| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5517294 | 1400959 | 2017 | 16 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
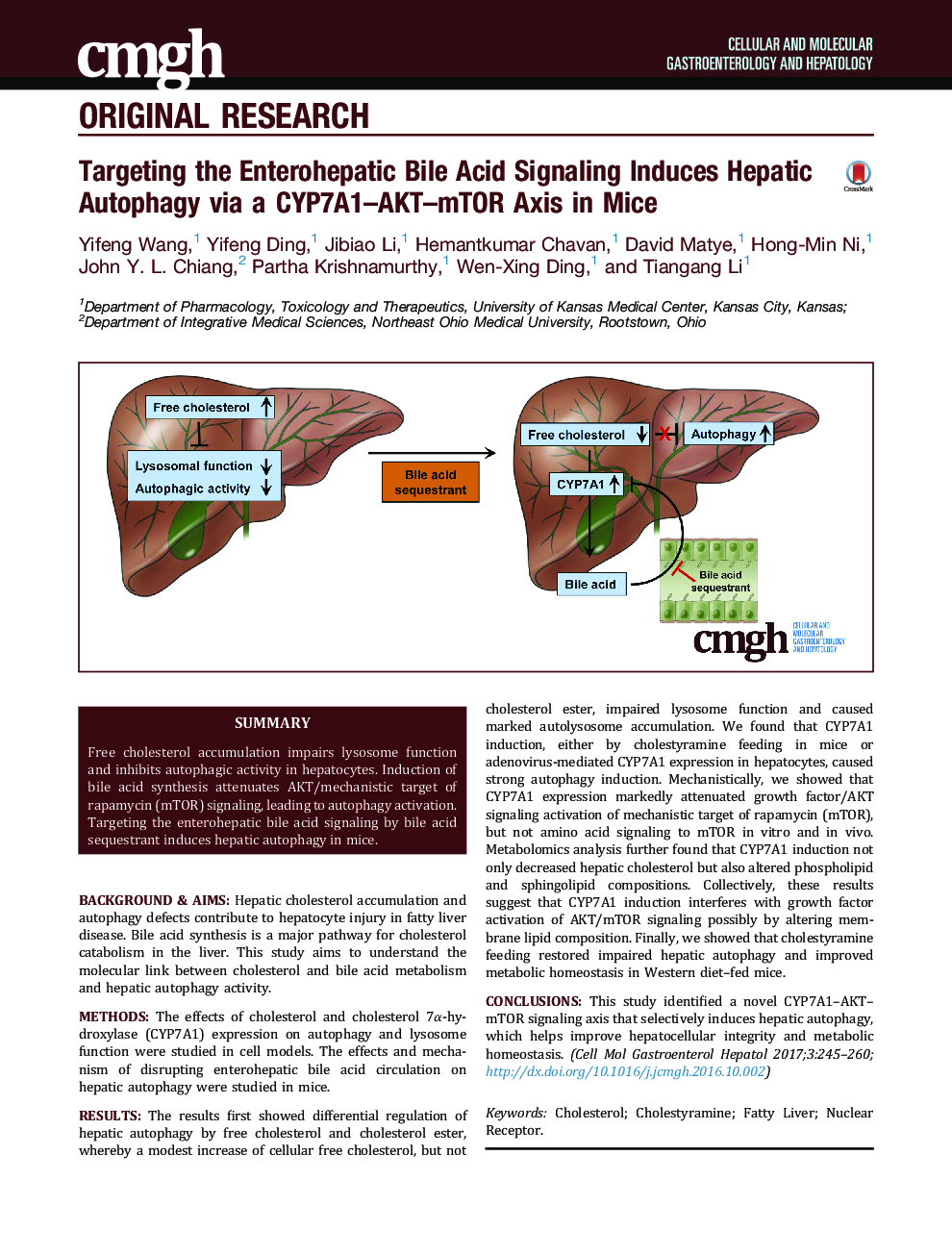
Background & AimsHepatic cholesterol accumulation and autophagy defects contribute to hepatocyte injury in fatty liver disease. Bile acid synthesis is a major pathway for cholesterol catabolism in the liver. This study aims to understand the molecular link between cholesterol and bile acid metabolism and hepatic autophagy activity.MethodsThe effects of cholesterol and cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) expression on autophagy and lysosome function were studied in cell models. The effects and mechanism of disrupting enterohepatic bile acid circulation on hepatic autophagy were studied in mice.ResultsThe results first showed differential regulation of hepatic autophagy by free cholesterol and cholesterol ester, whereby a modest increase of cellular free cholesterol, but not cholesterol ester, impaired lysosome function and caused marked autolysosome accumulation. We found that CYP7A1 induction, either by cholestyramine feeding in mice or adenovirus-mediated CYP7A1 expression in hepatocytes, caused strong autophagy induction. Mechanistically, we showed that CYP7A1 expression markedly attenuated growth factor/AKT signaling activation of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), but not amino acid signaling to mTOR in vitro and in vivo. Metabolomics analysis further found that CYP7A1 induction not only decreased hepatic cholesterol but also altered phospholipid and sphingolipid compositions. Collectively, these results suggest that CYP7A1 induction interferes with growth factor activation of AKT/mTOR signaling possibly by altering membrane lipid composition. Finally, we showed that cholestyramine feeding restored impaired hepatic autophagy and improved metabolic homeostasis in Western diet-fed mice.ConclusionsThis study identified a novel CYP7A1-AKT-mTOR signaling axis that selectively induces hepatic autophagy, which helps improve hepatocellular integrity and metabolic homeostasis.
Graphical Abstract167
Journal: Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology - Volume 3, Issue 2, March 2017, Pages 245-260