| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2041399 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 13 Pages |
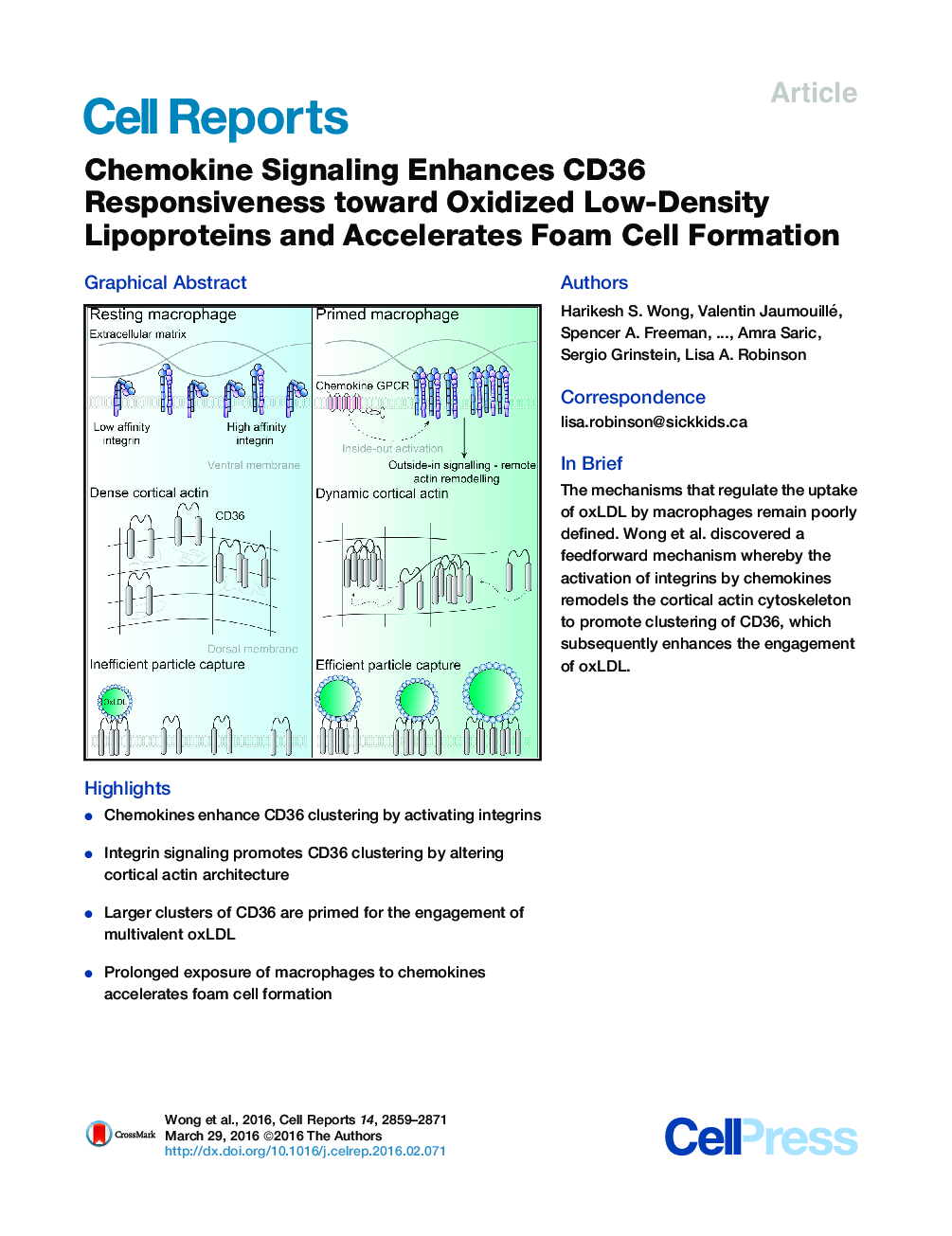
•Chemokines enhance CD36 clustering by activating integrins•Integrin signaling promotes CD36 clustering by altering cortical actin architecture•Larger clusters of CD36 are primed for the engagement of multivalent oxLDL•Prolonged exposure of macrophages to chemokines accelerates foam cell formation
SummaryExcessive uptake of oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDL) by macrophages is a fundamental characteristic of atherosclerosis. However, signals regulating the engagement of these ligands remain elusive. Using single-molecule imaging, we discovered a mechanism whereby chemokine signaling enhanced binding of oxLDL to the scavenger receptor, CD36. By activating the Rap1-GTPase, chemokines promoted integrin-mediated adhesion of macrophages to the substratum. As a result, cells exhibited pronounced remodeling of the cortical actin cytoskeleton that increased CD36 clustering. Remarkably, CD36 clusters formed predominantly within actin-poor regions of the cortex, and these regions were primed to engage oxLDL. In accordance with enhanced ligand engagement, prolonged exposure of macrophages to chemokines amplified the accumulation of esterified cholesterol, thereby accentuating the foam cell phenotype. These findings imply that the activation of integrins by chemokine signaling exerts feedforward control over receptor clustering and effectively alters the threshold for cells to engage ligands.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide