sensed and relayed to the Mtb transcriptional apparatus remains unclear. Here, we provide evidence that WhiB6 differentially regulates the ESX-1 and DosR regulons through its Fe-S cluster. When challenged with NO, WhiB6 continually activates expression of the DosR regulons but regulates ESX-1 expression through initial activation followed by gradual inhibition. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the holo- and reduced apo-WhiB6 complemented strains confirms these results and also reveals that WhiB6 controls aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, cell division, and virulence. Using the Mycobacterium marinum zebrafish infection model, we find that holo- and apo-WhiB6 modulate levels of mycobacterial infection, granuloma formation, and dissemination. These findings provide fresh insight into the role of WhiB6 in mycobacterial infection, dissemination, and disease development.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide