| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 594006 | 1453959 | 2012 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
The increased interest in architecting nanocomposites and in clarifying their impact on health and environment necessitates a standardized method of surface characterization, because the behaviour of nanoparticles is governed largely by their surface free energy and interfacial chemistry. Potentiometric acid–base titration has been used for decades to determine surface charge density of oxides, tremendously useful in understanding and modelling oxide/electrolyte interfaces. The method has solid theoretical and experimental foundation. Yet, published values of the point of zero charge (PZC) of chemically identical oxides scatter widely: the deviation of seven units of pH is the rule, rather than an exception. The PZC must reflect the inherent charging behaviour, linked exclusively to the protonation, and determined by the chemistry of the oxides. Assignment of PZC (just like assignment of equilibrium constant of any chemical reaction) requires strict conditions and consistent protocol. We present here such a protocol, and some examples of application. The protocol leads through the basic steps: pH buffer calibration, proton concentration calibration in the background electrolytes, and titrations of oxides. Built-in tests help to eliminate artificial side effects simultaneously from the measurement of pH and from the oxide/electrolyte interfacial equilibria. Although these may seem self-evident, literature survey proves the need to go back to basics in order to obtain precise, reliable and comparable pH-dependent charging of oxides. It is most general that the oxides contain some unrecognized surface impurities and have a strongly pH-dependent dissolution. These distort the results of titrations; their effect increases with decreasing particle size and can become dominant for nanoparticles. The protocol presented here contains the necessary feedback loops to easily recognize and exclude these side effects.
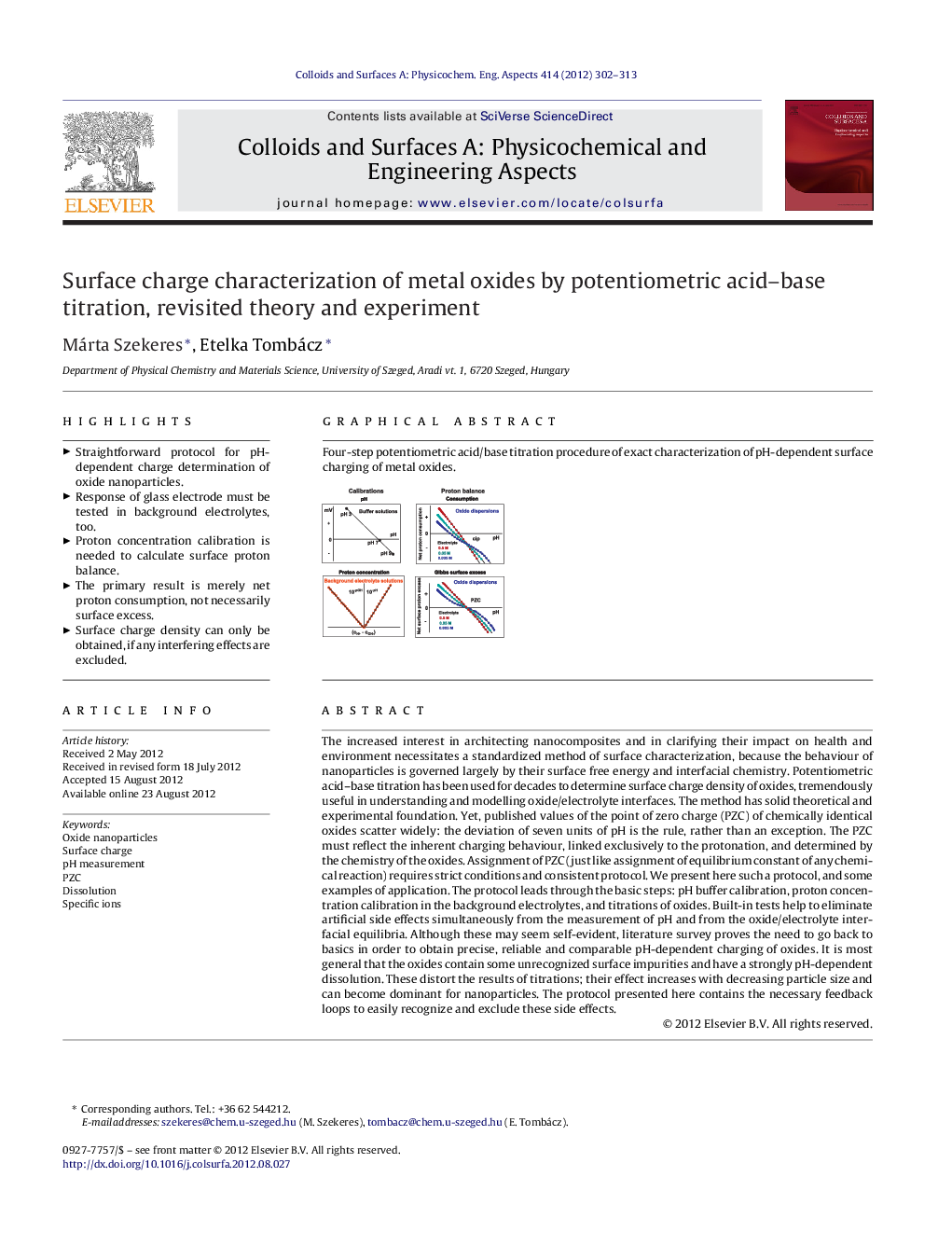
Four-step potentiometric acid/base titration procedure of exact characterization of pH-dependent surface charging of metal oxides.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Straightforward protocol for pH-dependent charge determination of oxide nanoparticles.
► Response of glass electrode must be tested in background electrolytes, too.
► Proton concentration calibration is needed to calculate surface proton balance.
► The primary result is merely net proton consumption, not necessarily surface excess.
► Surface charge density can only be obtained, if any interfering effects are excluded.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 414, 20 November 2012, Pages 302–313