| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040022 | Cell Reports | 2015 | 15 Pages |
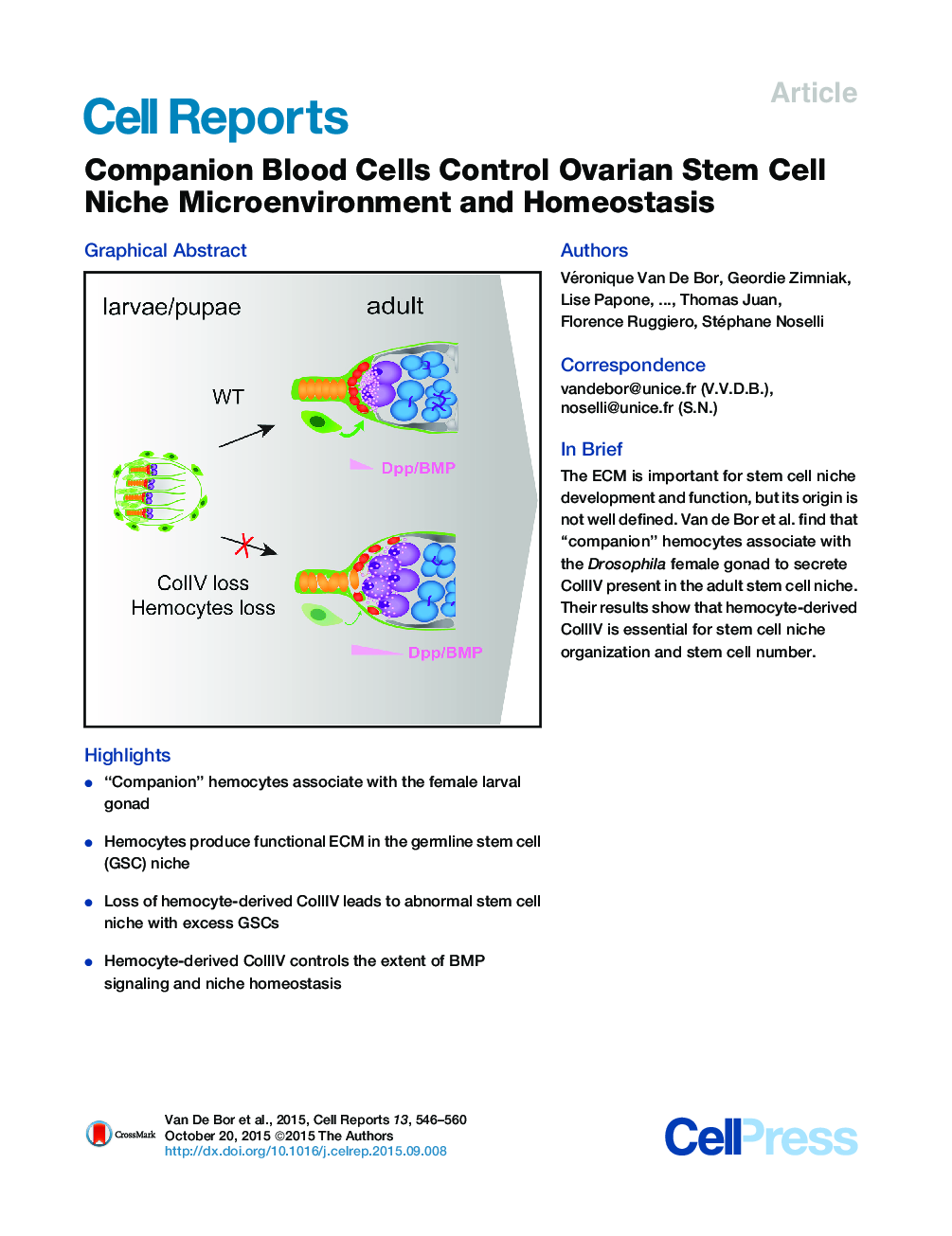
•“Companion” hemocytes associate with the female larval gonad•Hemocytes produce functional ECM in the germline stem cell (GSC) niche•Loss of hemocyte-derived CollIV leads to abnormal stem cell niche with excess GSCs•Hemocyte-derived CollIV controls the extent of BMP signaling and niche homeostasis
SummaryThe extracellular matrix plays an essential role for stem cell differentiation and niche homeostasis. Yet, the origin and mechanism of assembly of the stem cell niche microenvironment remain poorly characterized. Here, we uncover an association between the niche and blood cells, leading to the formation of the Drosophila ovarian germline stem cell niche basement membrane. We identify a distinct pool of plasmatocytes tightly associated with the developing ovaries from larval stages onward. Expressing tagged collagen IV tissue specifically, we show that the germline stem cell niche basement membrane is produced by these “companion plasmatocytes” in the larval gonad and persists throughout adulthood, including the reproductive period. Eliminating companion plasmatocytes or specifically blocking their collagen IV expression during larval stages results in abnormal adult niches with excess stem cells, a phenotype due to aberrant BMP signaling. Thus, local interactions between the niche and blood cells during gonad development are essential for adult germline stem cell niche microenvironment assembly and homeostasis.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide