| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2040206 | 1073102 | 2015 | 15 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
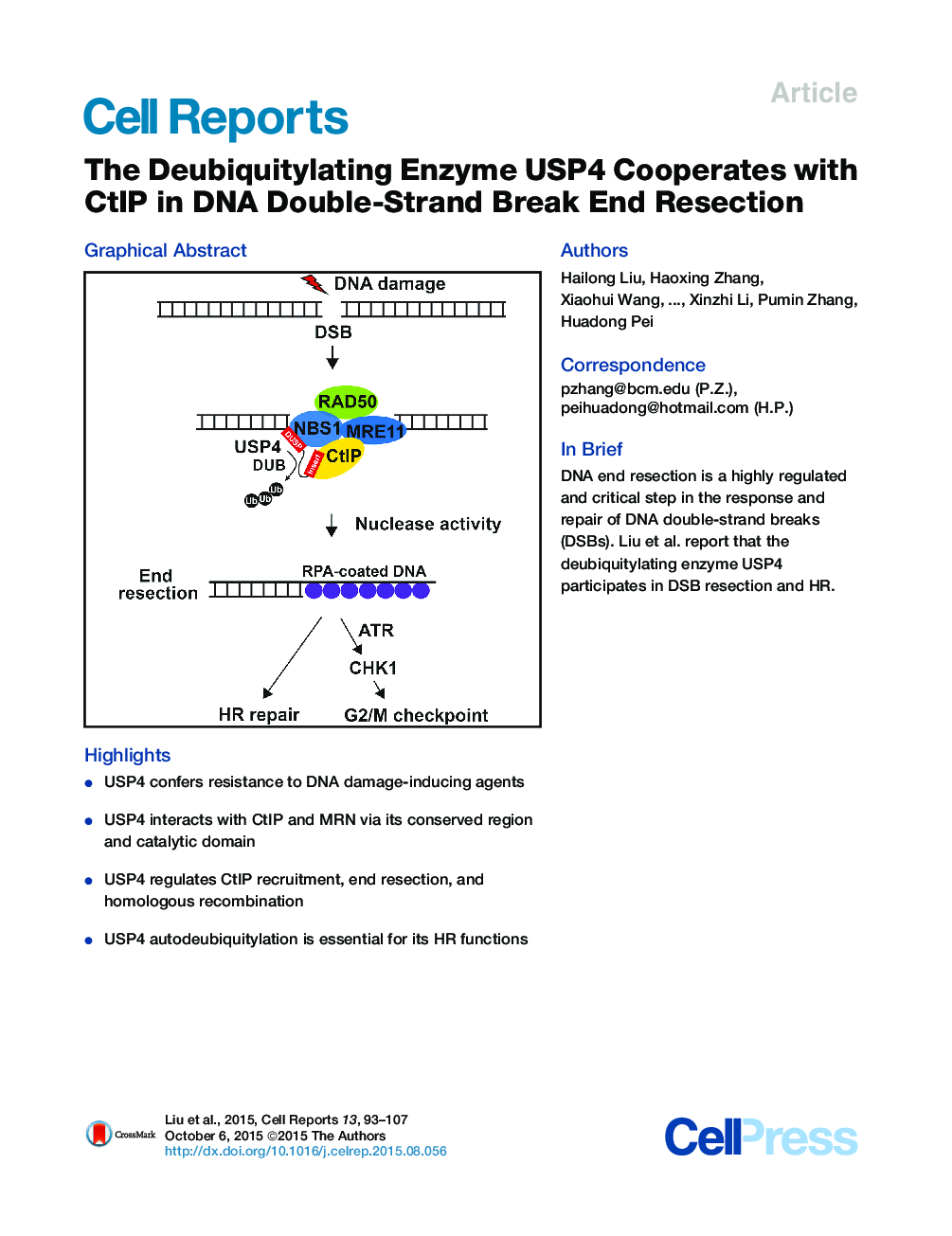
• USP4 confers resistance to DNA damage-inducing agents
• USP4 interacts with CtIP and MRN via its conserved region and catalytic domain
• USP4 regulates CtIP recruitment, end resection, and homologous recombination
• USP4 autodeubiquitylation is essential for its HR functions
SummaryDNA end resection is a highly regulated and critical step in DNA double-stranded break (DSB) repair. In higher eukaryotes, DSB resection is initiated by the collaborative action of CtIP and the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) complex. Here, we find that the deubiquitylating enzyme USP4 directly participates in DSB resection and homologous recombination (HR). USP4 confers resistance to DNA damage-inducing agents. Mechanistically, USP4 interacts with CtIP and MRN via a specific, conserved region and the catalytic domain of USP4, respectively, and regulates CtIP recruitment to sites of DNA damage. We also find that USP4 autodeubiquitylation is essential for its HR functions. Collectively, our findings identify USP4 as a key regulator of DNA DSB end resection.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 13, Issue 1, 6 October 2015, Pages 93–107