| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 154759 | 456860 | 2015 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
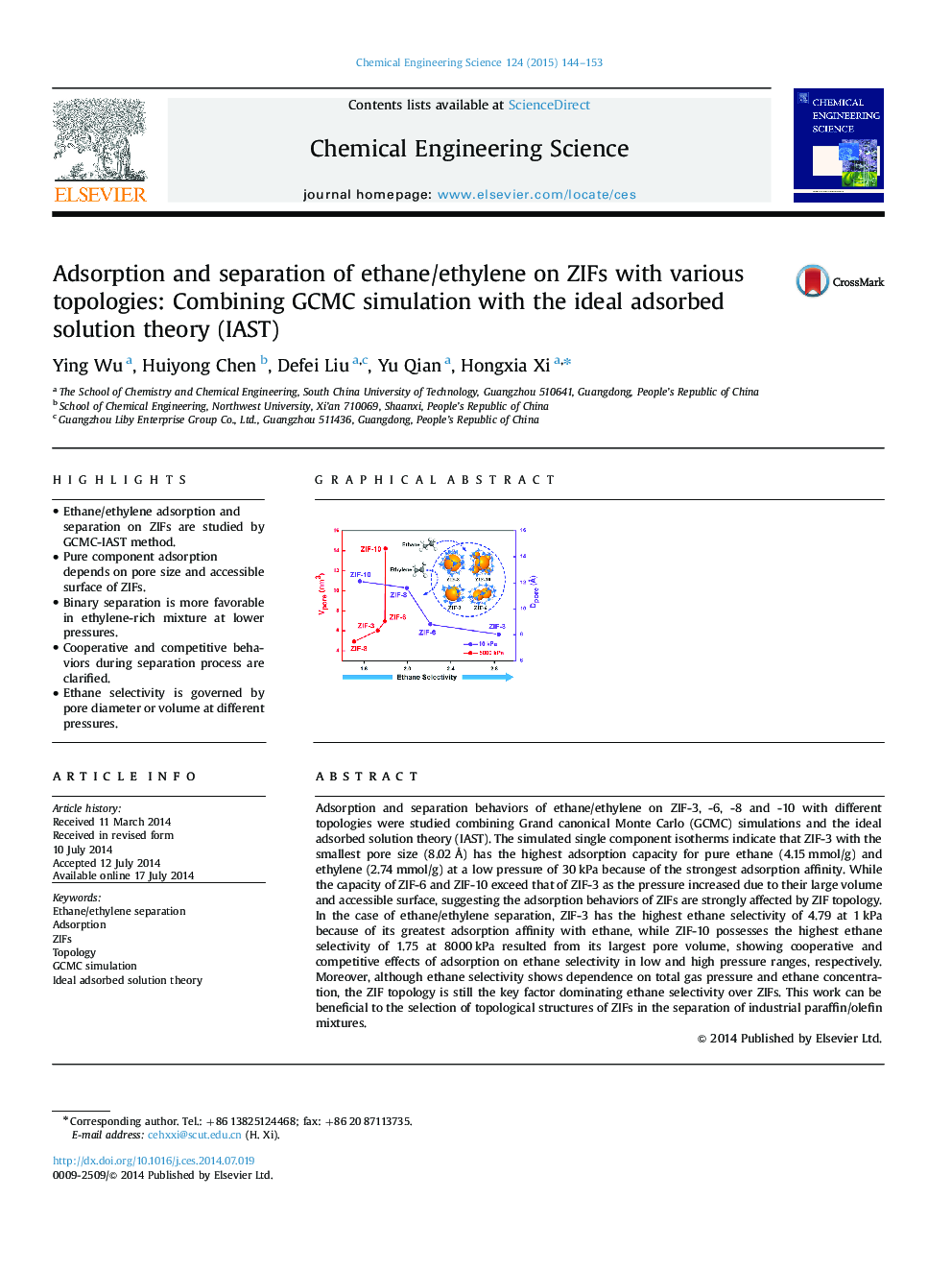
• Ethane/ethylene adsorption and separation on ZIFs are studied by GCMC-IAST method.
• Pure component adsorption depends on pore size and accessible surface of ZIFs.
• Binary separation is more favorable in ethylene-rich mixture at lower pressures.
• Cooperative and competitive behaviors during separation process are clarified.
• Ethane selectivity is governed by pore diameter or volume at different pressures.
Adsorption and separation behaviors of ethane/ethylene on ZIF-3, -6, -8 and -10 with different topologies were studied combining Grand canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations and the ideal adsorbed solution theory (IAST). The simulated single component isotherms indicate that ZIF-3 with the smallest pore size (8.02 Å) has the highest adsorption capacity for pure ethane (4.15 mmol/g) and ethylene (2.74 mmol/g) at a low pressure of 30 kPa because of the strongest adsorption affinity. While the capacity of ZIF-6 and ZIF-10 exceed that of ZIF-3 as the pressure increased due to their large volume and accessible surface, suggesting the adsorption behaviors of ZIFs are strongly affected by ZIF topology. In the case of ethane/ethylene separation, ZIF-3 has the highest ethane selectivity of 4.79 at 1 kPa because of its greatest adsorption affinity with ethane, while ZIF-10 possesses the highest ethane selectivity of 1.75 at 8000 kPa resulted from its largest pore volume, showing cooperative and competitive effects of adsorption on ethane selectivity in low and high pressure ranges, respectively. Moreover, although ethane selectivity shows dependence on total gas pressure and ethane concentration, the ZIF topology is still the key factor dominating ethane selectivity over ZIFs. This work can be beneficial to the selection of topological structures of ZIFs in the separation of industrial paraffin/olefin mixtures.
Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (230 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Science - Volume 124, 3 March 2015, Pages 144–153