| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593984 | 1453959 | 2012 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
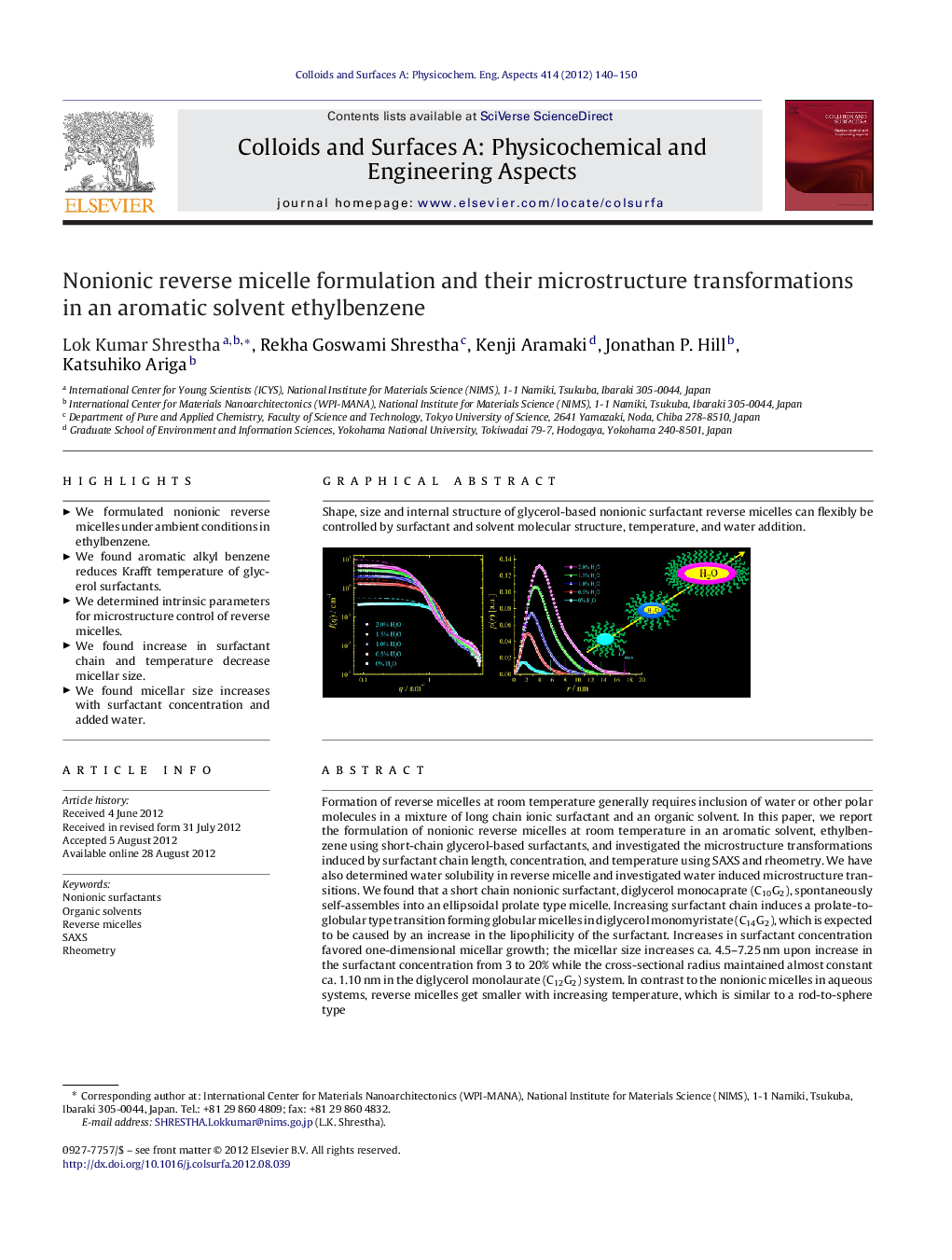
Formation of reverse micelles at room temperature generally requires inclusion of water or other polar molecules in a mixture of long chain ionic surfactant and an organic solvent. In this paper, we report the formulation of nonionic reverse micelles at room temperature in an aromatic solvent, ethylbenzene using short-chain glycerol-based surfactants, and investigated the microstructure transformations induced by surfactant chain length, concentration, and temperature using SAXS and rheometry. We have also determined water solubility in reverse micelle and investigated water induced microstructure transitions. We found that a short chain nonionic surfactant, diglycerol monocaprate (C10G2), spontaneously self-assembles into an ellipsoidal prolate type micelle. Increasing surfactant chain induces a prolate-to-globular type transition forming globular micelles in diglycerol monomyristate (C14G2), which is expected to be caused by an increase in the lipophilicity of the surfactant. Increases in surfactant concentration favored one-dimensional micellar growth; the micellar size increases ca. 4.5–7.25 nm upon increase in the surfactant concentration from 3 to 20% while the cross-sectional radius maintained almost constant ca. 1.10 nm in the diglycerol monolaurate (C12G2) system. In contrast to the nonionic micelles in aqueous systems, reverse micelles get smaller with increasing temperature, which is similar to a rod-to-sphere type transition. Addition of trace water promotes a significant micellar growth; both the maximum dimension and radius of micelles increases and the size of the water-incorporated micelles was approximately three times greater than the micelles in the absence of water. Microstructure transitions revealed by SAXS are supported by rheological measurements; the relative zero-shear viscosity decreased with increase in the chain length of surfactant. On the other hand, relative viscosity increased nearly one order of magnitude upon increase in surfactant concentration from 3 to 20%.
Shape, size and internal structure of glycerol-based nonionic surfactant reverse micelles can flexibly be controlled by surfactant and solvent molecular structure, temperature, and water addition.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► We formulated nonionic reverse micelles under ambient conditions in ethylbenzene.
► We found aromatic alkyl benzene reduces Krafft temperature of glycerol surfactants.
► We determined intrinsic parameters for microstructure control of reverse micelles.
► We found increase in surfactant chain and temperature decrease micellar size.
► We found micellar size increases with surfactant concentration and added water.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 414, 20 November 2012, Pages 140–150