| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2041733 | Cell Reports | 2016 | 11 Pages |
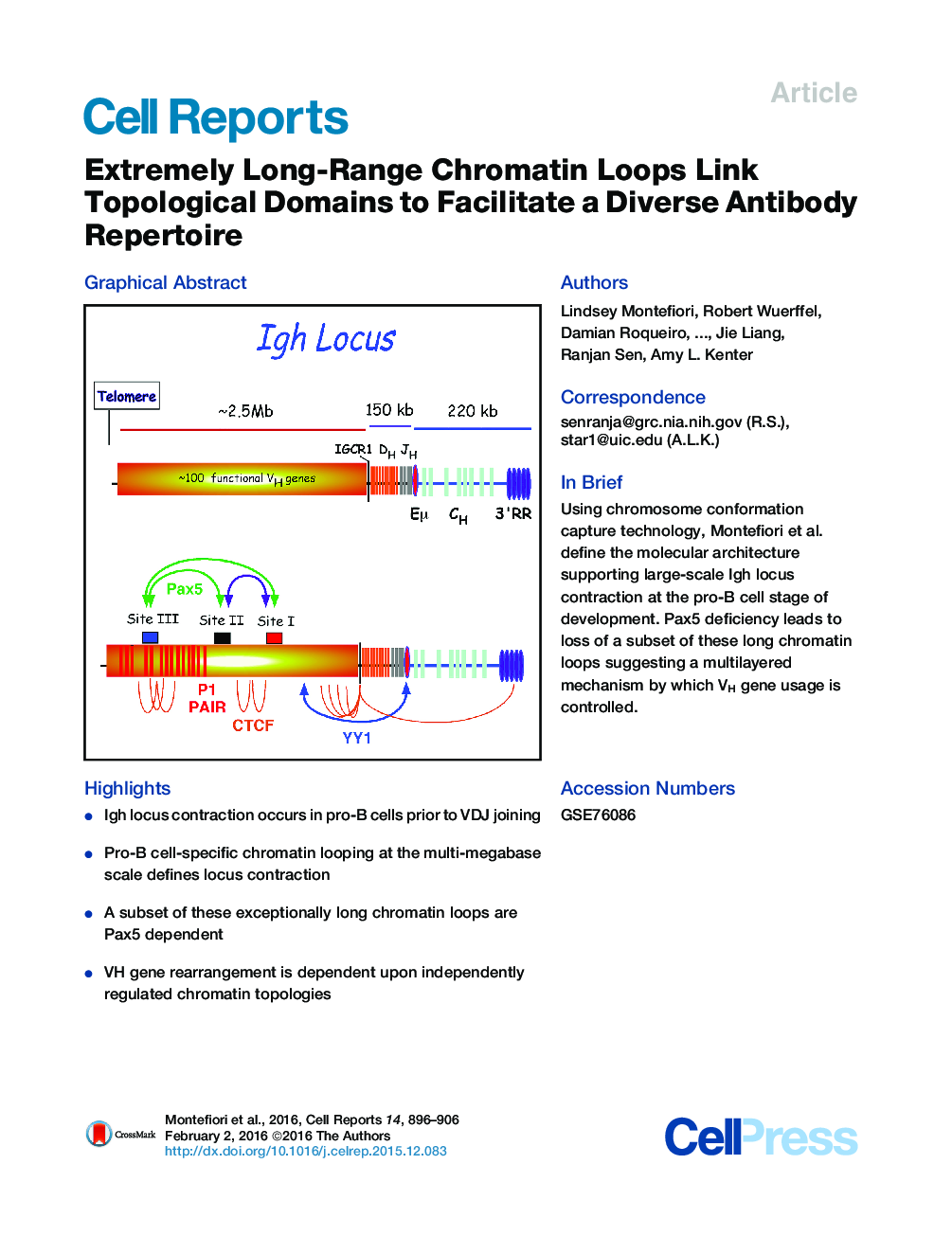
•Igh locus contraction occurs in pro-B cells prior to VDJ joining•Pro-B cell-specific chromatin looping at the multi-megabase scale defines locus contraction•A subset of these exceptionally long chromatin loops are Pax5 dependent•VH gene rearrangement is dependent upon independently regulated chromatin topologies
SummaryEarly B cell development is characterized by large-scale Igh locus contraction prior to V(D)J recombination to facilitate a highly diverse Ig repertoire. However, an understanding of the molecular architecture that mediates locus contraction remains unclear. We have combined high-resolution chromosome conformation capture (3C) techniques with 3D DNA FISH to identify three conserved topological subdomains. Each of these topological folds encompasses a major VH gene family that become juxtaposed in pro-B cells via megabase-scale chromatin looping. The transcription factor Pax5 organizes the subdomain that spans the VHJ558 gene family. In its absence, the J558 VH genes fail to associate with the proximal VH genes, thereby providing a plausible explanation for reduced VHJ558 gene rearrangements in Pax5-deficient pro-B cells. We propose that Igh locus contraction is the cumulative effect of several independently controlled chromatin subdomains that provide the structural infrastructure to coordinate optimal antigen receptor assembly.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide