| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792509 | 1155060 | 2015 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
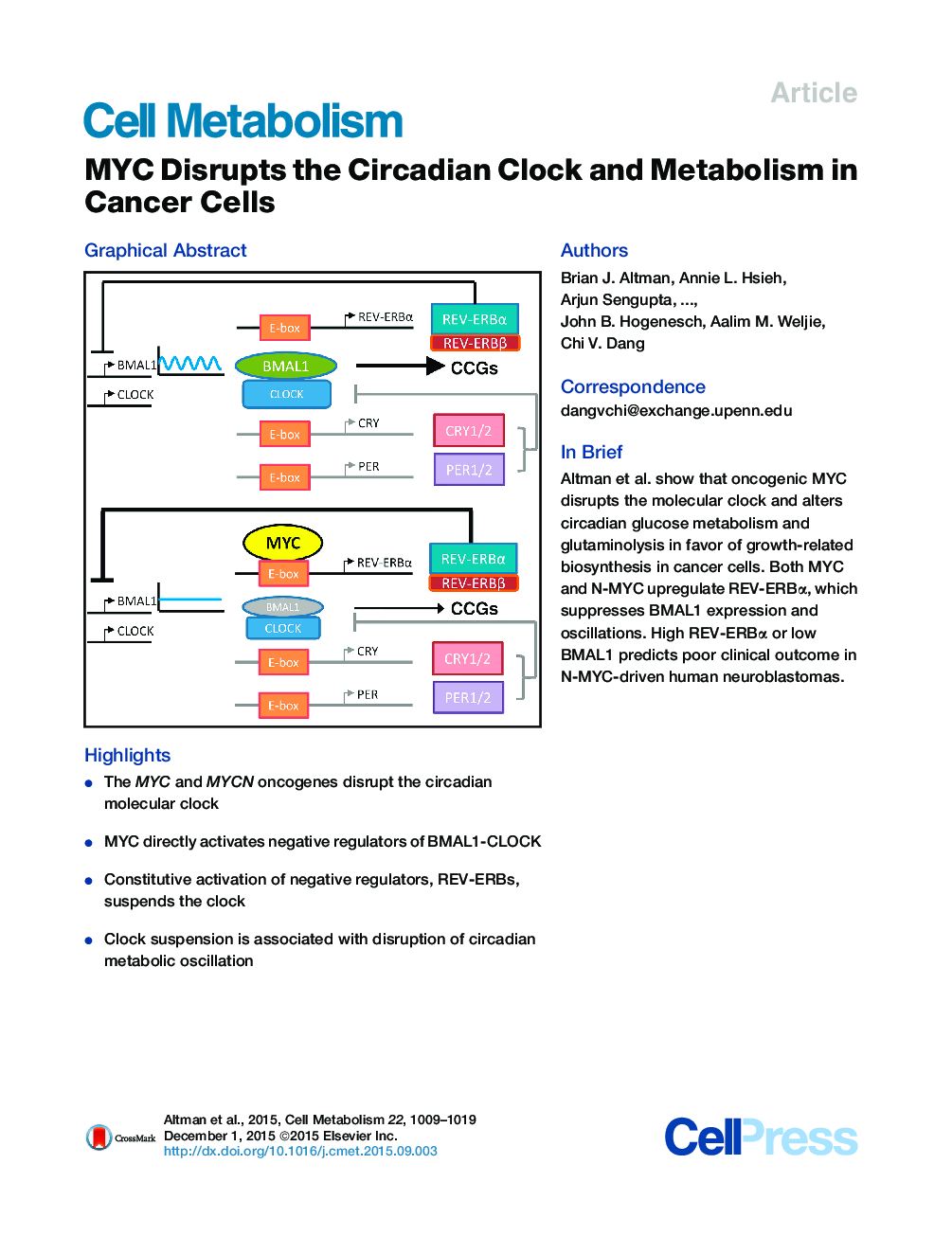
• The MYC and MYCN oncogenes disrupt the circadian molecular clock
• MYC directly activates negative regulators of BMAL1-CLOCK
• Constitutive activation of negative regulators, REV-ERBs, suspends the clock
• Clock suspension is associated with disruption of circadian metabolic oscillation
SummaryThe MYC oncogene encodes MYC, a transcription factor that binds the genome through sites termed E-boxes (5′-CACGTG-3′), which are identical to the binding sites of the heterodimeric CLOCK-BMAL1 master circadian transcription factor. Hence, we hypothesized that ectopic MYC expression perturbs the clock by deregulating E-box-driven components of the circadian network in cancer cells. We report here that deregulated expression of MYC or N-MYC disrupts the molecular clock in vitro by directly inducing REV-ERBα to dampen expression and oscillation of BMAL1, and this could be rescued by knockdown of REV-ERB. REV-ERBα expression predicts poor clinical outcome for N-MYC-driven human neuroblastomas that have diminished BMAL1 expression, and re-expression of ectopic BMAL1 in neuroblastoma cell lines suppresses their clonogenicity. Further, ectopic MYC profoundly alters oscillation of glucose metabolism and perturbs glutaminolysis. Our results demonstrate an unsuspected link between oncogenic transformation and circadian and metabolic dysrhythmia, which we surmise to be advantageous for cancer.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (173 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 22, Issue 6, 1 December 2015, Pages 1009–1019