| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040058 | Cell Reports | 2014 | 13 Pages |
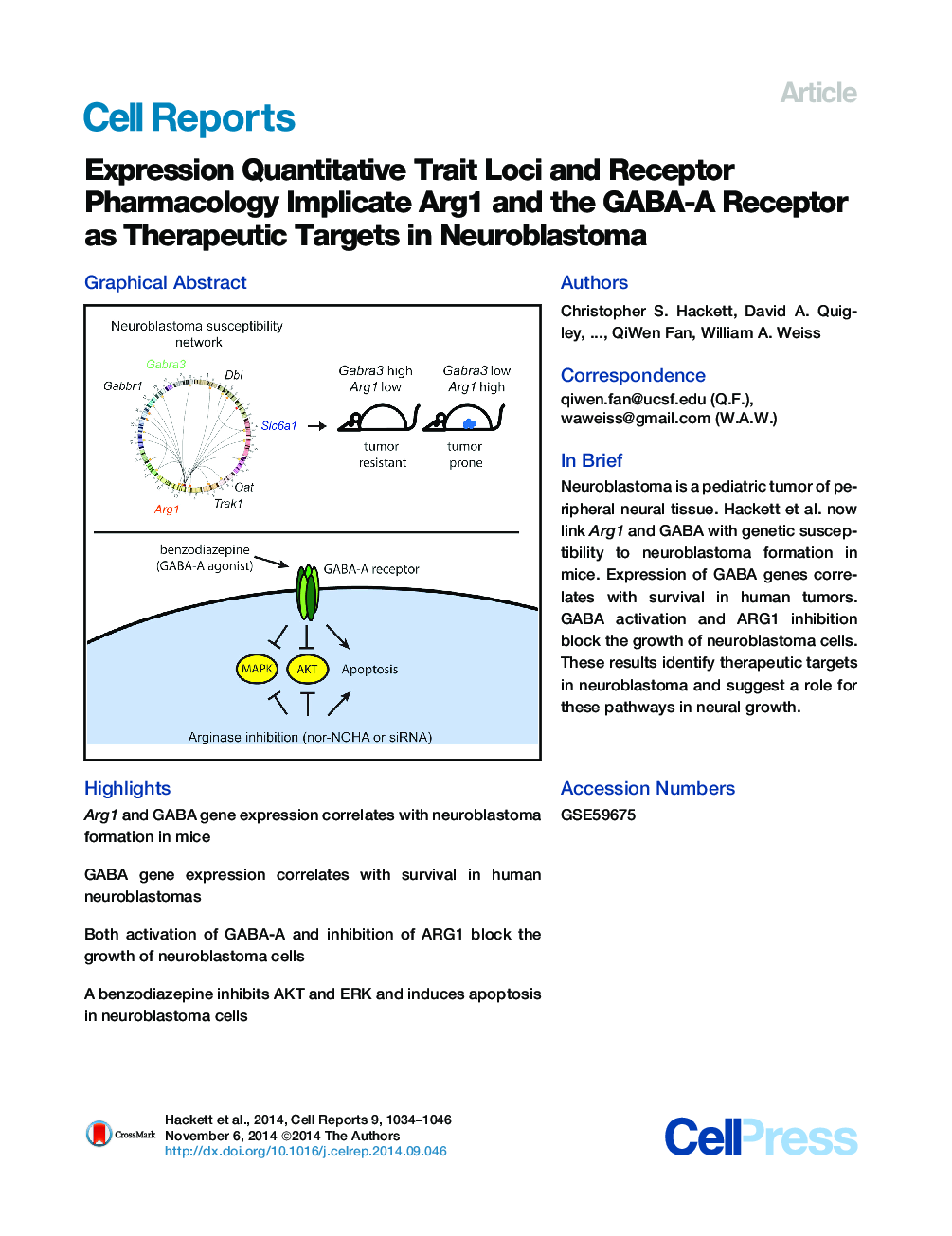
•Arg1 and GABA gene expression correlates with neuroblastoma formation in mice•GABA gene expression correlates with survival in human neuroblastomas•Both activation of GABA-A and inhibition of ARG1 block the growth of neuroblastoma cells•A benzodiazepine inhibits AKT and ERK and induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells
SummaryThe development of targeted therapeutics for neuroblastoma, the third most common tumor in children, has been limited by a poor understanding of growth signaling mechanisms unique to the peripheral nerve precursors from which tumors arise. In this study, we combined genetics with gene-expression analysis in the peripheral sympathetic nervous system to implicate arginase 1 and GABA signaling in tumor formation in vivo. In human neuroblastoma cells, either blockade of ARG1 or benzodiazepine-mediated activation of GABA-A receptors induced apoptosis and inhibited mitogenic signaling through AKT and MAPK. These results suggest that ARG1 and GABA influence both neural development and neuroblastoma and that benzodiazepines in clinical use may have potential applications for neuroblastoma therapy.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide