| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1347575 | 980314 | 2009 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
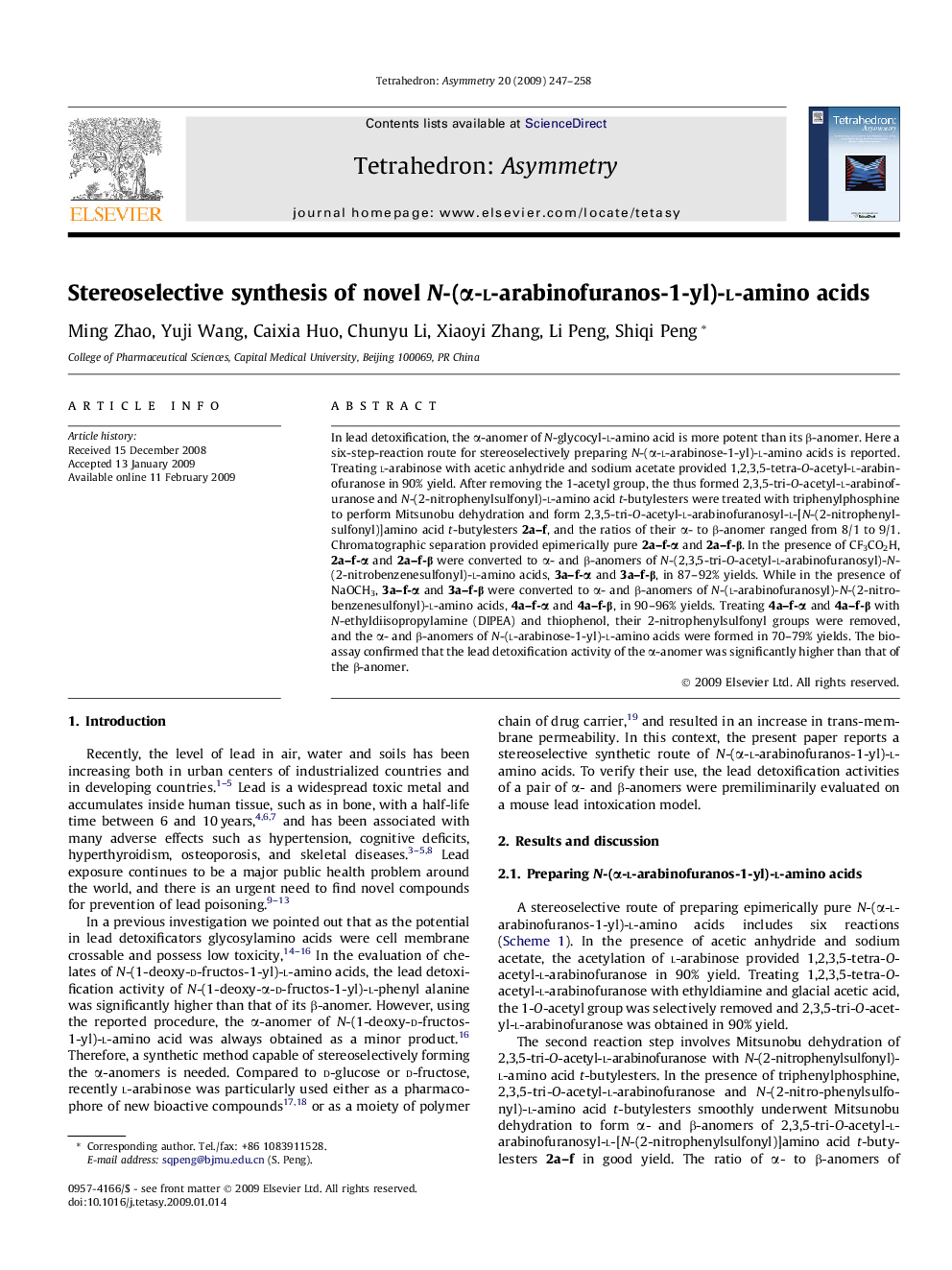
In lead detoxification, the α-anomer of N-glycocyl-l-amino acid is more potent than its β-anomer. Here a six-step-reaction route for stereoselectively preparing N-(α-l-arabinose-1-yl)-l-amino acids is reported. Treating l-arabinose with acetic anhydride and sodium acetate provided 1,2,3,5-tetra-O-acetyl-l-arabinofuranose in 90% yield. After removing the 1-acetyl group, the thus formed 2,3,5-tri-O-acetyl-l-arabinofuranose and N-(2-nitrophenylsulfonyl)-l-amino acid t-butylesters were treated with triphenylphosphine to perform Mitsunobu dehydration and form 2,3,5-tri-O-acetyl-l-arabinofuranosyl-l-[N-(2-nitrophenylsulfonyl)]amino acid t-butylesters 2a–f, and the ratios of their α- to β-anomer ranged from 8/1 to 9/1. Chromatographic separation provided epimerically pure 2a–f-α and 2a–f-β. In the presence of CF3CO2H, 2a–f-α and 2a–f-β were converted to α- and β-anomers of N-(2,3,5-tri-O-acetyl-l-arabinofuranosyl)-N-(2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl)-l-amino acids, 3a–f-α and 3a–f-β, in 87–92% yields. While in the presence of NaOCH3, 3a–f-α and 3a–f-β were converted to α- and β-anomers of N-(l-arabinofuranosyl)-N-(2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl)-l-amino acids, 4a–f-α and 4a–f-β, in 90–96% yields. Treating 4a–f-α and 4a–f-β with N-ethyldiisopropylamine (DIPEA) and thiophenol, their 2-nitrophenylsulfonyl groups were removed, and the α- and β-anomers of N-(l-arabinose-1-yl)-l-amino acids were formed in 70–79% yields. The bioassay confirmed that the lead detoxification activity of the α-anomer was significantly higher than that of the β-anomer.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
N-(α-l-Arabinofuranos-1-yl)-l-aspartic acidC9H15O8N[α]D25=+7.6 (c 1.1, H2O)Source of chirality: l-arabinose and l-amino acidAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R,3R,4S,2′S)
N-(α-l-Arabinofuranos-1-yl)-l-cysteineC9H17O7NS[α]D25=+38.1 (c 1.1, H2O)Source of chirality: l-arabinose and l-amino acidAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R,3R,4S,2′S)
N-(α-l-Arabinofuranos-1-yl)-l-glutamic acidC10H17O8N[α]D25=+10.0 (c 1.2, H2O)Source of chirality: l-arabinose and l-amino acidAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R,3R,4S,2′S)
N-(α-l-Arabinofuranos-1-yl)-l-serineC8H15O7N[α]D25=+20.0 (c 1.1, H2O)Source of chirality: l-arabinose and l-amino acidAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R,3R,4S,2′S)
N-(α-l-Arabinofuranos-1-yl)-l-phenylalanineC14H19O6N[α]D25=+6.7 (c 1.2, H2O)Source of chirality: l-arabinose and l-amino acidAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R,3R,4S,2′S)
N-(α-l-Arabinofuranos-1-yl)-l-theorineC14H19O6N[α]D25=+8.0 (c 1.1, H2O)Source of chirality: l-arabinose and l-amino acidAbsolute configuration: (1R,2R,3R,4S,2′S)
Journal: Tetrahedron: Asymmetry - Volume 20, Issue 2, 12 February 2009, Pages 247–258