| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040514 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 12 Pages |
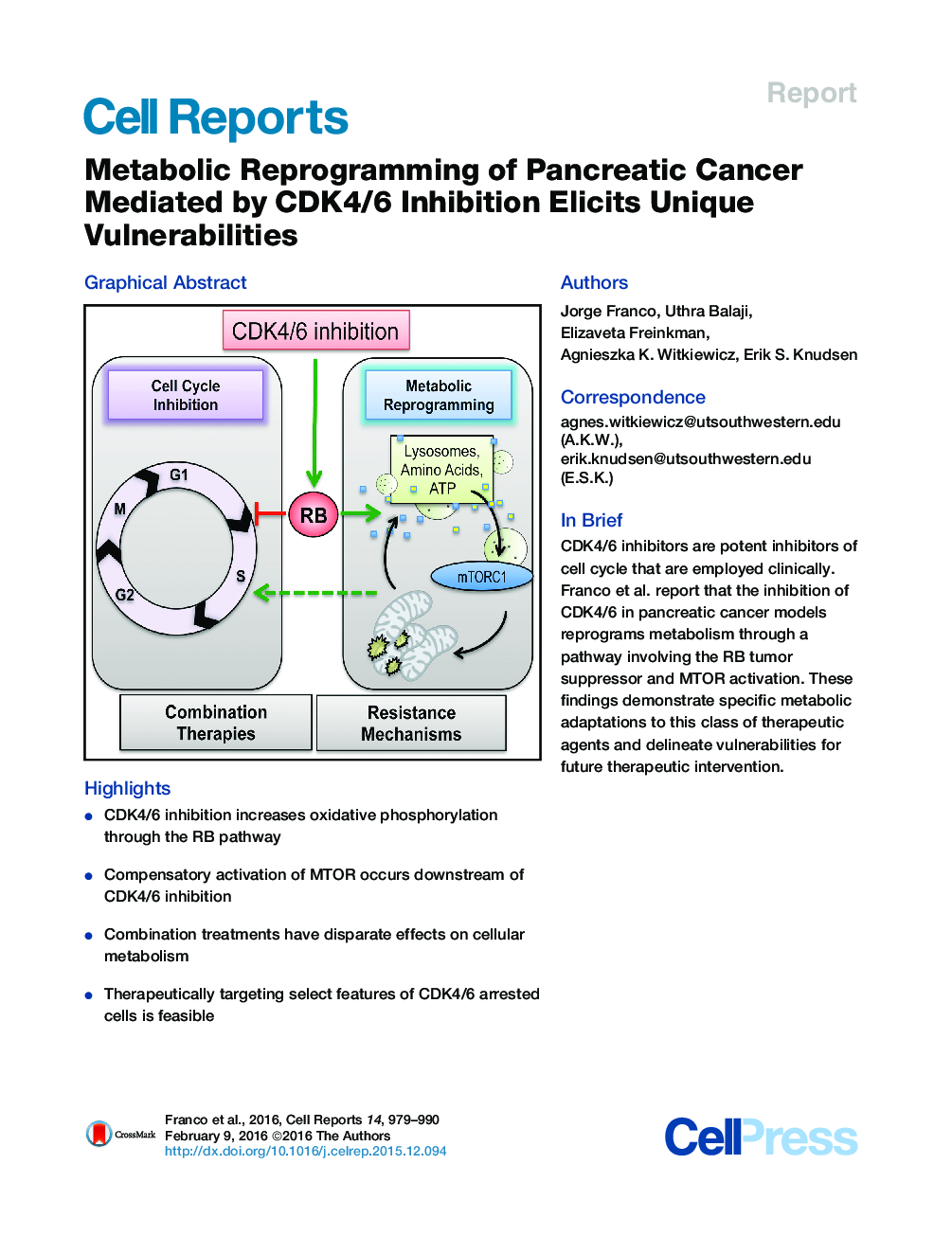
•CDK4/6 inhibition increases oxidative phosphorylation through the RB pathway•Compensatory activation of MTOR occurs downstream of CDK4/6 inhibition•Combination treatments have disparate effects on cellular metabolism•Therapeutically targeting select features of CDK4/6 arrested cells is feasible
SummaryDue to loss of p16ink4a in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA), pharmacological suppression of CDK4/6 could represent a potent target for treatment. In PDA models, CDK4/6 inhibition had a variable effect on cell cycle but yielded accumulation of ATP and mitochondria. Pharmacological CDK4/6 inhibitors induce cyclin D1 protein levels; however, RB activation was required and sufficient for mitochondrial accumulation. CDK4/6 inhibition stimulated glycolytic and oxidative metabolism and was associated with an increase in mTORC1 activity. MTOR and MEK inhibitors potently cooperate with CDK4/6 inhibition in eliciting cell-cycle exit. However, MTOR inhibition fully suppressed metabolism and yielded apoptosis and suppression of tumor growth in xenograft models. The metabolic state mediated by CDK4/6 inhibition increases mitochondrial number and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Concordantly, the suppression of ROS scavenging or BCL2 antagonists cooperated with CDK4/6 inhibition. Together, these data define the impact of therapeutics on PDA metabolism and provide strategies for converting cytostatic response to tumor cell killing.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide