| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6475143 | 1424967 | 2017 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
- The relationship between the KI-AC characteristics and Hg0 removal was established.
- The mechanism of Hg0 adsorption under various flue gas components was discussed.
- The binding abilities of mercury and different groups generated over the KI-AC were compared.
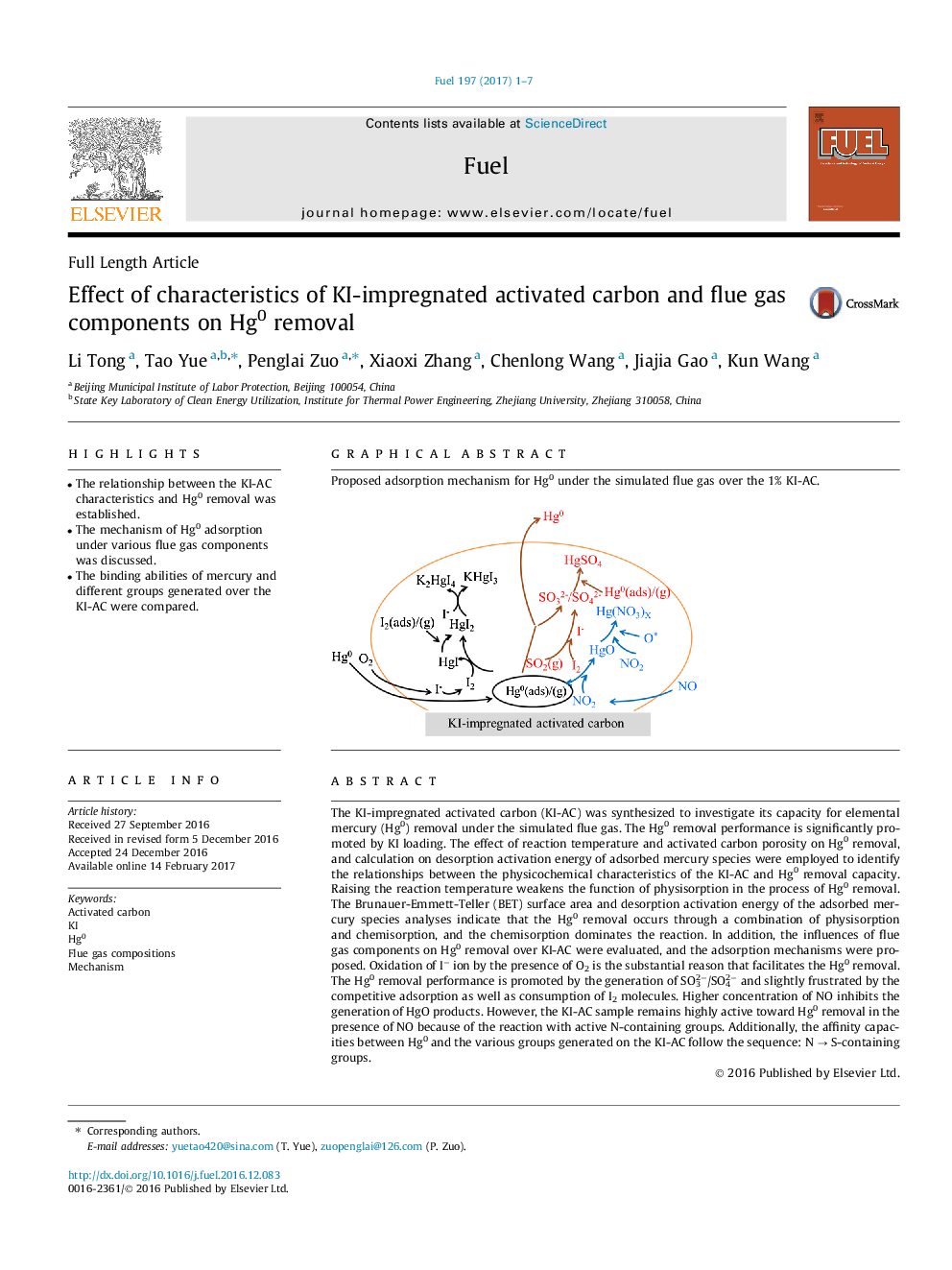
The KI-impregnated activated carbon (KI-AC) was synthesized to investigate its capacity for elemental mercury (Hg0) removal under the simulated flue gas. The Hg0 removal performance is significantly promoted by KI loading. The effect of reaction temperature and activated carbon porosity on Hg0 removal, and calculation on desorption activation energy of adsorbed mercury species were employed to identify the relationships between the physicochemical characteristics of the KI-AC and Hg0 removal capacity. Raising the reaction temperature weakens the function of physisorption in the process of Hg0 removal. The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area and desorption activation energy of the adsorbed mercury species analyses indicate that the Hg0 removal occurs through a combination of physisorption and chemisorption, and the chemisorption dominates the reaction. In addition, the influences of flue gas components on Hg0 removal over KI-AC were evaluated, and the adsorption mechanisms were proposed. Oxidation of Iâ ion by the presence of O2 is the substantial reason that facilitates the Hg0 removal. The Hg0 removal performance is promoted by the generation of SO32â/SO42â and slightly frustrated by the competitive adsorption as well as consumption of I2 molecules. Higher concentration of NO inhibits the generation of HgO products. However, the KI-AC sample remains highly active toward Hg0 removal in the presence of NO because of the reaction with active N-containing groups. Additionally, the affinity capacities between Hg0 and the various groups generated on the KI-AC follow the sequence: N â S-containing groups.
Proposed adsorption mechanism for Hg0 under the simulated flue gas over the 1% KI-AC.75
Journal: Fuel - Volume 197, 1 June 2017, Pages 1-7