| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2039359 | 1400967 | 2016 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• CD4+ and CD8+ T cells preferentially occupy separate areas of the splenic T cell zone
• DC-intrinsic CCR7 is required for migration within the spleen after i.v. immunization
• 33D1+ and XCR1+ DCs migrate into CD4+ and CD8+ T cell areas, respectively
• Loss of DC subset and T-cell-lineage pairing abrogates either CD4+ or CD8+ T cell immunity
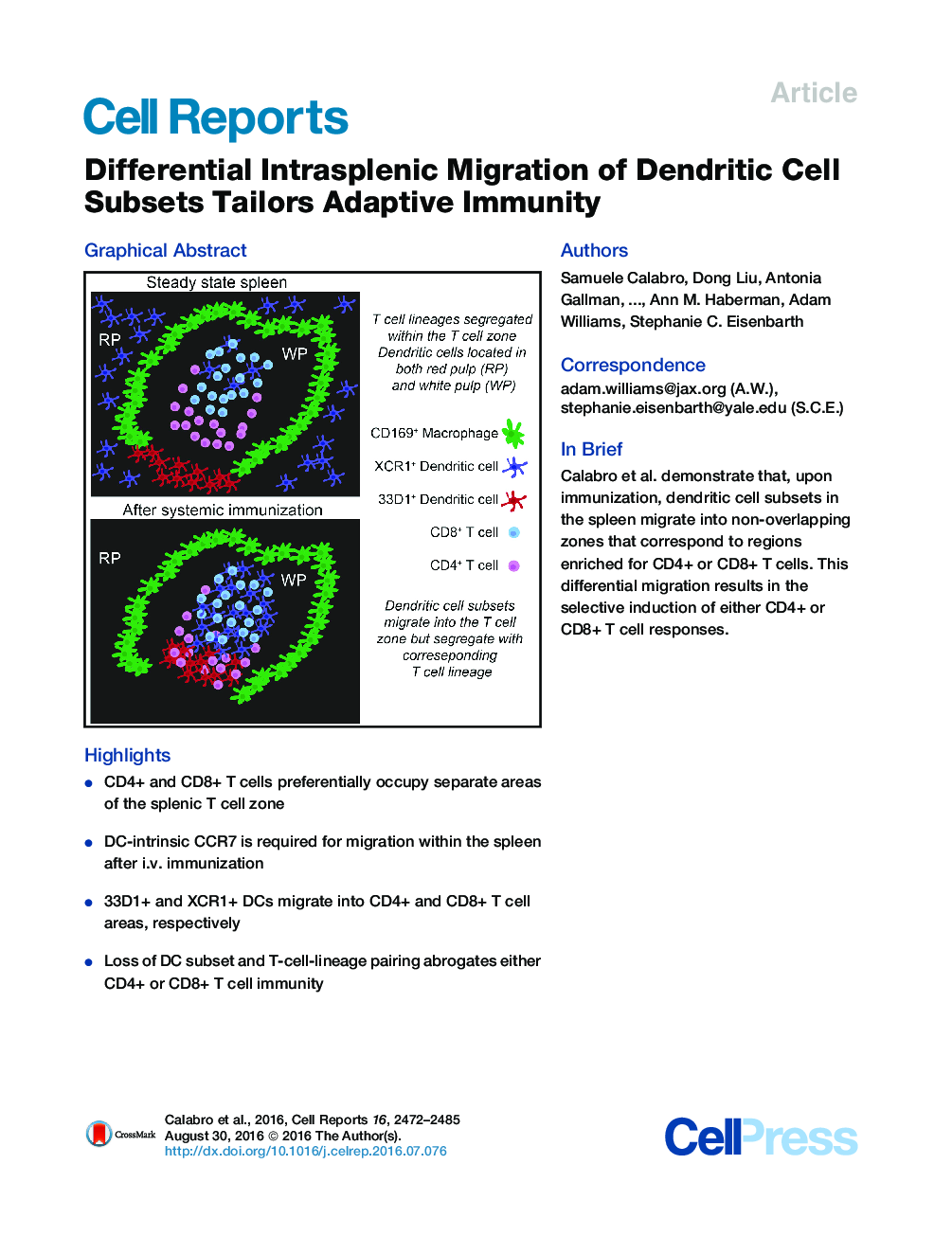
SummaryEvidence suggests that distinct splenic dendritic cell (DC) subsets activate either CD4+ or CD8+ T cells in vivo. This bias has been partially ascribed to differential antigen presentation; however, all DC subsets can activate both T cell lineages in vitro. Therefore, we tested whether the organization of DC and T cell subsets in the spleen dictated this preference. We discovered that CD4+ and CD8+ T cells segregated within splenic T cell zones prior to immunization. After intravenous immunization, the two major conventional DC populations, distinguished by 33D1 and XCR1 staining, migrated into separate regions of the T cell zone: 33D1+ DCs migrated into the CD4+ T cell area, whereas XCR1+ DCs migrated into the CD8+ T cell area. Thus, the post-immunization location of each DC subset correlated with the T cell lineage it preferentially primes. Preventing this co-localization selectively impaired either CD4+ or CD8+ T cell immunity to blood-borne antigens.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 16, Issue 9, 30 August 2016, Pages 2472–2485