| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593982 | 1453959 | 2012 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
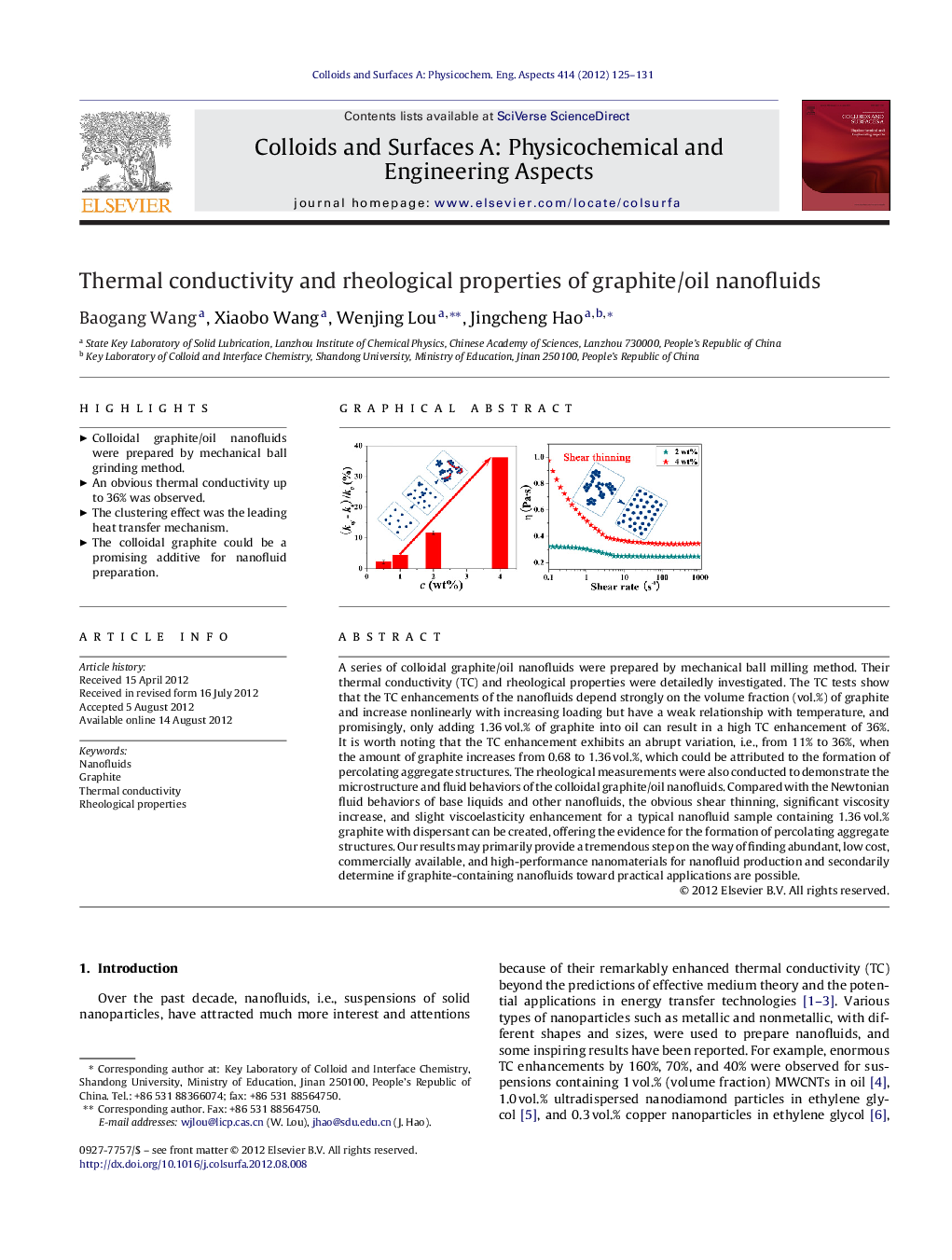
A series of colloidal graphite/oil nanofluids were prepared by mechanical ball milling method. Their thermal conductivity (TC) and rheological properties were detailedly investigated. The TC tests show that the TC enhancements of the nanofluids depend strongly on the volume fraction (vol.%) of graphite and increase nonlinearly with increasing loading but have a weak relationship with temperature, and promisingly, only adding 1.36 vol.% of graphite into oil can result in a high TC enhancement of 36%. It is worth noting that the TC enhancement exhibits an abrupt variation, i.e., from 11% to 36%, when the amount of graphite increases from 0.68 to 1.36 vol.%, which could be attributed to the formation of percolating aggregate structures. The rheological measurements were also conducted to demonstrate the microstructure and fluid behaviors of the colloidal graphite/oil nanofluids. Compared with the Newtonian fluid behaviors of base liquids and other nanofluids, the obvious shear thinning, significant viscosity increase, and slight viscoelasticity enhancement for a typical nanofluid sample containing 1.36 vol.% graphite with dispersant can be created, offering the evidence for the formation of percolating aggregate structures. Our results may primarily provide a tremendous step on the way of finding abundant, low cost, commercially available, and high-performance nanomaterials for nanofluid production and secondarily determine if graphite-containing nanofluids toward practical applications are possible.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Colloidal graphite/oil nanofluids were prepared by mechanical ball grinding method.
► An obvious thermal conductivity up to 36% was observed.
► The clustering effect was the leading heat transfer mechanism.
► The colloidal graphite could be a promising additive for nanofluid preparation.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 414, 20 November 2012, Pages 125–131