| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 155193 | 456886 | 2013 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
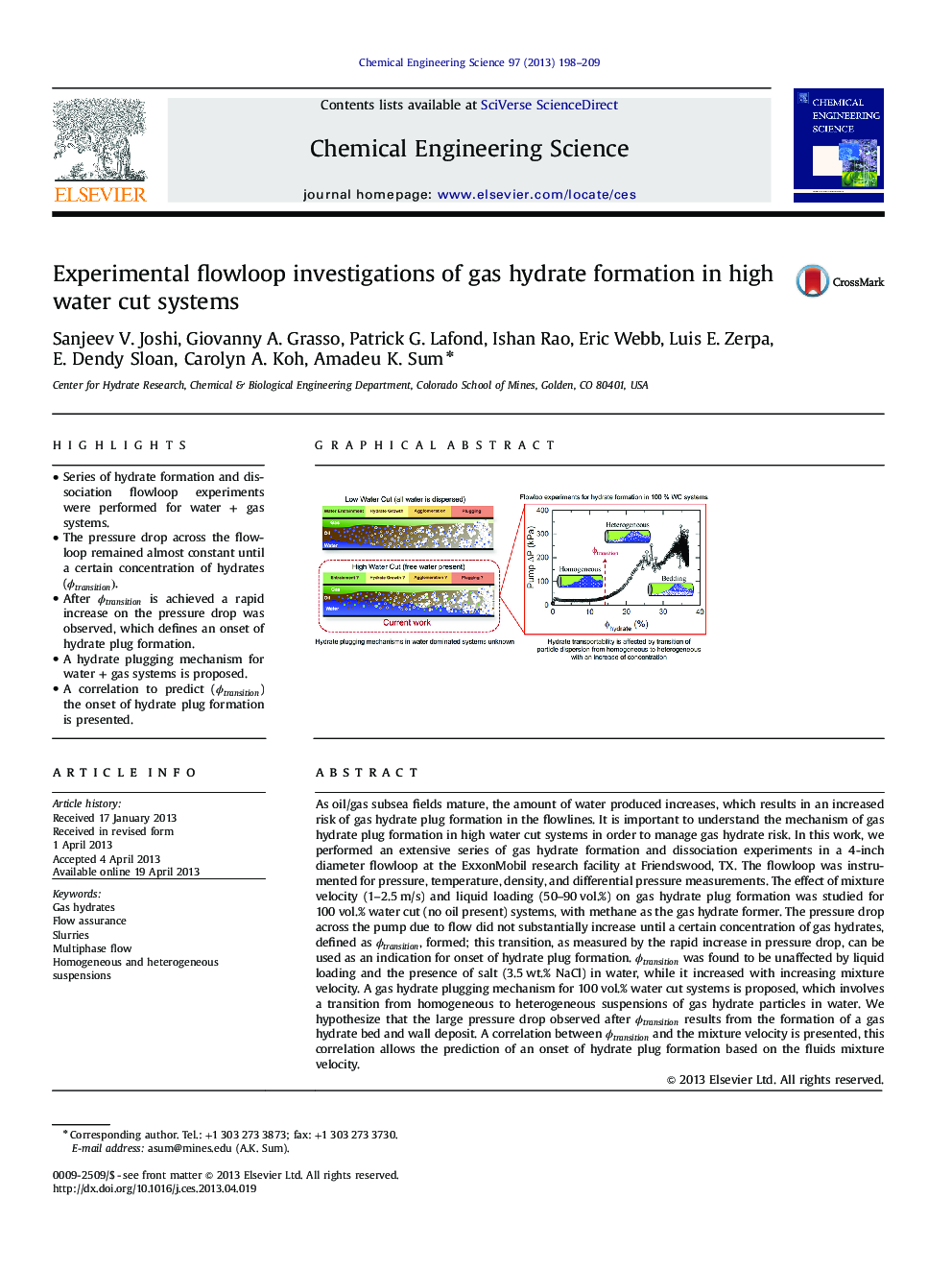
• Series of hydrate formation and dissociation flowloop experiments were performed for water + gas systems.
• The pressure drop across the flowloop remained almost constant until a certain concentration of hydrates (ϕtransition)ϕtransition).
• After ϕtransitionϕtransition is achieved a rapid increase on the pressure drop was observed, which defines an onset of hydrate plug formation.
• A hydrate plugging mechanism for water + gas systems is proposed.
• A correlation to predict (ϕtransitionϕtransition) the onset of hydrate plug formation is presented.
As oil/gas subsea fields mature, the amount of water produced increases, which results in an increased risk of gas hydrate plug formation in the flowlines. It is important to understand the mechanism of gas hydrate plug formation in high water cut systems in order to manage gas hydrate risk. In this work, we performed an extensive series of gas hydrate formation and dissociation experiments in a 4-inch diameter flowloop at the ExxonMobil research facility at Friendswood, TX. The flowloop was instrumented for pressure, temperature, density, and differential pressure measurements. The effect of mixture velocity (1–2.5 m/s) and liquid loading (50–90 vol.%) on gas hydrate plug formation was studied for 100 vol.% water cut (no oil present) systems, with methane as the gas hydrate former. The pressure drop across the pump due to flow did not substantially increase until a certain concentration of gas hydrates, defined as ϕtransitionϕtransition, formed; this transition, as measured by the rapid increase in pressure drop, can be used as an indication for onset of hydrate plug formation. ϕtransitionϕtransition was found to be unaffected by liquid loading and the presence of salt (3.5 wt.% NaCl) in water, while it increased with increasing mixture velocity. A gas hydrate plugging mechanism for 100 vol.% water cut systems is proposed, which involves a transition from homogeneous to heterogeneous suspensions of gas hydrate particles in water. We hypothesize that the large pressure drop observed after ϕtransitionϕtransition results from the formation of a gas hydrate bed and wall deposit. A correlation between ϕtransitionϕtransition and the mixture velocity is presented, this correlation allows the prediction of an onset of hydrate plug formation based on the fluids mixture velocity.
Figure optionsDownload high-quality image (377 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Science - Volume 97, 28 June 2013, Pages 198–209