| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2041758 | Cell Reports | 2015 | 15 Pages |
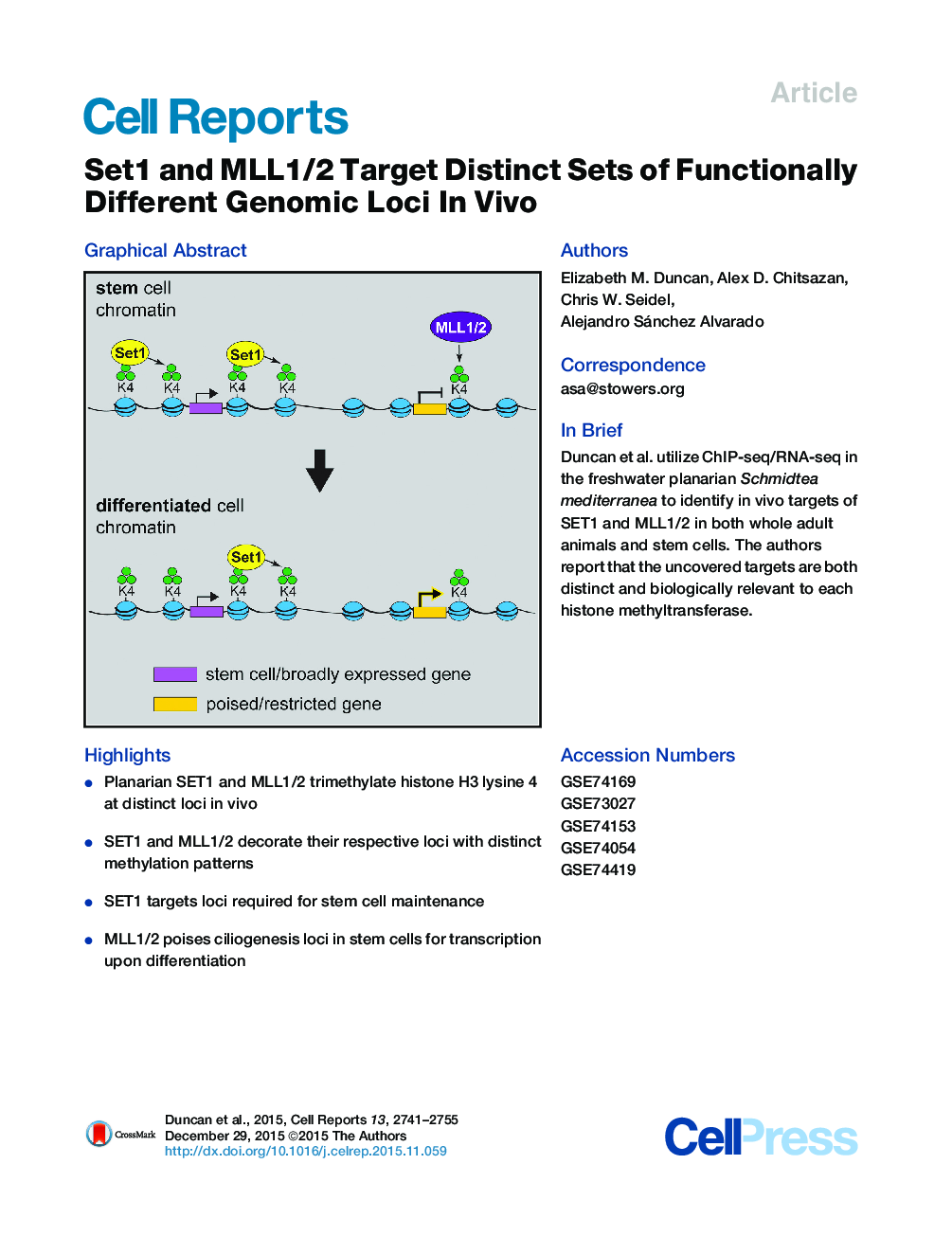
•Planarian SET1 and MLL1/2 trimethylate histone H3 lysine 4 at distinct loci in vivo•SET1 and MLL1/2 decorate their respective loci with distinct methylation patterns•SET1 targets loci required for stem cell maintenance•MLL1/2 poises ciliogenesis loci in stem cells for transcription upon differentiation
SummaryHistone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is known to correlate with both active and poised genomic loci, yet many questions remain regarding its functional roles in vivo. We identify functional genomic targets of two H3K4 methyltransferases, Set1 and MLL1/2, in both the stem cells and differentiated tissue of the planarian flatworm Schmidtea mediterranea. We show that, despite their common substrate, these enzymes target distinct genomic loci in vivo, which are distinguishable by the pattern each enzyme leaves on the chromatin template, i.e., the breadth of the H3K4me3 peak. Whereas Set1 targets are largely associated with the maintenance of the stem cell population, MLL1/2 targets are specifically enriched for genes involved in ciliogenesis. These data not only confirm that chromatin regulation is fundamental to planarian stem cell function but also provide evidence for post-embryonic functional specificity of H3K4me3 methyltransferases in vivo.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide