| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593617 | 1453944 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
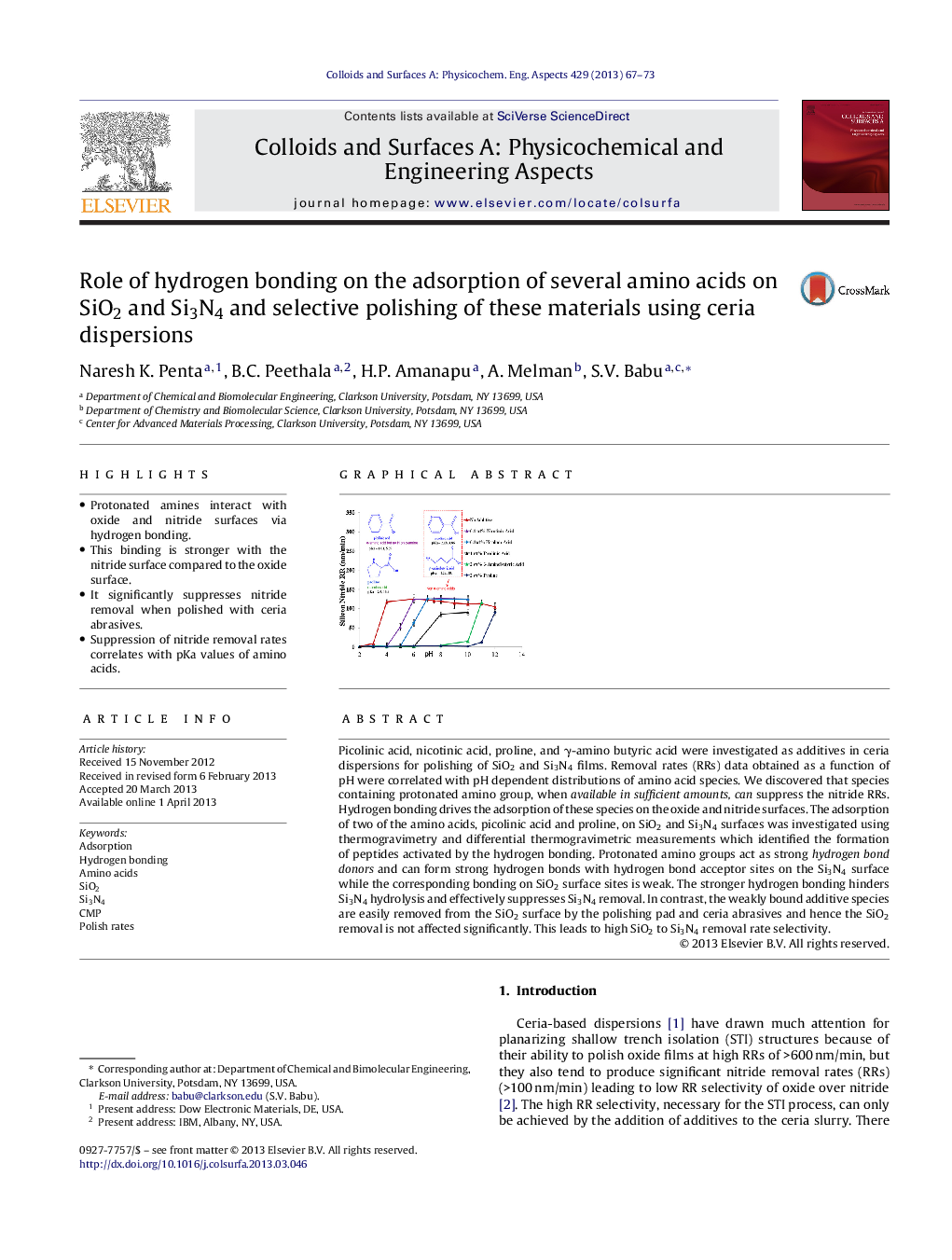
• Protonated amines interact with oxide and nitride surfaces via hydrogen bonding.
• This binding is stronger with the nitride surface compared to the oxide surface.
• It significantly suppresses nitride removal when polished with ceria abrasives.
• Suppression of nitride removal rates correlates with pKa values of amino acids.
Picolinic acid, nicotinic acid, proline, and γ-amino butyric acid were investigated as additives in ceria dispersions for polishing of SiO2 and Si3N4 films. Removal rates (RRs) data obtained as a function of pH were correlated with pH dependent distributions of amino acid species. We discovered that species containing protonated amino group, when available in sufficient amounts, can suppress the nitride RRs. Hydrogen bonding drives the adsorption of these species on the oxide and nitride surfaces. The adsorption of two of the amino acids, picolinic acid and proline, on SiO2 and Si3N4 surfaces was investigated using thermogravimetry and differential thermogravimetric measurements which identified the formation of peptides activated by the hydrogen bonding. Protonated amino groups act as strong hydrogen bond donors and can form strong hydrogen bonds with hydrogen bond acceptor sites on the Si3N4 surface while the corresponding bonding on SiO2 surface sites is weak. The stronger hydrogen bonding hinders Si3N4 hydrolysis and effectively suppresses Si3N4 removal. In contrast, the weakly bound additive species are easily removed from the SiO2 surface by the polishing pad and ceria abrasives and hence the SiO2 removal is not affected significantly. This leads to high SiO2 to Si3N4 removal rate selectivity.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 429, 20 July 2013, Pages 67–73