| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 166121 | 1423442 | 2010 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
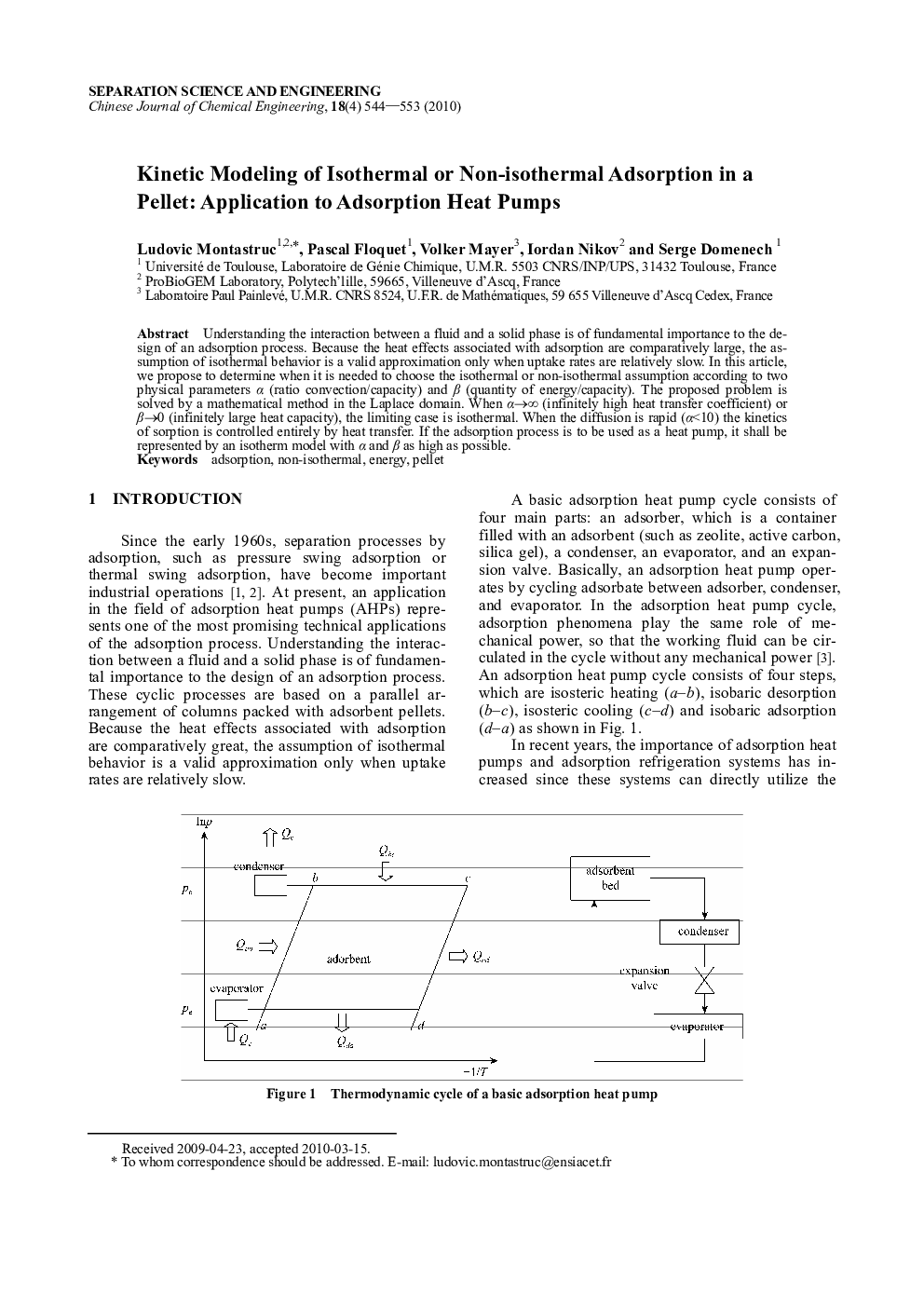
Understanding the interaction between a fluid and a solid phase is of fundamental importance to the design of an adsorption process. Because the heat effects associated with adsorption are comparatively large, the assumption of isothermal behavior is a valid approximation only when uptake rates are relatively slow. In this article, we propose to determine when it is needed to choose the isothermal or non-isothermal assumption according to two physical parameters α (ratio convection/capacity) and β (quantity of energy/capacity). The proposed problem is solved by a mathematical method in the Laplace domain. When α→∞ (infinitely high heat transfer coefficient) or β→0 (infinitely large heat capacity), the limiting case is isothermal. When the diffusion is rapid (α<10) the kinetics of sorption is controlled entirely by heat transfer. If the adsorption process is to be used as a heat pump, it shall be represented by an isotherm model with α and β as high as possible.
Journal: Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering - Volume 18, Issue 4, August 2010, Pages 544-553