| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039555 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 12 Pages |
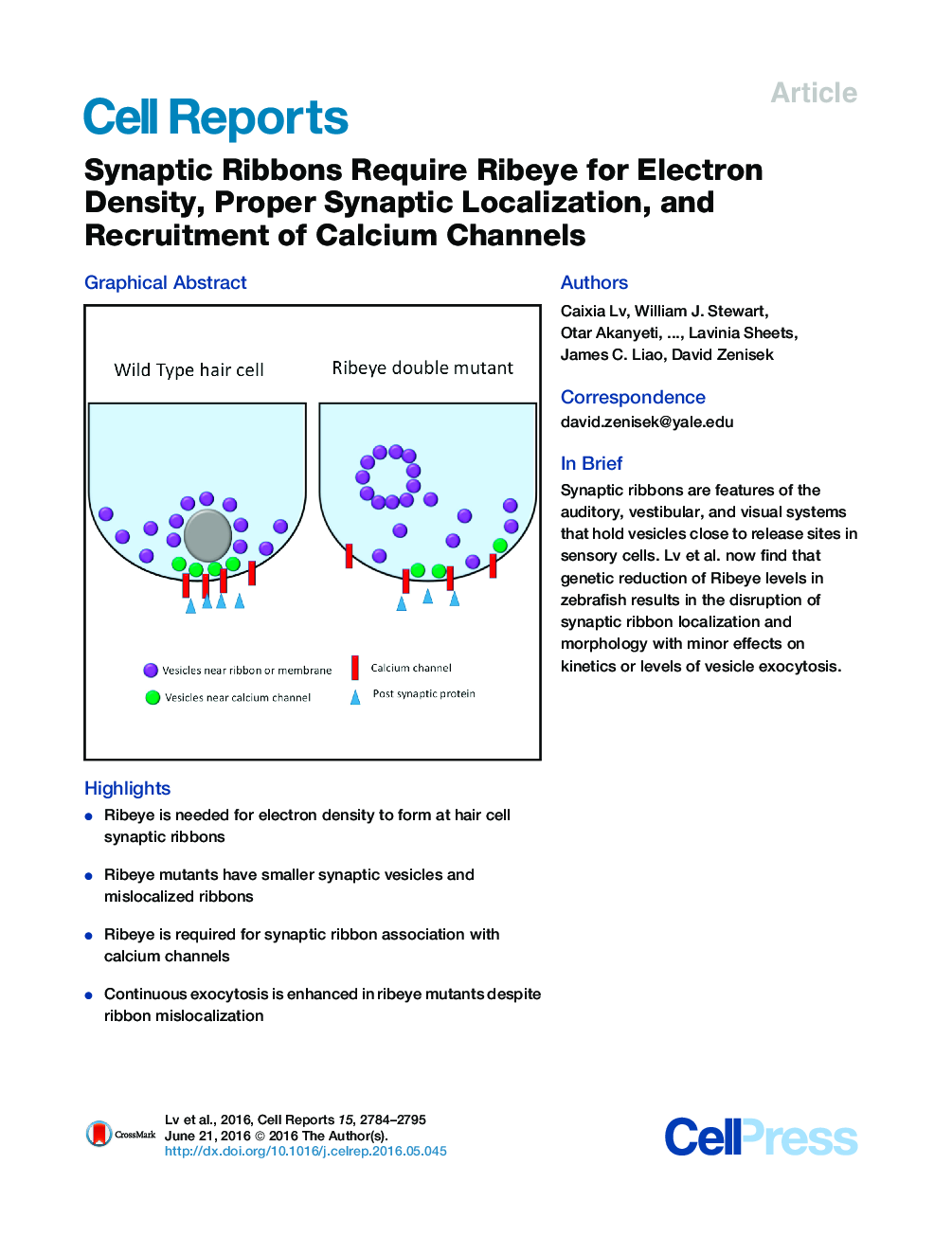
•Ribeye is needed for electron density to form at hair cell synaptic ribbons•Ribeye mutants have smaller synaptic vesicles and mislocalized ribbons•Ribeye is required for synaptic ribbon association with calcium channels•Continuous exocytosis is enhanced in ribeye mutants despite ribbon mislocalization
SummarySynaptic ribbons are structures made largely of the protein Ribeye that hold synaptic vesicles near release sites in non-spiking cells in some sensory systems. Here, we introduce frameshift mutations in the two zebrafish genes encoding for Ribeye and thus remove Ribeye protein from neuromast hair cells. Despite Ribeye depletion, vesicles collect around ribbon-like structures that lack electron density, which we term “ghost ribbons.” Ghost ribbons are smaller in size but possess a similar number of smaller vesicles and are poorly localized to synapses and calcium channels. These hair cells exhibit enhanced exocytosis, as measured by capacitance, and recordings from afferent neurons post-synaptic to hair cells show no significant difference in spike rates. Our results suggest that Ribeye makes up most of the synaptic ribbon density in neuromast hair cells and is necessary for proper localization of calcium channels and synaptic ribbons.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide