| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5741140 | 1616990 | 2017 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
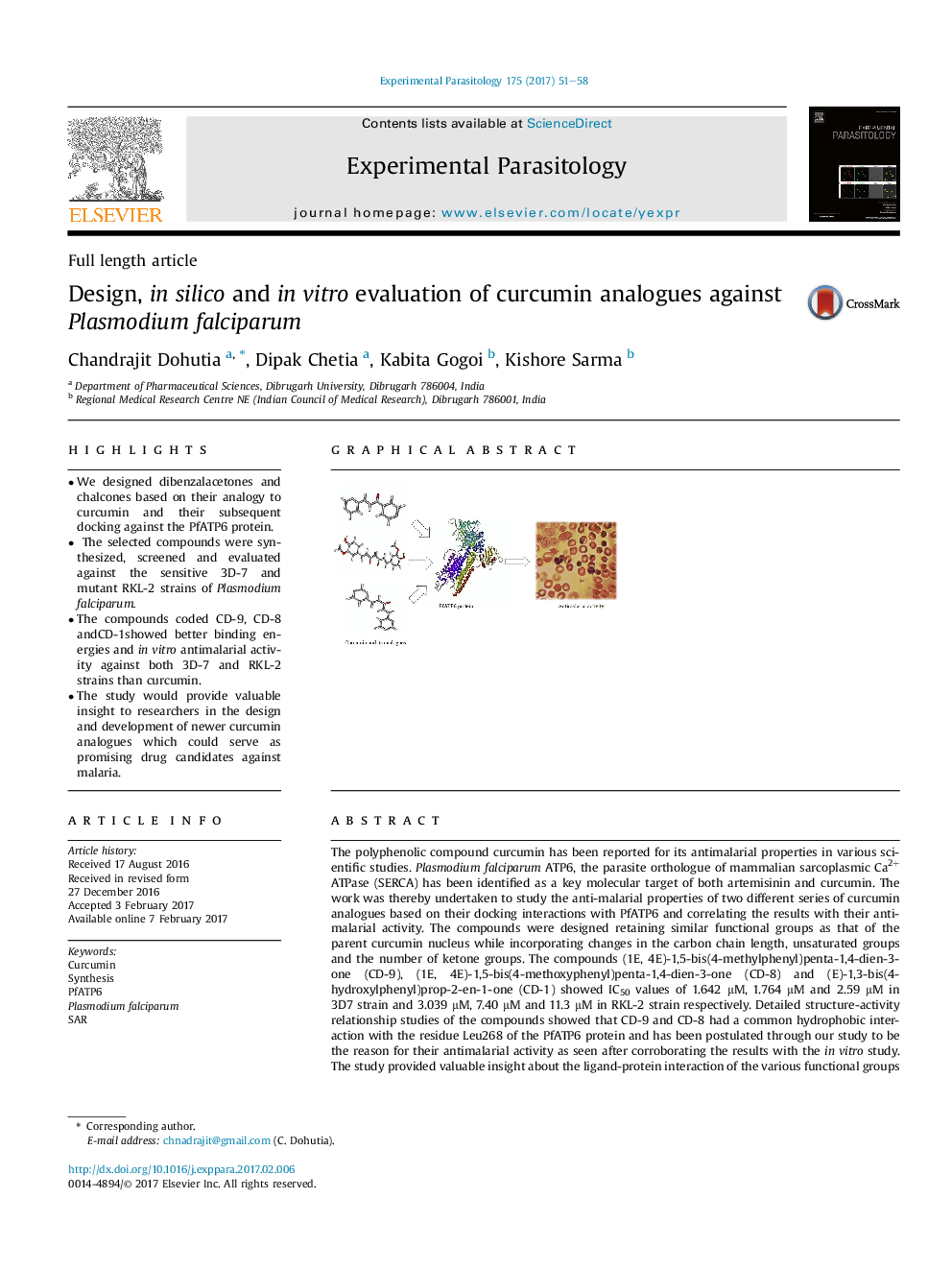
- We designed dibenzalacetones and chalcones based on their analogy to curcumin and their subsequent docking against the PfATP6 protein.
- The selected compounds were synthesized, screened and evaluated against the sensitive 3D-7 and mutant RKL-2 strains of Plasmodium falciparum.
- The compounds coded CD-9, CD-8 andCD-1showed better binding energies and in vitro antimalarial activity against both 3D-7 and RKL-2 strains than curcumin.
- The study would provide valuable insight to researchers in the design and development of newer curcumin analogues which could serve as promising drug candidates against malaria.
The polyphenolic compound curcumin has been reported for its antimalarial properties in various scientific studies. Plasmodium falciparum ATP6, the parasite orthologue of mammalian sarcoplasmic Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) has been identified as a key molecular target of both artemisinin and curcumin. The work was thereby undertaken to study the anti-malarial properties of two different series of curcumin analogues based on their docking interactions with PfATP6 and correlating the results with their anti-malarial activity. The compounds were designed retaining similar functional groups as that of the parent curcumin nucleus while incorporating changes in the carbon chain length, unsaturated groups and the number of ketone groups. The compounds (1E, 4E)-1,5-bis(4-methylphenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one (CD-9), (1E, 4E)-1,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one (CD-8) and (E)-1,3-bis(4-hydroxylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (CD-1) showed IC50 values of 1.642 μM, 1.764 μM and 2.59 μM in 3D7 strain and 3.039 μM, 7.40 μM and 11.3 μM in RKL-2 strain respectively. Detailed structure-activity relationship studies of the compounds showed that CD-9 and CD-8 had a common hydrophobic interaction with the residue Leu268 of the PfATP6 protein and has been postulated through our study to be the reason for their antimalarial activity as seen after corroborating the results with the in vitro study. The study provided valuable insight about the ligand-protein interaction of the various functional groups of curcumin and its analogues against the PfATP6 protein and their importance in imparting antimalarial action.
242
Journal: Experimental Parasitology - Volume 175, April 2017, Pages 51-58